- User-Centered Design System Interaction Design Principles Usability User Experience Goals Sweet Home
- 1.0 Introduction: User-Centered Design System Interaction Design Principles Usability User Experience Goals Sweet Home
- 2.0 Discussion
- 2.1. Activity: 1
- 2.2. Activity: 2
- 2.2.1 Design Principles
- 2.2.2 Prototype
- 2.2.3 Key Users and persona creation
- 2.2.4 Work Domain Analysis
- 2.2.5 The User interface is illustrated in the form of a sketch
- 2.2.6 User-centric design using agile methodologies
- 2.2.7 Cultural differences
User-Centered Design System Interaction Design Principles Usability User Experience Goals Sweet Home
1.0 Introduction: User-Centered Design System Interaction Design Principles Usability User Experience Goals Sweet Home
The user-centered design is one of the essential features of the energy monitoring of any smart household where all the connections are centralised to one and are easily monitored. Energy is one of the most important parameters which is required for survival and for daily processes of livelihood. The need to conserve energy is the most common demand rising in present conscious times. The changes in climates in several regions of the world have different effects on the devices and it affects the working efficiency of the devices. Complete information on the energy consumption and other parameters of the device that are using the energy resources to work is very essential to stay aware of the conditions of the devices. Interaction of the devices with the user maintains communication between the user and the machine with the help of which efficient measures can be planned to reduce the consumption of energy and to ensure the smooth running of the devices.
Have a confusing assignment brief? Get Help with Assignment for clear understanding and precise execution. We decode your brief and deliver excellence. Start today!
2.0 Discussion
2.1. Activity: 1
2.1.1 Usability and User Experience Goals
Many usability goals and goals for the experience of the user are being considered and taken into focus to build a user-centric system which is efficient in saving energy consumption in the household through an efficient system of energy monitoring. The chosen usability goals are Effectiveness, efficiency, learnability, utility and memorability and the chosen goals are to construct a system with a better user experience the user experience goals which are chosen are user satisfaction, helpful, rewarding, entertainment and motivational (Ui/Uxbooks.com (2020)). The user-centric energy monitor system is based on all these 10 usability and user experience goals.
- Usability Goals
- Effectiveness

Figure 1: Effectiveness of the system
It is the parameter of the system which defines the thoroughness and the accuracy with which the system has achieved the predicted goal. The effectiveness of the system should be high to be advantageous in terms of usage by the users. The effectiveness of the system is presented in the form of the quality which means the effectivity of the system influences other physical parameters such as the accuracy of the achieved goal, and the time taken to complete the goal is such parameters which are affected by the effectiveness of the system (Abbas et al, 2022). The system is designed to be humanly centered which means the tasks that will be completed with human intervention and the tasks should consider the essential characteristic features of the persona of the user to make the processes more user-friendly and smooth.
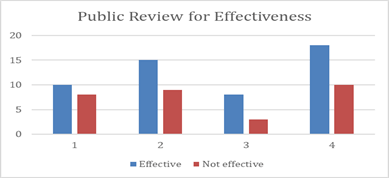
Figure 2: Public Review for Effectiveness
Efficiency

Figure 3: Efficiency of the system
This is another parameter of the system which refers to the resources that are exhausted by the user to achieve the goals. This parameter is used to evaluate the output that is obtained from the system concerning the input that is provided to the system (Agarina et al. 2019). If the system provides high output in comparison to the input that is provided, the system is said to have high efficiency whereas when the output of the system is not meeting the expected level in comparison to the input that is provided the system is said to have low efficiency. The user-centric design of the energy monitor that is to be built, should have a high efficiency so that the energy consumption can be kept in check.
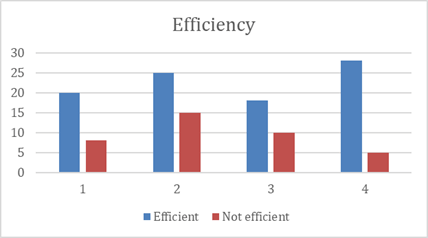
Figure 4: Public Reviews for Efficiency
Learnability

Figure 5: Learnability of the system
This is a parameter of the system which defines the level of effort that is needed to learn the system and the user. The learnability of the system should be important as user-centric systems are focused on the habit patterns and decisions of the user, so the user should be able to learn the system easily (Al-Hunaiyyan et al. 2022). It is also the quality which makes the system easily familiar to users so that the users can make good use of the system to achieve their goals.
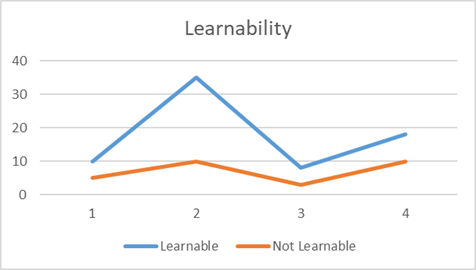
Figure 6: Review of Learnability
Utility

Figure 7: Utility of the system
This is another parameter of the system which is stated as the inclusion of the activities and the functions which the user needs in the first place. The utilities of the system should cover the significant requirements, demands and needs of the users (Barambones et al. 2020). The utilities of the user-centric energy monitor device should be based on the parameters to conserve energy. Utility along with usability makes the system usable for the users and is one of the important usability goals for any system.
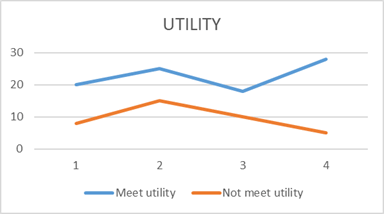
Figure 8: Review of Utility
Memorability

Figure 9: Memorability of the system
This is a parameter of the system which is used to define the level of handling history activities so that the user can get it easy to get back to the platform exactly at the point left. The memorability of the user-centric system should be high as the time-lapse can make the user lose important data or information. Efficient systems should efficiently manage time-lapse and session time-outs to prevent loss of data. Memorability is being measured by the use of the system and with proper analytics of the system. The proficiency of the system is presented with the help of the memorability of the system.
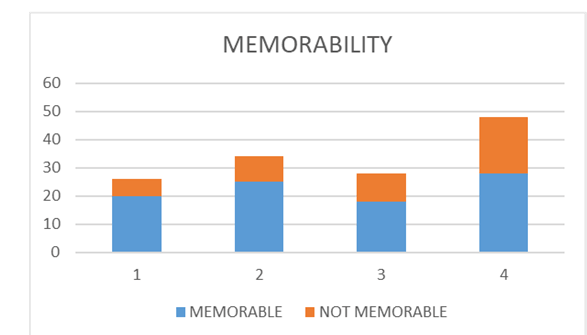
Figure 10: Review of Memorability of the system
- User Experience Goals
- Satisfaction

Figure 11: Satisfaction of the system
This is a parameter of the system which measures the usability of the device based on feedback provided by the user when the desired task is being achieved by the system. In the user-centric energy monitor system user satisfaction is essential since the satisfaction of the user leads to better use of the system to monitor parameters of the system. The satisfaction of the user is measured with the help of a set of questions which are being asked by the system to the user after the desired task is achieved. Through this process, the problem of asking millions of people is solved and mass answers can be used to get insights into the satisfaction of the system to the masses.
Helpful
This is a goal of user experience that measures the level of usefulness of the system and the ways in which the system helps the user in different ways. The user-centric energy monitor system should be useful to the user so that the desired activities can be done with the help of the system to measure the level of energy consumption under a few particular conditions. The user-centric energy monitor device that is built should be helpful and should be useful to the user.
Rewarding
This is a parameter of the system which is used to maintain user loyalty and to enhance the reinforcement of the services positively. This is a way of extrinsic motivation for the users to bring in repeat demands of the services. Examples of reward systems can be providing discounts, cashback or gift cards or social points. The user-centric systems must be rewarding as the rewards are the parameters to retain high customers in the business.
Entertaining
This is the most essential user experience goal which is kept in focus to design a user-centric system. The users should enjoy their time while working in the system to prevent exhaustion and to provide better quality work. Entertainment is a factor which is being measured from the perspectives of the user and when compared to similar products providing similar services. The fun experience is very essential to make a system commonly used among the users.
Motivational
This is a factor which is stated as the level of drive the system provides the users, to bring similar services to the market. The parameter of motivation defines how the system can become popular among users because of the motivational values (Uxfol. (2020).). The user-centric system to monitor energy consumption should have high motivational features to promote the idea of conserving energy and cutting domestic electric costs. The parameter of motivation accelerates the rate at which the predicted goal is achieved.
2.1.2 Energy usage in terms of spending & usage
Energy is an essential resource that is needed to complete many tasks and to perform many operations. In the present time, human beings are surrounded by the vast devices which work on electrical energy. Reduction of the consumption of energy is essential to bring a reduction of the costs of electric consumption at the household level (Yu et al. 2020). This can also help to save the non-renewable sources of energy are consumed in a controlled manner in the households. Electrical Energy can be also generated from renewable sources of energy such as solar energy and wind energy which are clean sources of energy and are less expensive. There are a number of ways in which the household consumption of electrical energy can be reduced such as the use of energy-efficient devices in the household, the use of natural light instead of artificial lights in the houses to cut the costs of the lights in the daytime, effective methods of electric space heating and cooling should be applied and lastly, the dependencies on the appliances should be reduced to bring an effective savings of energy and costs for the consumption of electric energy (Ceccherini. 2022). The spending of the costs of consumption of domestic energy in the appliances can be reduced by the reduction of time based consumption in which the appliances are used but for a shorter interval of time to control the consumption of electrical energy in the households and to cut down the domestic expenditure of electricity consumed.
2.1.3 Setting Up the initial programme
The initial programme to run the user-centric energy monitor of the system to conserve the usage of the electrical energy that is consumed is being evaluated in the flow diagram of the process which is provided below.
The system should have a system of installation in the domestic circuit and once installed, the usage parameters which are generated are evaluated in real-time in real-time use. The live parameters are then evaluated which is followed by the creation of a personalised account of the user since the system is user-centric (Godoy et al. 2022). The security of the user data should be managed by keeping a unique login password system where the login is being done by the user using credentials. Then the devices that need to be evaluated are connected to the system and then the dashboard of the system represents all the evaluated parameters of the devices. From the evaluations, the tariff which can be generated from this consumption is evaluated and calculated for the user along with providing essential information regarding the energy consumption by the devices.
2.2. Activity: 2
2.2.1 Design Principles
The designing of the user-centric energy monitor system is done with a focus on the 5 design principles that are being stated as Visibility, feedback, constraints, consistency and affordable. The designs and the prototype of the system are being built based on these principles (Lyon et al. 2020). The designing of the prototype of the system is being done in the software FIGMA and the flow of the models is used to define the process flow or the prototype of the design.
The 5 principles are expanded as:
Visibility
This is a parameter of design that defines the level of clarity and understandability in the system on which the user is performing operations. The visibility of the system should be high to maintain the status of the system and to maintain the easy flow of information between the user and the computerised system. The system should translate all the information which are needed by the user in the dashboard to make the processes easy and understandable for the user. The visibility of the system should maintain a balance between the motivations of actions and should be easily understood. The user interface of the system is very essential as it is the primary step to attract customers towards the process and the company. The value of the system can be increased with enhanced visibility and advanced tools that can be used to increase visibility.
Feedback
This is the parameter which brings information from the users and customers to the company to give the company an idea of how the system is performing in the market with the users. The feedback system is very essential as it provides the estimations of satisfied and happy customers of the service to the company. The feedback of the users is very important to maintain communication between the company and the users and to maintain customer loyalty. The user-centric energy monitor system is designed with a system of feedback where the satisfaction of the user is being questioned to evaluate the feedback system and the satisfaction of the users. The ultimate goal that is kept in focus is to design a system prototype that is responsive to the user and can collect feedback from the users in the form of reviews or questions or surveys. The user-friendly approach of the user interface of a system can be estimated by the level of visibility and the level of feedback the system has created while interacting with the users. Visual and graphic elements should be present in the user interface of the system to make the system understandable and easy. The system of feedback encourages and guides the users to perform certain tasks in an easy manner and helps to reduce time and to increase the perfection of the process.
Constraints
This is the parameter which is used to define the limit of operation of the system, this parameter restricts the user to perform a certain operation. The constraints are functional limits of the system which restrict the access of the user for certain operations. The number of choices the user can make in the design of the system is evaluated with the constraints of the system. There are 4 categories in which the parameter of constraints can be subdivided further. The divisions are cultural, physical, logical and semantic where the actions that are grayed out are being mentioned below their respective category. The actions can be greyed out because of precautionary reasons too or to limit the input of the user. The user-centric energy monitor system that is designed is also introduced to certain constraints such as the estimation of costs of other households cannot be monitored and the estimation can be done monthly not quarterly and yearly to prevent confusion for the users.
Consistency
This is the parameter of the system designing which defines the level of retaining of the advantageous properties of the system. Consistency maintains the reputation of the company and the system. The consistency of the user-centric system should be high so that the users can be satisfied with the services provided by the system and to ensure correct outcomes of the evaluations of energy consumption (Nati et al. 2013). The creativity of the designers brings new enhanced features in the designs of the systems and this is how the consistency of the system is being lost. This parameter also measures the quality that the same reaction in the system is obtained every time a certain action is applied in the system. The recognition of the brand and the company is being brought down to the market with help of consistency when a certain property of the system or the company remains unchanged for a long time and gets noticed among the users, such a property can be the logo of the company.
Affordable
This is the parameter of the system that makes the system within the understanding range of the population. Affordance can be stated as the relationship between the uses of the system and what the system looks like to perform. The more a system is clear to understand to predict the service of the system, the more is the affordability of the system. For example, if a mug is being kept in the market the purpose of the mug can be easily guessed and therefore the affordability is high. The energy monitor which is built with clear visibility and hence the affordability is high for the system and the prototype that is designed.
2.2.2 Prototype
The prototype of the design is being designed in the FIGMA software where the frames are being connected with arrows to make the prototype of the application. The aim of the process is to monitor the energy consumption of the different appliances of the household and to ensure the reduction of energy consumption (Bauk et al. 2020). The costs of the domestic electric consumption are intended to be cut down to reduce the consumption of electric energy in the household and by the household appliances. Electricity and energy are very essential in the present times and the focus on environmental conservation can be successful only if the consumption of electrical energy in the household on a daily basis is reduced.
In the above prototype diagram, the frames of the several processes such as login authentication, evaluation of energy parameters, evaluation of device parameters, and evaluation of tariffs from the appliances are all the processes that are needed to complete the process. The flow between the frames determines the prototype of the system.
2.2.3 Key Users and persona creation
The key users of the user-centric system are the people who are interested to bring change in environment by decreasing the consumption of electrical energy by the electrical appliances. The key stake holders are the management of the company Sweet Home and the board of directors of the organisation and the designers of the application are also one of the key stake holders of the system. The persona creation is necessary as to include the requirements and interests of the customers in the business and application of the application. The template for the persona creation of the engineer is also made to make the interests parallel.
2.2.4 Work Domain Analysis
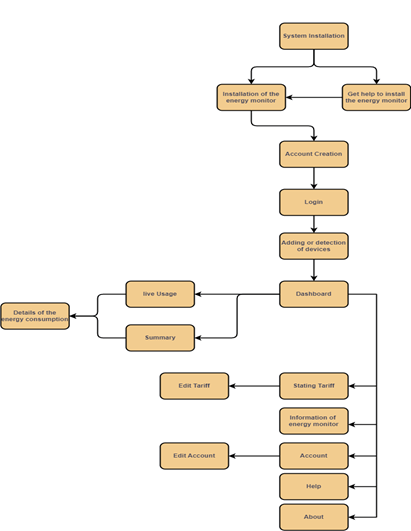
Figure 12: Work Domain Analysis
2.2.5 The User interface is illustrated in the form of a sketch
The sketch of the user operations is being provided for a better understanding as below. The flow of the operations is from the login of the system to the estimation of tariff and application details.
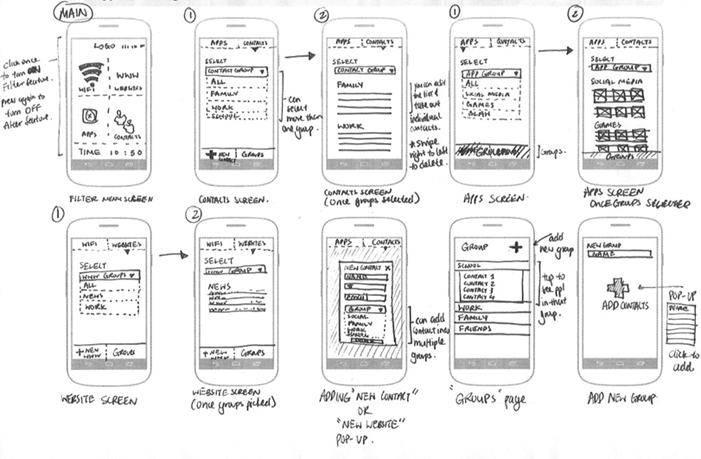
Figure 13: Sketch of User Interface
2.2.6 User-centric design using agile methodologies
The user-centric design is being made to conserve the electrical energy consumption of electrical appliances of the household and to design a sustainable and responsible house interface to monitor the consumption and to evaluate the tariff. The demands of the user are being identified and agile methodologies are being used. The development testing and release of the system is being done in an agile method where the development and the testing of the system is being done cyclically.
The demands and the purpose of the system are being evaluated in the performance of the system. The objectives that are being targeted to be met using this user-centric design are monitoring and evaluation of the consumption of the energy by the electrical appliances of the household and to calculate the electrical energy tariffs based on the consumption. The time taken to meet the needs in the respective development and testing phases are stated.
2.2.7 Cultural differences
If sweet home were to introduce similar services in India then several parameters were needed to be focused on to provided correct insight of the energy consumption. The parameters of cultural and social differences were to be focused to make the system suitable for their Indian system and Indian market.
Power distance
The power distance represents the level of equality and the level of power distribution in the society. The power distance of UK is 35 whereas the power distance of India is 75 so policies and factors of the designing should be be based on matters important for all the sections of the society since India is a nation where power is more or less evenly distributed in the society.
Individualism
The individualism refers to the responsibilities of the people shared in the society, which means that if people are responsible to take care of their own and their family they are stated as individualists whereas if people take care of a group in return of loyalty or services then they are said as collective. India is in the border line of this property and therefore the policies of the company should be somehow based on both individualistic and collective traits where as in UK the people are generally individualists and individualistic approaches are being used there.
Masculinity
This parameter represents the basic manifestation of elements of the society and the majority gender of the society. The rank of UK is high in the scale of masculinity holding 66 points where as India holds about 56 in the scale of masculinity. The policies of the company should be based on more masculine approaches in UK and should be of less masculine approach in India.
Uncertainty Avoidance
This cultural and social parameter refers to the level of toleration of the ambiguity in the society. The nations of India is low in the scale of uncertainty avoidance, and therefore the business assignment policies in the two nations are both risk taking and aims for innovations and success. The risk taking market of both the nations have brought high chances of development for the nations.
Long Term Orientation
This parameter is used to evaluate the connection of the past with the present and future goals and challenges. India is nation with a rich past a nation which is very much connected to the roots. Therefore the scale of Long term Orientation is low for India and this means that the nation has conserved the culture and have very few adapted to the changes of the times and the enhancement of the technology. The policies of the company in India should be connected to traditional methods to increase their hold in the Indian market.
Indulgence
The scale of indulgence is used to denote the level of restrains and constricts in the society. The society of India is a restrained society and therefore the scale is low in the scale of indulgence. The policies of the business for the company need not to be based on western indulgences to bring public attention in India.
Conclusion
The assignment is done as a case study on the company Sweet Home to evaluate the user experience of a system which is used to monitor the consumption of energy in the appliances of a household. The cost of the consumed energy is also evaluated in the system and the satisfaction of the user is maintained. The control of the appliances along with the consumed unit of electric energy are evaluated in the system. Several user experience goals and usability goals have been set as standards while designing the process and designing the prototype of the process of the system. In present times, energy is one of the most essential resources and the conservation of the energy consumed is very essential to bring many advantages to the environment and to preserve many energy sources of the world. The cost of electricity is also rising because of similar reasons and in present times the reduction of domestic energy consumption costs is very critical and can be done with the help of energy consumption monitors.
Reference List
Journals
Abbas, A.M., Ghauth, K.I. and Ting, C.Y., 2022. User Experience Design Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access.
Agarina, M., Karim, A.S. and Sutedi, S., 2019, December. User-Centered Design Method in the Analysis of User Interface Design of the Department of Informatics System’s Website. In Proceeding International Conference on Information Technology and Business (pp. 218-230).
Alarcón, J., Balcázar, I., Collazos, C.A., Luna, H. and Moreira, F., 2022. User interface design patterns for infotainment systems based on driver distraction: A Colombian case study. Sustainability, 14(13), p.8186.
Al-Hunaiyyan, A., Alhajri, R., Alghannam, B. and Al-Shaher, A., 2021. Student information system: investigating user experience (UX).International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications,12(2), pp.80-87.
Barambones, J., Moral, C., Ferre, X. and Villalba-Mora, E., 2020. A Scrum-based development process to support co-creation with elders in the eHealth domain. In Human-Centered Software Engineering: 8th IFIP WG 13.2 International Working Conference, HCSE 2020, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, November 30–December 2, 2020, Proceedings 8 (pp. 105-117). Springer International Publishing.
Bauk, S. and Fajardo-Flores, S., 2020. Matching interaction design principles and integrated navigation systems in an electronic classroom. Transactions on Maritime Science, 9(01), pp.90-98.
Borean, C., Ricci, A. and Merlonghi, G., 2011. Energy@ home: A" user-centric" energy management system.Metering International,3, p.52.
Ceccherini, E., 2022. User-friendly services in Public Administration: the Passport website: analysis and redesign for a fluid user experience.
Ciuti, G., Ricotti, L., Menciassi, A. and Dario, P., 2015. MEMS sensor technologies for human centred applications in healthcare, physical activities, safety and environmental sensing: A review on research activities in Italy.Sensors,15(3), pp.6441-6468.
Ferreira, P.M.D.S.D.R., 2016.A Human-Centred Approach for Residential Energy Efficiency Improving(Doctoral dissertation).
Godoy, P.L.S., Neris, V.P.D.A., Rodrigues, K.R.D.H. and Masoodian, M., 2021. Human-centred technology for sustainable development goals: challenges and opportunities.
Kang, Y., 2019. Redesigning CATME's Web Interface to Improve User Experience (Doctoral dissertation, Purdue University Graduate School).
Lyon, A.R., Brewer, S.K. and Areán, P.A., 2020. Leveraging human-centered design to implement modern psychological science: Return on an early investment. American Psychologist, 75(8), p.1067.
McCarthy, K.S., Watanabe, M. and McNamara, D.S., 2020. The Design Implementation Framework: Guiding Principles for the Redesign of a Reading Comprehension Intelligent Tutoring System.Grantee Submission.
Muslim, E., Lestari, R.A., Hazmy, A.I. and Alvina, S., 2019, April. User interface evaluation of mobile application krl access using user experience approach. InIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering(Vol. 508, No. 1, p. 012110). IOP Publishing.
Muslim, E., Moch, B.N., Wilgert, Y., Utami, F.F. and Indriyani, D., 2019, April. User interface redesign of e-commerce platform mobile application (Kudo) through user experience evaluation to increase user attraction. InIOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering(Vol. 508, No. 1, p. 012113). IOP Publishing.
Nati, M., Gluhak, A., Abangar, H. and Headley, W., 2013, June. Smartcampus: A user-centric testbed for internet of things experimentation. In2013 16th International symposium on wireless personal multimedia communications (WPMC)(pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Nguyen, J. and Dupuis, M., 2019, September. Closing the feedback loop between UX design, software development, security engineering, and operations. InProceedings of the 20th Annual SIG Conference on Information Technology Education(pp. 93-98).
Nguyen, T., 2020. Improving students’ UX in online learning platform: Case study: LAB faculty of business and hospitality management.
RANA, T., 2022. Devising a Usability Development Life Cycle (UDLC) Model for Enhancing Usability and User Experience in Interactive Applications. Sir Syed University Research Journal of Engineering & Technology, 12(2), pp.81-94.
Shabrina, G., Lestari, L.A., Iqbal, B.M. and Syaifullah, D.H., 2019, May. Redesign of user interface zakat mobile smartphone application with user experience approach. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 505, No. 1, p. 012088). IOP Publishing.
Silva‐Rodríguez, V., Nava‐Muñoz, S.E., Castro, L.A., Martínez‐Pérez, F.E., Pérez‐González, H.G. and Torres‐Reyes, F., 2020. Classifying design‐level requirements using machine learning for a recommender of interaction design patterns. IET Software, 14(5), pp.544-552.
Tanta, J.N., 2019. UX Re-Designing for Baudoin Wash System’s Website. Jurnal DKV Adiwarna, 1(14), p.11.
Tseng, P.H., Hsiu, P.C., Pan, C.C. and Kuo, T.W., 2014, June. User-centric energy-efficient scheduling on multi-core mobile devices. InProceedings of the 51st Annual Design Automation Conference(pp. 1-6).
Xu, Y.J., Chiou, S.C. and You, M., 2020. Effects of improving the interactive design of a Chinese character learning system on the learning performance of Chinese as foreign language students.Computer Assisted Language Learning,33(8), pp.916-935.
Yi, M., Wang, Y., Tian, X. and Xia, H., 2021. User experience of the mobile terminal customization system: the influence of interface design and educational background on personalized customization.Sensors,21(7), p.2428.
Yu, F., Ruel, L., Tyler, R., Xu, Q., Cui, H., Karanasios, S., Nguyen, B.X., Keilbach, A. and Mostafa, J., 2020. Innovative UX methods for information access based on interdisciplinary approaches: practical lessons from academia and industry. Data and Information Management, 4(1), pp.74-80.



