- BE275 Industrial IoT and Its Impact on Manufacturing SMES
- Introduction: BE275 Enabling Supply Chain Visibility through Industrial IoT
- How can IIoT influence the competitiveness of manufacturing SMEs?
- How can IIoT increase the geographical scope of SMEs?
- How can IIoT influence the operation of manufacturing SMEs?
- How can IIoT influence the supply chain operations in manufacturing SMEs?
BE275 Industrial IoT and Its Impact on Manufacturing SMES
Explore the various facets of our assignment help services tailored to your academic needs.
Introduction: BE275 Enabling Supply Chain Visibility through Industrial IoT
The report is revolving around the industrial internet of things and its use in manufacturing SMEs. A new era of interconnection has been brought in by the Internet of Things, or IoT as it is popularly called. IIOT technology intends to build massive networks of interconnected devices, extending from autonomous automobiles to intelligent home appliances. It has the power to completely change the business landscape and it has been recognized as a significant turning moment in the advancement of modern innovation.
According Ghobakhloo and Ching, (2019) the aim of this report is to evaluate the effect of the operation actions of IIOT, the Industrial Internet of Things. This report is designed to help SME owners to understand what they can do to utilize IIOT to influence it. The report is primarily an analysis of competition in the manufacturing sector for SMEs as well as how IIOT can impact the competition. It is predicted that the Internet of Things will play an important part in the evolution of Industry 4.0 with its ability to connect physical devices with digital platforms, creating the ideal environment for supply chain and manufacturing management. Industrial 4.0 represents a brand new stage of the Industrial Revolution that heavily focuses on different technologies that will significantly impact the business of all kinds. There are automation machines, machine learning, and interconnectivity.
How can IIoT influence the competitiveness of manufacturing SMEs?
The industrial internet of things has a great influence on the competitiveness of manufacturing SMEs. The ability of a firm to offer, in relation to its competitors, products of higher value at equal or lower cost. It is to build competitive positions that enable superior economic performance as cited by Serumaga Zake and van der Poll, (2021). IIOT helps in creating a competitive advantage by improving the performance of manufacturing SMEs. Following are the competitive area of SMEs which is influenced by IIOT
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
IIoT gadgets let manufacturers track materials and parts rapidly as well as globally. For example, Manufacturers can receive notifications when important ingredients will arrive by using Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) labels on items or shipping containers. The use of technology can improve accuracy in managing the inventory of firms. This can help in optimizing inventory management and create a competitive advantage for SMEs.
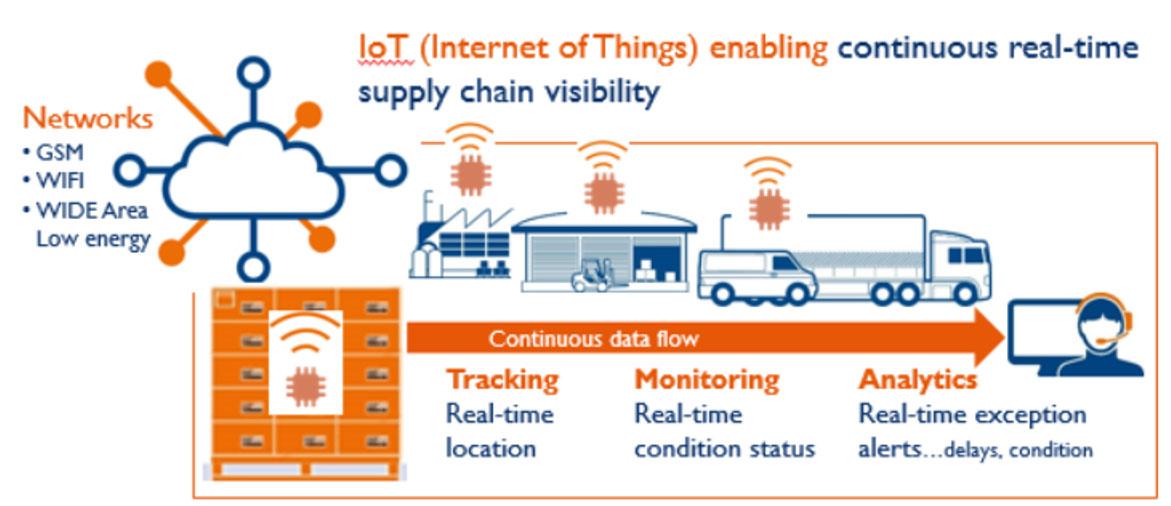
Figure 1 Internet of Things, your enabler of Supply Chain Visibility
Predictive Maintenance
IIOT also helps in predictive management which future influences the competitiveness of the manufacturing SMEs. The use industrial internet of things can help in better maintenance of production lines, IIoT sensors will help in tracking humidity, heat, and vibration.
Benefit: By collecting data from whole assembly lines, manufacturers may predict exactly when their machinery needs maintenance, reducing maintenance costs and time and increasing profitability. Additionally, integrated technology might aid in identifying issues earlier as they impact the whole supply chain (Dutta, Kumar, Sindhwani and Singh, (2021).
Operational Efficiency
The IIOT influence the operational efficiency of manufacturing SMEs and have several benefits with some risk. IIoT technology enables enterprises to track a crucial performance measure known as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), which measures the proportion of effective manufacturing time. According to Hoerlsberger, 2019 with the help of sensors, the Information can be gathered and distributed across the whole operating system of SMEs. This enables businesses to see trends more clearly, like unplanned downtime on particular equipment or production lines. The benefit of IIOT for improves the competitiveness of SMEs, Manufacturers can obtain the knowledge they can utilize to design capability, enhance functionality, reduce energy usage, improve growth, and cheaper costs per made product. By being open with this information, firms could be able to land agreements with strict performance requirements. The risk of using IIOT can lead to technological failure which will result in operational disaster for SMEs.
How can IIoT increase the geographical scope of SMEs?
The impact of the geographical scope of a SME based on the current internalization theory shown in figure 2, which is a theoretical framework suggests that SMEs geographical scope positively affects the rate of growth of their business but it also causes it to be less reliable, i.e., a positive impact in both the average as well as the variation of growth. According to Müller, Maier, Veile and Voigt, (2017) the benefits of growing scope will only be realized when firms are able to manage the increasing complexity of governance operations by making use of the managerial skills internationally obtained, e.g., through international education and knowledge with IIOT and limiting the geographical expansion of their home regions. The theoretical framework proposed suggests that the amount of countries where an SME operates has a positive impact on its growth rate, while making its reliability less secure. This means that theoretically and investigate empirically is a two-pronged consequence of an increase in geographical area: higher SME revenue growth however, it also results in an increased variation of expected revenue, resulting in greater risks, more uncertain outcomes, and a higher chance of SMEs failing.
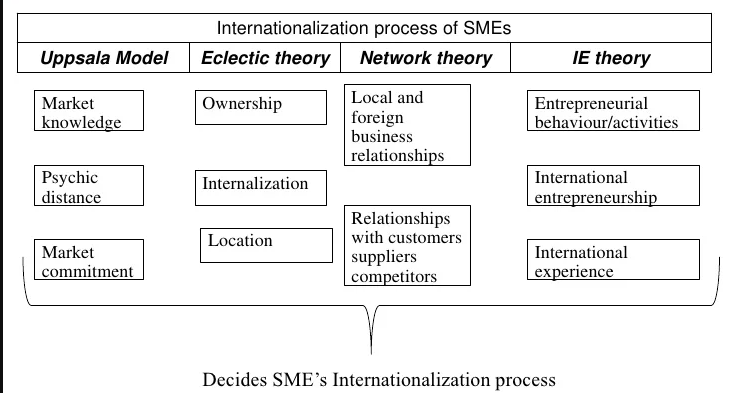
Figure 2 Internationalization theory
The theoretical framework is tested empirically with information from SMEs by using the multiplicative heteroskedasticity model that allows for separating the impact on the magnitude and the variability of the result using an endogenously modeled the geographic coverage. Greater scope offers significant benefits due to access to more markets and diversification, but it also comes with significant costs and difficulties related to the administration of operations. Sensors, smart devices as well as Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) software solutions are the primary elements to achieving smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0. SMEs must begin installing these innovative solutions to the integration and adoption the IIoT technologies (Kumar, Sindhwani and Singh, 2021). The principal reason behind using IIoT solutions is to boost growth by enhancing products in geographically targeted area, increasing the efficiency of manufacturing and providing top-quality customer service and focusing on implementing more effective factory operational management capabilities. The general strategy is to cut down on the complexity of their IT infrastructure by working to decrease the number of various technologies used such as LAMP stacks AD, Windows, O365, old systems etc. which will result in better management and reduced maintenance costs for the entire IT ecosystem geographically.
How can IIoT influence the operation of manufacturing SMEs?
The operation of manufacturing SMEs is very important for the business. IIOT influence the operation of manufacturing SMEs in very positive ways. IIOT creates a good ecosystem for the operations of SMEs in the manufacturing industry. This ecosystem influenced SMEs operation in the following ways:
Connected manufacturing: The manufacturers can utilize numerous analytical models for increasing productivity and lowering process defects by integrating in-store information with the overall company data. Real-time data collection for various metrics across the manufacturing equipment is how the industry leaders in car components have increased their operating effectiveness by lowering their energy costs, maximizing capacity utilization, and doing so.
Connected assets: Manufacturers can successfully use analytics tools and IIoT to increase monetization, collect data on customer behavior, machine utilization, impact on the environment, etc., to comprehend the needs of the consumer and offer new services to fulfill those needs. According Deflorin, Scherrer and Schillo (2021) the manufacturers and suppliers for the construction sector now communicate with their equipment on the job sites in real-time. To provide benefits to dealers and end users, they can remotely check their performance and health. Good online data management services, like those offered by Remote DBA.com, were necessary for such a system.
Connected supply chain: When it relates to Network infrastructure, it can offer end-to-end accessibility as well as authenticity. Customers and suppliers may effectively exchange information to enable quick decision-making, lowering the chance of any interruptions. Various items and the flow of information are merging when sensors are integrated into physical reality. Additionally, this guarantees fine-grained visibility of the organizational resources across all of their locations Manavalan and Jayakrishna, (2019). By enabling flexible and learner-responsive supply chains, it consequently assesses project and conformity with the anticipated delivery dates on the supplier side and captures customer patterns to keep compliance on the demand side.
Connected services & products: The manufacturer is unaware of how and where the product is used once it has been created and delivered to the consumer. Numerous new services, like planned maintenance, wireless connectivity, fraud protection, performance appraisal, etc., can be enabled when a device of this type begins to provide data to the creator (as cited by Müller and Voigt 2017). Many SMEs now collect information from their tools for customer support and preventive maintenance, including tool and automotive part makers. Additionally, this will cut down on setup time and help to prevent any tool failures.
How can IIoT influence the supply chain operations in manufacturing SMEs?
Industrial IIoT systems have completely changed supply chain top management operational efficiencies and income prospects because they have increased transparency throughout the supply chain. Supply chains today not just to make it possible for SMEs to monitor goods but also give the business a competitive advantage. The based global Industrial Internet of things (IIoT) on conventional manufacturing is examined in the Snow and Sullivan market study on the digital supply chain. There are many different IIOT concepts, and each of these concepts, including robotics, Big Data, data modeling, blockchain, enhanced and augmented worlds, and 3D printing, can be applied to specific supply chain components, beginning with raw material sourcing to retailing as cited by Müller and Voigt, (2018).
IIoT has the ability to significantly enhance internal logistics, supply chain response, employee satisfaction, and customer happiness when used to its fullest capacity. The extended production process is about to undergo a significant transition because of ground-breaking developments in instrumentation and distant communication technology, supported by simultaneous breakthroughs in programming.
Industry 4.0, also known as IIoT, has primed the world for the next transformation. It imagines electronic structures characterized by all-pervasive interconnectivity, wise decision-making, and real-time monitoring as cited by Radanliev, Roure and Burnap, (2020). A new era of confluence is emerging, one that will use easily accessible useful knowledge to boost quality and productivity to unprecedented heights. Creating digital supply chains has various benefits, including increased risk reduction, real-time inventory tracking, and real-time logistical management. Technologies are at the center of this change because it gives users the freedom and resources they need to create application-centric functions that are specific to each business and that support ultimate decision taking. Following are the major impact of IIOT on the supply chain operation of manufacturing SMEs.
Real-time location-tracking
Managers have access to a consistent stream of actual data on the product's placement and the environment surrounding transportation because of the Internet of Things. SMEs can keep track of the delivery of both finished goods and natural resources, and SMEs will be notified if the product is transported in a different path (Akpan, Udoh and Adebisi, 2022).
Storage condition monitoring
Environmental sensors allow management to track cargo circumstances and take action right away whenever it changes. For illustrate, one of the most popular IoT supply chain technologies collects information on pressure, moisture, the temperature within vehicles, and other variables that could endanger the integrity of the goods, and then automatically adjusts the environment accordingly.
Conclusions and recommendations
The report concluded that the supply chain worldwide and operations management are important. The research offers critical insights into the sustainable supply chain and the supplier chain. Included are the function and nature of the connections between the supply chain, Industry 4.0, and the environment. The industrial internet of things has a significant effect on the profitability of manufacturing enterprises. The ability of a company to offer products that are better than those of its competitors while charging the same price or less for products, as well as to create international competitiveness that enables superior economic performance. In the report, it was discussed how IIOT broadens the geographic reach of SMEs. For both SMEs and large businesses, security is a crucial component. It is recommended that SMEs must take care of every part of IT architecture for the correct implementation and activation of sensors as well as Big Data programmers because IIOT is not immune to dangers. In this regard, SMEs must consider the software and hardware components of the IIOT model, paying particular attention to the various networks, communications, and backup options.
References
Akpan, I. J., Udoh, E. A. P., & Adebisi, B. (2022). Small business awareness and adoption of state-of-the-art technologies in emerging and developing markets, and lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 34(2), 123-140.
Deflorin, P., Scherrer, M., & Schillo, K. (2021). The influence of IIoT on manufacturing network coordination. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 32(6), 1144-1166.
Deflorin, P., Scherrer, M., & Schillo, K. (2021). The influence of IIoT on manufacturing network coordination. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 32(6), 1144-1166.
Dutta, G., Kumar, R., Sindhwani, R., & Singh, R. K. (2021). Adopting Shop Floor Digitalization in Indian Manufacturing SMEs—A Transformational Study. In Advances in Industrial and Production Engineering (pp. 599-611). Springer, Singapore.
Ghobakhloo, M., & Ching, N. T. (2019). Adoption of digital technologies of smart manufacturing in SMEs. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 16, 100107.
Hoerlsberger, M. (2019). Innovation management in a digital world. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management.
Kumar, R., Sindhwani, R., & Singh, P. L. (2021). IIoT implementation challenges: analysis and mitigation by blockchain. Journal of Global Operations and Strategic Sourcing.
Manavalan, E., & Jayakrishna, K. (2019). A review of Internet of Things (IoT) embedded sustainable supply chain for industry 4.0 requirements. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 127, 925-953.
Müller, J. M., & Voigt, K. I. (2018). Sustainable industrial value creation in SMEs: A comparison between industry 4.0 and made in China 2025. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 5(5), 659-670.
Müller, J., & Voigt, K. I. (2017, May). Industry 4.0—integration strategies for small and medium-sized enterprises. In Proceedings of the 26th International Association for Management of Technology (IAMOT) Conference, Vienna, Austria (pp. 14-18).
Müller, J., Maier, L., Veile, J., & Voigt, K. I. (2017). Cooperation strategies among SMEs for implementing industry 4.0. In Digitalization in Supply Chain Management and Logistics: Smart and Digital Solutions for an Industry 4.0 Environment. Proceedings of the Hamburg International Conference of Logistics (HICL), Vol. 23 (pp. 301-318). Berlin: epubli GmbH.
Radanliev, P., De Roure, D., Page, K., Nurse, J. R., Mantilla Montalvo, R., Santos, O., ... & Burnap, P. (2020). Cyber risk at the edge: current and future trends on cyber risk analytics and artificial intelligence in the industrial internet of things and industry 4.0 supply chains. Cybersecurity, 3(1), 1-21.
Serumaga-Zake, J. M., & van der Poll, J. A. (2021). Addressing the impact of fourth industrial revolution on South African manufacturing small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Sustainability, 13(21), 11703.
ZETES Industries, 2022. Internet of Things, your enabler of Supply Chain Visibility(Online). < https://www.zetes.com/en/technologies-consumables/iot-in-supply-chain#footer> accessed on 12.12.22



