Introduction: Business Ethics and Sustainability Post COVID: Report
This essay will examine on how business ethics is appropriate to business practices and policies regarding potentially contentious subject,counting corporate insider trading, governance, fiduciary responsibilities, corruption, favoritism, corporate social responsibility, and a lot more.The essay will consider Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) that a firm plays a positive role in the society and believe the ecological and social impact of company decisions. It is closely associated to sustainability create social, financial, and environmental value and(ESG) ecological, community, and governance (Ferrell, et. al. 2019). This focuses onnon-financialfactors that firms, both huge and small, should reflect on while making business decisions. The essay will explore these ideas about stakeholders which can be individuals or groups that the firm owes or is needy of for its achievement. Stakeholder theory identifies who will be benefits and who will sacrifice to give that benefit. Firms must provide reimbursement to all the stakeholders within a corporation to be measured ethically. The essay will highlight on travel and hospitality industry and how this industry maintains its sustainable business practices in its activities. Sustainability has turn into the major apprehension of business organizations, as it offer development opportunities, enduring growth, financial feasibility and competitive advantages to the companies all around the world. To consider theseareas,the essay will begin with developing sustainable business operations which can be a difficult task, as it requires wide agreement and communal effort of all stakeholders (Sroka, and Szántó, 2018). Key features of the essay will discuss about managers as leaders of organizations those demonstrate sustainability ideas that can turn on behavioral purpose of workers toward ecological protection to improve sustainable performance and competitive advantage. This implies that suitable leadership can inspire ethical values, mutual learning, and standards and encourage voluntary ecological behavior that strengthens the dynamic capability of the companies to accomplish superior presentation in societal as well as financial aspects. Workers as the frontline soldiers of the organization also play important role in beginning and put into practice organizational goals, leaders' values and ideas, and objectives which massively influence organizational performance (Ugwuozor, 2020). It will then go on to function of leadership in cheering pro-social, pro-organizational, and pro-environmental actions are sound recognized in research studies (Belitski, et. al. 2022). The argument being put forward with effectiveness and efficiency of the leaders' that influences dependences of other factor such as supporters ability and attitude, managerial climate and culture, and further situational factor. The essay will explore these ideas in relation to examination of moral leaders that influence on sustainable performance requiring an extra holistic advancement by putting together both supporter’s ethical climate and values of the organizations. In order to achieve the objective of the essay, it will include Covid-19 poses challenges to companies and organizations with consideration to CSR.Unavoidably this crisis has put travel and tourism industry under examination for its obligation to ethical business demeanor and CSR (Nosratabadi, et. al. 2019). Some may disagree that the economic strain, both long term and short-term, caused by the epidemic could considerably pushed companies to follow short-term benefits, infrequently even through misbehavior and fraud, and decrease long-term corporate social responsibility speculation, perhaps due to lack of drooping resources and rising pressure for endurance.
Academic goals are easier to achieve when you have the right support. Our Assignment Help UK connects you with skilled writers who are experts in their fields. We pay close attention to your guidelines and marking criteria to create assignments that impress professors and earn high scores. Whether you’re an undergraduate or pursuing a master’s degree, we provide content that reflects your level of study. With our help, you’ll gain confidence, save time, and see real improvement in your academic performance.
Ethical implications and impacts of business objectives on stakeholders
Business objectives arethe detailed, quantifiable outcome that firms hope to preserve as their association grows. When firms create a set of business objectives, they focus on particulars. This means assessing, analyzing, and understanding where the company is now and where they want to be in the future. Objectives are required in each area where outcomes and performance directly have an effect on the endurance and wealth of a company. The accurate choice of objectives is significant for the accomplishment of the industry. The objectives of a company can be classified into 2 main categories; this includes economic and social objectives which the business must accomplish for its long term growth and development. Customer service is the main objective of travel and hospitality industry (Ferreira Gregorio, et. al. 2018). Tourists arrive in contact with diverse people in the hospitality business for their requirements. This can happen from the early of the tour booking plan to ending of the tour package. Tourists are necessitating assistance in numerous forms from the time of book trip packages to choose the correct menu throughout the tours. A stakeholder is a group, person, or organization that is impact by the effect of a mission or a business project. Stakeholders contain awareness in the achievement of the scheme and can be inside or exterior the association that sponsor the plan. They are fundamental because they can have a positive and negative influence on the development with their decision. There are 2 types of stakeholders i.e. internal and external stakeholders. It is significant to reflect on how a company’s decisions can influence stakeholders because they frequently have the perspective to modify the priority of how a business function (Bendtsen, et. al. 2021).An internal stakeholder is an inside party that is directly or economically part of the company’s operations. This includes managers, employees, owners, and many other internal parties. An external stakeholder is someone who a firm recognizes that decides on operations. This includes communities, customers, shareholders, trade unions, and government (Dimitrovski, et. al. 2021). The government's roles include but are not inadequate to rising and maintaining infrastructures including railways, roads, and ports, promoting destination to global and local tourist; and ensure wellbeing and security of tourists. Local governments with precise competence in travel and hospitality also play a significant role in tourism expansion.Tourism concerns and projects play a diversity of roles in tourism growth (Wijethilake and Lama, 2019). There are several other stakeholders that tourism planners should reflect on. For instance, an organization engaged in financing tourism plans, trade unions of workers and specialized working in tourism, tourism enlightening centers, and further tourism professional organizations play a multiplicity of roles in tourism enlargement.
Stakeholder mappingis the procedure of illustrating avisual representationof the range of people concerned with or exaggerated by the project.Itcan provide the impending projects that require concluding smoothly. This method plays a key role instakeholder management. They are designed to assist in the appraisal of an organization's environment by stressing what power is at play to assist or delay the progress of the company’s project (Kivits and Sawang, 2021). The benefits of usingstakeholder mapsshould not be disregarded. These make it easier to identify key players to monitor, target, or inform at each stage of the project. This also helps in making decisionsquickly without overlooking significant stakeholders. It assesses the powerandappreciates the interestsof each stakeholder to describe strategy andcommunication plansconsequently (Macke and Genari, 2019).
Project stakeholdersare groups or organizations exaggerated by the venture of industry or by its action at large. It is the key when it comes to evaluating the authority and awareness ofproject stakeholders. Knowing how to arrange and handle stakeholders will affect the outcome of the company's project, and with an appropriate stakeholder map, the companies will be able tonavigate their way around obstacles more successfully (Fabio and Peiró, 2018). Large firms must find ways toreview their potential impactand theriskconnected with their projects.Stakeholder communicationsshould be leaning toward the right interlocutors and contest their prospects. Firms working in tourism and hospitality industry give feedbacks and rating to the agency based upon the performance factors chosen by the consumers. The superiority of products which are serving to the consumers should be high-quality otherwise there will be negative performance ratings from the consumers.
The goal definite for every class of service in the hospitality industry varies and the principles for measuring the superiority of products also vary.Many big companies spend a humongous quantity of capital in their research and growth section to increase innovation. Other than that consumption of resources is an appropriate use of employees, capital, raw material, expertise, skills and knowledge used in the business (Priyono, et. al. 2020). Business exists in the first position to convince the requirements of the society. It is the first and main community objective of the business.Productsand services should be of superior class and these should be providing at rational costs.It is the societal purpose of a business to give chances to valuable employment to persons of the society. Commerce is a set of actions undertake with the view of transaction for the principle of earning an income.Profit is essential for rising and increasingbusiness activities. Profit guarantees a constant stream of capital for the transformation and expansion of business actions in the future.
COVID-19 hasimproved the requirement for technology within the tourism sector.Vaccination passports are being brought in across the globe toprevent thespread of COVID-19as travel limitations are raised. Inadding up to this,somehotel business hasturned to digital technologiesto make their procedure more proficientand tokeeppersonal contact to a minimum (Haseeb, et. al. 2019).The effortlessness and competence of check-out and check-in knowledge are enhanced by giving hotel visitors admittance to their rooms using facial acknowledgment software. From preparing food in-room dining services, repetition as waiters in lodge restaurants, delivering housekeeping items, and provision facemasks, and hand sanitizers, automaton is used in the vanguard to defend hotel guests and workers and prevent the broaden of COVID-19 (Davahli, et. al. 2020). There has been an important focus ontransformation after the pandemic in a sustainable manner. With weather change such a pressing issue, thelesseninginglobaltravelhas beenviewed as an opportunity for businesses and industries to reformtheir process to turn out to be more environmentfriendly.In response to the critical issue of climate change, sustainability must become a core constituent ofhigher learning, teachingand researchin the field oftourism and hospitality (Carletti, et. al. 2020).The use of technologies, emerging trends, use of digital marketing, and teamwork with unrelated and medical-related firms is an opportunity arising after the calamity which can be modified by tourism firms in their strategy to reconstruct the business volume after the COVID-19 crisis (Freudenreich, et. al. 2020).
To bring to a close, the alteration of the security and sanitation standards is vital for tourism companies to fit with tourists’ travel priorities and reconstruct the trade quantity in the post-COVID-19 pandemic.
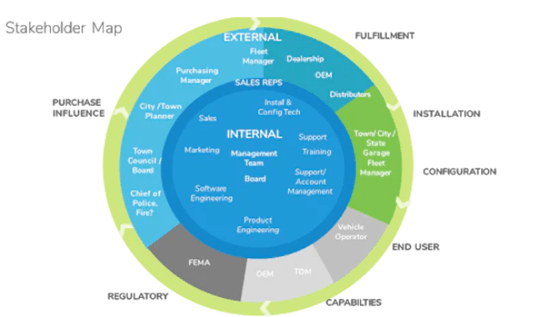
Figure 1: Shareholder mapping
Ethical implications and impacts of sustainable leadership
The lessening of Covid-19 lockdown limitations along with continuous social pressure has agreed mounted a rising number of a challenge to the stage of sustainable leadership being observed across present businesses. Nowadays, the prioritization of sustainability begins at the top. Leaders have an approach to understand that a sustainable business approach is not only excellent for the environment but also helpful to the company’s bottom line. In revolve; boardrooms around the globe are now using an ESG (environment, social, and governance) structure for a planned review of the firm’s sustainability (Saha, et. al. 2020). Sustainable leadership is about approving an accountable approach to the means that lead, and discontinuing thinking about the wide impact of the actions on culture and the environment. This may mean considering the wider stakeholder group,the natural system inside which they are in use, and their limits.
Leaders motivate and sustain their team or employees to act together towards achieving a vision and goals. Green leaders motivate their employees to perform together towards accomplishing a better world. They are frequently seen as modification agents as they enable, initiate, or promote change. In sustainability, leadership is vital in driving the transformation process (Khan, et. al. 2019). The international tourism industry is in front of the perfect storm of continuing uncertainty, augmented by worrying inflation, concern about depression, geo-political ambiguity, and growing fuel prices. Sustainability is a lot more than ecological management, waste management, and water consumption; it is also about financial progress and social growth (Mahdi, et. al. 2019). Factual sustainability must include all aspects including culture, environment, conservation, and livability.In an ever-changing globe, the global pandemic has brought into focus the requirement more so than ever to entrust sustainable and accountable tourism growth. Even pre-pandemic, customers were more watchful of sustainability and travel in an accountable and determined way and this tendency is only accelerating. In a current report from Booking.com, an enormous 80% of worldwide travelers established that sustainable travel is significant to them. An 11% increase over 2021 data with 49% saying that current news about climate change has prejudiced them to make more sustainable journey choices. Sustainability must at the present be top of mind for any location’s long-term investment and hospitality growth to strike into this developing landscape. Examination of ethical leaders influence on sustainable presentation requires holistic advancement by integrate both followers' principles and ethical atmosphere of the organizations. Workers biosphere values exposed to be a forecaster of workers environmental behavior which could eventually influence sustainable performance of the organization (Baum and Hai, 2020). These include Jesper Brodin from IKEA, Paul Polman Unilever’s CEO,Claus Aagaard from Mars, and Tim Cook from Apple. For example, TerraCycle which is incorporated in 2001 has been a captivating hard-to-recycle waste and revolving it into raw material for making use in new products.Originator and CEO of the company Tom Szaky started the firm by selling worm poop tea as nourishment. For the reason that CEO had less money to work with, use superfluous plastic soda bottles as packaging. The manufactured goods gained some slight popularity. In today’s fast-forward world Terracycle operates in more than 19 countries. They associated with organizations like Mars, Proctor & Gamble (P&G), Nestle, and Unilever to produce ultra-durable wrapping forms that will be owned by the producer.
Post-pandemic sustainability, business ethics, governance, and corporate social responsibility
Sustainable competitive advantages are a set of individuality, assets, or capability that allows an association to gather its customer requirements better than its opposition can. Sustainable competitive advantages are difficult to duplicate or replicate. A corporation that has skills to boost prices not including losing market share is supposed to have pricing control (Almeida, et. al. 2020). Firms that have price power are frequently taking advantage of elevated barriers to entrance or have earned the leading situation in their marketplace. It takes a huge investment in money and time to construct a brand. A superior brand is precious because it causes consumers to have a preference of the product over competitors. Being the marketplace head and comprising an enormous corporate reputation can be element of an influential brand and a competitive advantage. Trademarks, patents, copy rights, and long-term contract are the examples of strategic wealth that offer sustainable competitive advantages. Firms with outstanding research and development may have precious strategic assets (Khouroh, et. al. 2020). For instance, Simon Winfield, the managing leader of Hays is the biggest travel company in the UK and Ireland. The company has become a carbon-neutral business in 2021 and is at present on a path to net zero carbon emissions. This is a worldwide commitment across Hays and follows a numeral of initiatives in the UK to assist its sustainability. Not merely is there a strong commerce case for being more sustainable. For example, rising energy efficiencies and decreasing waste help reduce costs, the company is also focusing on being more sustainable which enables them to be superior and able to adapt to regulatory changes, should they occur. Plus, its consumers and workers feel powerful about sustainability issues and want the community that they have been working with to recognize that the company has represented their interests and values. Many leaders foresee a predictable tip point when their organization will no longer be able to resourcefully adapt to their market and will merely fall off the group. This more and more cutthroat profitable landscape is being described as VUCA which stands forvolatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (Millar, et. al. 2018). This approach to concluding the gap between the rapidly accelerating world of VUCA and a company’s ability to not only endure but bloom is to exploit truly effective leadership. It is a globe where product and demographics, capital markets, geopolitics, technology, and competitive scenery are becoming more and more uncertain, volatile, complex, and ambiguous (Luthans and Broad, 2022). Human resource plays a major role in creating this ambition a reality in a VUCA world.
Firms and the operating atmosphere have been strictly impacted by the global pandemic, which has highlighted the difficulty of the trade situation and the significance and dependence on stakeholder relations (Bennett and Lemoine, 2014). Finance and board leaders have found the way to these complexities as they reacted to the calamity and must still do so at the present as under their stewardship they describe and organize new or sophisticated strategies as part of the post-pandemic reconstruct. CSR is a divisive concept as there is always thought that corporate social responsible programmes are only about community image. If firms interpret CSR that manner, they will not obtain lasting benefit, though. Actual added value can only occur from outside independent and monitoring and certification. In Germany, the TourCert proposal has introduced the “CSR-Tourism authorized” label. It is a private-sector corporation, the shareholders of which comprise Germany’s Bonn-based Protestant Church Development Service (EED). Travel firms need to get back the expenditure of CSR programmes. Place in a different way, this way that tourists, to the amount that they are keen to pay for environmental and social efforts, have an impact on the company’s performance. Firms that have upheld corporate social responsibility are doing extremely well in the marketplace because the society needs to hold up the firms so that they can carry on doing superior for the society. CSR is about carrying out business according to the code of ethics that are lay down for the industry. The culture has prospect from the hospitality industry, and it is merely fair that they should be meet. This makes the companies in the hospitality industry to severely obey the laid out system so that they do not sustain damage to the society. Though the policies and laws set by the government require being superior to effect CSR. The sales approach that some company use to publicize their products has enable them to be recognized in the whole globe. Thus CSR is the way to acknowledgment for many companies if they want to be recognized globally. These businesses in the travel and hospitality industry are assessing on their economic strengths using the monetary statements.
Conclusion
This essay has concluded with the universal society requirements to identify and encourage sustainable leaders to entrench the standard of sustainable leadership until it becomes the standard and an essential part of every business strategy. The essay highlights on COVID-19 virus that has increased around the world. This global pandemic has origin of a socio-economic response not merely as a well-being crisis but also distressing the nation's safety, the life of society, economic actions, and transformation of the work culture of firms globally. The essay was made to understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, leaders also have to tackle unforeseen changes in the economic and social crisis, and to master that situation, leadership is necessary. At such points in time of difficulty, leaders are required to make decisions speedily. For instance, to discontinue manufacturing or work remotely, team up with ecosystems, customers, and workers, as per hierarchy of needs and the public's basic requirements, come across the vagueness of the situation individually while directing their team and companies through it as leaders. The argument being put forward therefore, much policy resulting from the COVID-19 global pandemic will directly have an effect on leadership in companies, since leaders are the navigator of organizations. To achieve the objective of the essay companies by working towards setting up the purpose as a leader in sustainable tourism can improve the lives of people and personnel, defend and improve the unique natural environment and conventional community, and also address the requirements of the guests and the industry. The essay was made to discuss sustainability which is an essential use of a resource so that it is not damaged concerns a fundamental role in the travel and hospitality industry. Travel and hospitality firms’ success depends on their conserving the cultural and natural attractions that induce tourists to visit their destinations. The effective leader must work with superior management to conceptualize, border, and support the necessary culture. The culture that creates and sustains competitive advantages will require being thrilling, supple, and highly opportunistic. The leader needs toregulate their collective aptitude and organizational tools to be reliable with the inconsistency of modification. A good leader itself will require exemplifying the culture and practice that will be necessary in a world of micro-competitive rewardin a VUCA globe. By spending on sustainability, companies are also protecting their savings and ensuring that tourists and visitors carry on returning for years to arrive. While the global pandemic may have in use the spotlight of the travel & hospitality industry’s most awful immoderation, many customers have emerged from lockdowns and tour bans with an enlarged awareness of sustainability. Companies while using monitoring software can inspect whether customers already outlook the brand as a sustainable option and determine which changes are mainly efficient at winning over the company’s audience.
Reference
Almeida, F., Santos, J.D. and Monteiro, J.A., 2020. The challenges and opportunities in the digitalization of companies in a post-COVID-19 World.IEEE Engineering Management Review,48(3), pp.97-103.
Baum, T. and Hai, N.T.T., 2020. Hospitality, tourism, human rights and the impact of COVID-19.International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management,32(7), pp.2397-2407.
Belitski, M., Guenther, C., Kritikos, A.S. and Thurik, R., 2022. Economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on entrepreneurship and small businesses.Small Business Economics,58(2), pp.593-609.
Bendtsen, E.B., Clausen, L.P.W. and Hansen, S.F., 2021. A review of the state-of-the-art for stakeholder analysis with regard to environmental management and regulation.Journal of environmental management,279, p.111773.
Bennett, N. and Lemoine, G.J., 2014. What a difference a word makes: Understanding threats to performance in a VUCA world.Business horizons,57(3), pp.311-317.
Carletti, E., Claessens, S., Fatás, A. and Vives, X., 2020.Post-Covid-19 World. Centre for Economic Policy Research.
Davahli, M.R., Karwowski, W., Sonmez, S. and Apostolopoulos, Y., 2020. The hospitality industry in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic: Current topics and research methods.International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,17(20), p.7366.
Di Fabio, A. and Peiró, J.M., 2018. Human Capital Sustainability Leadership to promote sustainable development and healthy organizations: A new scale. Sustainability,10(7), p.2413.
Dimitrovski, D., Lemmetyinen, A., Nieminen, L. and Pohjola, T., 2021. Understanding coastal and marine tourism sustainability-A multi-stakeholder analysis.Journal of Destination Marketing & Management,19, p.100554.
Ferreira Gregorio, V., Pié, L. and Terceño, A., 2018. A systematic literature review of bio, green and circular economy trends in publications in the field of economics and business management.Sustainability,10(11), p.4232.
Ferrell, O.C., Harrison, D.E., Ferrell, L. and Hair, J.F., 2019. Business ethics, corporate social responsibility, and brand attitudes: An exploratory study.Journal of Business Research,95, pp.491-501.
Freudenreich, B., Lüdeke-Freund, F. and Schaltegger, S., 2020. A stakeholder theory perspective on business models: Value creation for sustainability.Journal of Business Ethics,166(1), pp.3-18.
Haseeb, M., Hussain, H.I., Ślusarczyk, B. and Jermsittiparsert, K., 2019. Industry 4.0: A solution towards technology challenges of sustainable business performance.Social Sciences,8(5), p.154.
Henri Gisslard-biondi, 2021. Stakeholders mapping. What iss stakeholders mapping? Definition, guide, tools and matrix. [Online]. [Available on]. :<https://www.appvizer.com/magazine/operations/project-management/stakeholder-mapping>. [Assessed on 26/12/2022].
Khan, S.Z., Yang, Q. and Waheed, A., 2019. Investment in intangible resources and capabilities spurs sustainable competitive advantage and firm performance.Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management,26(2), pp.285-295.
Khouroh, U., Sudiro, A., Rahayu, M. and Indrawati, N., 2020. The mediating effect of entrepreneurial marketing in the relationship between environmental turbulence and dynamic capability with sustainable competitive advantage: An empirical study in Indonesian MSMEs.Management Science Letters,10(3), pp.709-720.
Kivits, R. and Sawang, S., 2021. Stakeholder Analysis. InThe Dynamism of Stakeholder Engagement(pp. 29-43). Springer, Cham.
Luthans, F. and Broad, J.D., 2022. Positive psychological capital to help combat the mental health fallout from the pandemic and VUCA environment.Organizational dynamics,51(2), p.100817.
Macke, J. and Genari, D., 2019. Systematic literature review on sustainable human resource management.Journal of cleaner production,208, pp.806-815.
Mahdi, O.R., Nassar, I.A. and Almsafir, M.K., 2019. Knowledge management processes and sustainable competitive advantage: An empirical examination in private universities.Journal of Business Research,94, pp.320-334.
Millar, C.C., Groth, O. and Mahon, J.F., 2018. Management innovation in a VUCA world: Challenges and recommendations.California management review,61(1), pp.5-14.
Nosratabadi, S., Mosavi, A., Shamshirband, S., Zavadskas, E.K., Rakotonirainy, A. and Chau, K.W., 2019. Sustainable business models: A review.Sustainability,11(6), p.1663.
Priyono, A., Moin, A. and Putri, V.N.A.O., 2020. Identifying digital transformation paths in the business model of SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic.Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity,6(4), p.104.
Saha, R., Cerchione, R., Singh, R. and Dahiya, R., 2020. Effect of ethical leadership and corporate social responsibility on firm performance: A systematic review.Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management,27(2), pp.409-429.
Sroka, W. and Szántó, R., 2018. Corporate social responsibility and business ethics in controversial sectors: Analysis of research results.Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation,14(3), pp.111-126.
Ugwuozor, F.O., 2020. Students' perception of corporate social responsibility: analyzing the influence of gender, academic status, and exposure to business ethics education.Business Ethics: A European Review,29(4), pp.737-747.
Wijethilake, C. and Lama, T., 2019. Sustainability core values and sustainability risk management: Moderating effects of top management commitment and stakeholder pressure.Business Strategy and the Environment,28(1), pp.143-154.



