- Part: 1
- Introduction: Unit 8 Innovation and Commercialization
- An analysis of how innovation is sourced and fostered
- Innovation at Sainsbury
- Analyses on types and processes of innovation at Tesco and Sainsbury
- A critical evaluation of the success (or failure) of the innovation in Tesco and Sainsbury
- Part 2
- Recommended innovative products/processes for a new online grocery retailer, supported by innovation risk and benefit analysis
- Comprehensive business case for innovation for an organization
- Innovation Risk and benefit analysis
- Risk analysis in recommended innovation
- Ways to access funding
- Evidence-based business case analysis for innovation that emphasizes the business value for a potential investment
- Evaluate the range of methods for protecting innovation within organizations
- The exploitation of knowledge in addition to intellectual property rights
- Key Intellectual Property tools
- Limitations of Intellectual Property in wider business environment context
- A commercially driven business case for innovation
Part: 1
Introduction: Unit 8 Innovation and Commercialization
Innovation and commerce management is the set of work that allows any company to fulfil its long-run aims. Business innovation is the procedure of classifying new thoughts, and ideas and the arrangement of the purposes for the improvement of procedures and strategies in the attainment of purposes (Amabile and Pratt 2016). The report includes two parts, the first part is made to develop an understanding related to exciting cases of innovation in the Uk’s grocery retail industry. In this report two major grocery retailers of the UK market are picked up that is Tesco plc. and Sainsbury company. The report highlights how innovation is sourced and fostered in these two companies. To understand the impact of innovation on the success of the organization, an critical evaluation is done. The second part of the record determines the commercialization. For commercialization, a company needs to check possible industry partners in the UK market which are already successful. A new player entering the UK's retail market needs to check market readiness before commercializing its product into the market.
Looking for Assignment Help in the UK? Look no further than Native Assignment Help. Our team of experienced professionals is dedicated to providing top-notch assistance to students across the UK, ensuring they excel in their academic endeavours.
Tesco is an international grocery company in the UK and it has 30% of the total market share of the domestic industry. It is also the third-largest food retailer in the world. The company is founded by Jack Cohen in the year of 1919. Its headquarter is in Welwyn Garden city in the UK. Sainsbury is the second biggest food retailer in the UK and it has 14.9% of the total market share in the industry. The company was founded by John James Sainsbury in the year of 1969. Its headquarter is in London, UK.
An analysis of how innovation is sourced and fostered
Innovation at Tesco
Tesco has an extended narration of innovation; Tesco plc has constantly looked for innovative ideas to make sure Tesco plc foresees and reacts to its consumer's changing requirements. At the current time, Tesco plc keeps on searching for new associates to assist the company in developing more scalable, extended-term chances, in the region that might even be presently unknown and untapped (Bilińska-Reformat et.al. 2018). The company’s management teams bring expert information and knowledge to work for the exploration of innovation develop and nurture ideas to make them an actuality. Following are some steps taken by the company to source and foster innovation in the organization.
Partnering with “Manna Groceries” by drone
The company is always trying to find ways to assist its customers and use innovation to fulfill their demands at the right time.
Partnership with Manna will be used for delivering groceries items to its various consumers stay in two cities of Ireland that is Oranmore and Balbriggan. This is a useful innovation sourced by Tesco plc in its operation and business. Consumers can put an order with the help of the app and take delivery of it in very little time by drone from their neighboring store (Fernieet.al. 2018). This will transform those eleventh-hour shops for very urgent things or absent components for a recipe. This innovation has many advantages such as it is greener, quieter, faster, and safer than other ways of delivering the products. It is very convenient for its users and consumers. The drones are even proficient to open its wing in rain, and reasonable wind as well as in high temperatures and the Manna grocery is functioning directly with the Irish Aviation power on this experiment. This corporation puts together Manna and Tesco at the front position of scalable deliverance using innovative drones.
Use of Turing
Turing is an AI that is used for the transformation of product development. Turing is a thrilling new tech company and Tesco has partnered with it to explore the use of Artificial Intelligence in manufactured goods of its Brand products (Lončar 2017). Turing’s explanation permits the company to develop its products in authentic time, precisely forecasting buyer appeal, according to multiple supplies of information, permitting for much more rapid feedback than conventional product development technique. Eventually, the endeavor is to provide customers with improved products, quicker and more successfully.
Urban Fulfillment Centers
With the requirement for online grocery buying rising, Tesco has been investigating inventive paths to enlarge its capacity. Urban fulfillment is an example of this kind of innovation; Tesco is the first grocery retailer in the whole world which opens one in the back of a store. This UFC relocates the majority of choosing from the shop floor to a more condensed area that is separate from the consumer (Bitterman and Hess, 2021). This technology will carry products to colleagues so they don't have to walk every row of the store, allowing them to finish more order information each day. The company opened its first urban fulfillment center in 2020 and many are planned for the upcoming years. This innovation has the possibility to be game-altering for online grocery shopping for order fulfillment.
Innovation at Sainsbury
Sainsbury plc has continuously searched for new, creative ways to ensure that it can anticipate and respond to the changing needs of its customers. Sainsbury plc is currently looking for new partners to help the business generate more scalable, long-term opportunities in areas that may even be currently undiscovered and unexplored. The management teams of the organization use their specialized information and knowledge to explore innovations and foster ideas so they can become reality. The company has taken the following actions to encourage innovation within the company.
“Plant pioneers” a plant-based partnership
Sainsbury has launched its Plant Pioneers; it is purely based on plant-based foods for everyone. This innovation is sourced and fostered by partnerships with Derek Sarno, who is a chef with the mission to make extraordinary foods based on the plant. The Wicked Kitchen includes products exceed than 150, it is providing the market's most important option and brilliant quality to persons who want to consume a plant-based diet. Derek and the company's development chef are working together, directly and constantly fetching new and innovative plant-based food to shelves of the Sainsbury's outlets. Helping and supporting ever-rising customer attention and order. This collaboration started in 2018 with only 20 products and day by day it now had a wide range of products.
Sainsbury’s SmartShop
This is one of the most important innovations fostered by Sainsbury, the Smart Shop launched by the company last year. The aim of it was to take off the pressure on the buyer in the checkout lines by allowing them to add items to the basket by immediately scan process. Instead of needing to bag all the items at the checkout point, all customers need bring their scanner to the cash register point and detect a barcode before finishing payment as usual (Johnson, 2019). SmartShop is accessible at most of Sainsbury's stores, last year this is extended to almost every store in Sainsbury because of the pandemic. A handset is provided in Sainsbury's Smartshop, consumers can use these handsets as scanners while shopping in the store. the consumer can also use their cell phones as scanners, android and apple users need to install the app of the company then they can use their phones for effective scanning. Buyers need Separate verification for the usage of one of the handsets and are yet able to receive vouchers using the facility.
Deliveroo Platform
Sainbury is partnered with Deliveroo for providing fast delivery of its products. This is a very important innovation fostered by the company and it is sourced from Deliveroo. This plant includes a range of products such as ready meals, vegetables, fresh fruits, etc. this initiative was taken by the company the last year, and currently, it is one of the important innovations sourced by Sainsbury.
Analyses on types and processes of innovation at Tesco and Sainsbury
There is various type of innovation available in the grocery market of the Uk. Innovation is mainly related to three areas that are product innovation, process innovation, and business model innovation.
Product innovation
Product innovation includes the development of new products and improvement in the existing product. This kind of innovation also includes the addition of new features to the products. Product innovation can be done because of technological progressions, variations in customer necessities, or old-fashioned product design (Kahn, 2018). Product innovation is usually noticeable to the purchaser and must affect a bigger demand for produce. Product innovation and the quality of the product is a very important factors of success. Both companies recently launched their plant based product range, which provides vegan foods to their consumer.
Process innovation
Process includes the grouping of amenities, skills, and expertise used to manufacture, transport, and backup of products or delivery services. Within these comprehensive classifications, there are numerous ways by which processes can enhance. Process innovation also takes in the changes in the technology and equipment used in various functions of the company. It includes software used at grocery stores as well as product design and development (Lyytinenet.al. 2016). This innovation is applied to improve accounting and customer service procedures, supply chain and delivery system approaches, and software solutions. It also modifies the instruments used to sell and manage goods. In the case of Tesco plc, the company id partnership with manna for drone delivery, which will improve its delivery process. Another process of innovation example at Tesco plc is innovation in its product development, such as Urban FulfillmentCenters. On the other hand, At Sainsbury process innovation is done by partnering with diliveroo and urban eats.
Business model innovation
Business model innovation does not essentially imply modifications in the merchandise or even in the manufacturing process, but in the technique as it is taken to the marketplace. Business model innovation is possibly the utmost stimulating of the innovation kinds as it will possibly exist as a business with main necessities for transformation (Azar and Ciabuschi 2017). Targets for transformation are frequently the real competencies or processes that have been optimized to make a firm effective and lucrative. Certain aspects of the firm identity may be threatened by these changes, and they may also clash with claims made by the brand.
A critical evaluation of the success (or failure) of the innovation in Tesco and Sainsbury
This part of the report will evaluate the success and failure of innovation done by Tesco and Sainsbury. In 1869, Sainsbury's launched its first shop on Drury Lane in London. Since then, it has expanded to become one of the biggest merchants in the UK. Through ongoing innovation, Sainsbury's expanded the first half of the 20th century to become the top grocery store in the UK. The supermarket industry continued to evolve throughout the 1990s, but Sainbury lagged behind the competition rather than setting the pace for innovation. As a result, Sainsbury's lost ground to an inventive and brilliantly expanding Tesco and no longer ranks as the largest retailer in the UK.
Tesco
Tesco is extremely successful for the reason that of the growth approach that has allowed it to deliver its goods plus services to numerous nations from corner to corner of the eco sphere. The business inventive utilize expertise is one of the motives for being successful and effective. Implementing change by innovation is a extremely complicated process and involves many challenges. Tesco has conquer these confront by innovating and integrate technology into its business operation. The company's contacts center make use of technology to assist customers (Alexander, 2020). This service considerably improves the level of customer service that Tesco offers. Technology is also utilized in stores to make possible quick and simple shopping. For example, consumers can examine fraction of their purchase before coming to the investigate counter thanks to the scan-as-you-shop technology. These innovative technologies have improved the efficiency in operations and business processes in a multiplicity of ways, lesser operating costs and raising revenues. These technologies have advanced in many key regions with some illustration being Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems, high-tech checkout systems, amplified reality software, face-scanning equipment, scan-as-you-shop technology, and electronic shelf labeling. Private computer, retail locations, and mobile device are some of these places. Tesco also collaborates with customers, providers, shareholder, and some other stakeholders via information technology. This method has fashioned numerous reward. They consist of fewer accumulate catalog, a wider assortment of products, better supplier administration, superior incorporation of own-label products into Tesco's organization, reduced waste, augmented sales, and better efficiency and competence. Information technology is crucial to Tesco's business strategy formulation and the smooth functioning of essential business activities (Tangboriboonsuk 2015). The corporation uses several technical innovations to streamline its operations and processes.
Sainsbury
Sainsbury’s risen in the first half of the 20th era to turn out to be an important UK grocery retailer through continuous innovation. Sainsbury was the oldest and biggest grocery company. The company was the first one which opened its self-service supermarkets in the 1950s. and it turn out to be the biggest trend in the industry and the company's income increased. Later in the 1960s, Sainbury used computerized distribution in its operations and this innovative step helps in tracking deliveries and other activities (Sainsbury, 2020). The company was the first grocery retailer to use this innovation in the Uk industry. When the food and non-food item's demand were increasing the company introduced a range of organic goods with a bag made of recycled material. All these innovations made Sainsbury a leader in the grocery market, and bring immense success to the company in the domestic market as well as the international market. But by the 1990s period, the company fall behind in innovation and implantation of change into its practice, which made the company fall behind its key competitor that is Tesco plc. The most recent example of Sainsbury's failure is the company's failed in one of the important international markets that Egypt County’s market (Wake et.al. 2020). The company has used a go-to-market strategy in Uk, which lead to success in the UK market. The Company's same strategy applied to the Egypt market and it turned out to be a complete failure of the company. Innovation has historically been important to the grocery industry, but in the coming years, it may take on new forms that change the core motives behind why customers shop at their neighborhood supermarkets. So the company needs to focus more on innovation and sustainability in the industry.
Part 2
Recommended innovative products/processes for a new online grocery retailer, supported by innovation risk and benefit analysis
The procedure required to commercialize innovation within an business
Commercializing innovation is very important because it is the general way to reach the public and show the inventive product produced by the grocery retailer. It is not given that a new idea or innovation will succeed in the market just because the company files an invention disclosure, earn a patent, or secures a copyright (Gault, 2018). The company needs to evaluate its commercial possibility and further improve its go-to-market plan. There are several factors that affect a retail food product's commercial success on the market. For commercialization, a company needs to check possible industry partners in the UK market which are already successful. A new player entering the UK's retail market needs to check market readiness before commercializing its product into the market. Following are the commercialization process which it involves for the commercialization of products:
- The first one is to find the opportunity, a new player needs to identify the opportunity in the UK grocery retail market and also find ways to access the fund for the same.
- In the second step, an initial market assessment is needed to be done; it also includes competitive analysis (Kroh al. 2018).
- The third step includes product roadmap, technology validation, and business model canvas.
- And then comes the most important part of commercialization which is the actual launch of the product into the UK's retail market.
- The last step is making changes after customers review and control of innovation.
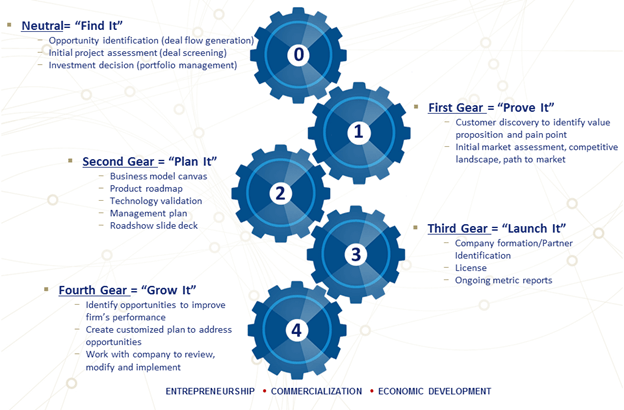
Figure 1 Commercializing Innovation
Comprehensive business case for innovation for an organization
For the comprehensive business case for innovation for an organization include recommendation of some innovative products for a new online grocery retailer in the UK grocery market with a risk and benefit analysis of the innovation and new products (Schaltegger and Burritt, 2018). A new company can use innovations used by leaders of the grocery market in the UK. Some of the most important product and process innovations are given below:
- Enable voice ordering
- Automate tasks with robots
- Eliminate checkout with grab-and-go concepts
Innovation Risk and benefit analysis
There are various benefits and risks involved in launching new innovative products and processes. Following are some benefits recommended for products and processes are given:
Enhance productivity and reduced costs
- Improved quality
- More added value
- Construction of product range
- Increasing exactness and customization
- Transformed the whole customer journey
The objective of a lot of procedure innovation is to lesser the unit expenses. These stores allow customers to go in, decide their matter, and be charged immediately while they stroll out by means of the most recent progression in machine knowledge as well as sensors (Foster et.al. 2015). Another benefit is better quality service and product; it is more probable to meet purchaser needs. The next benefit of automation and Robert is, Customers can then check their receipts, leave, and an instantaneous charge will be applied. Make sure you can accommodate these new modes of shopping as hands-free shopping becomes more popular by having an eCommerce website optimized for voice commands and providing compatibility for the most widely used voice assistants (De Massis et.al. 2015).
Risk analysis in recommended innovation
A strategy of spending in R&D and modernism can carry considerable rewards, but it is not free from the risk (Ramanathan et.al. 2017). Amongst the probable drawback is:
- Competition
- Availability of finance
- Uncertain commercial returns
UK's grocery industry is very competitive, and it will be difficult for a new company to create a significant market share. Even though copyright tender are some lawful protection, lots of original matter and methods are hard to guard (Blok and Lemmens, 2015). The exposure that opponent investigate will also be exceeded increases with the span of the expansion timeline. One of the major risks involved in getting funding or raising finance for the innovation.
Ways to access funding
- Bank loan – This funding technique is effortlessly available to grocery retail companies in the UK. In this business has the option of choosing a bank loan and agreeing to pay the set interest rate at a later period (Ključnikov al. 2016). The only drawback to this approach is that it has a greater impact on total retail company expenses when the interest rates are high for the loan amount.
- Venture capitalist - Venture capitalists provide funds to the start-up company in an exchange for interest. To boost future profitability, venture capitalists frequently make early investments in businesses. New companies can use this kind of funding to enter into a newly developed market like the UK.
- Crowdfunding –The retail Company can raise capital using this kind of financing from the general public rather than through banks or venture capitalists. The business can raise funds and offer the community for different benefits, such as environmental protection and development initiatives (Belleflamme al. 2015). This is more preferable kind of financing and has fewer restrictions.
- Government funding –This repayment includes tax payback, subsidies, short-rate credit facilities, etc. The major obstacle to this kind of financial support is there are numerous legal official procedures and eligibility criteria determined by the UK government. Funding by the UK government takes more time than the bank loan and venture capital.
Evidence-based business case analysis for innovation that emphasizes the business value for a potential investment
Angela Maurer, the director of Tesco Labs, spoke on innovation at Tesco at a recent CIO Summit in London. Two inputs are used at the start of the business: client requirements and future forces. Demands from internal departments and retailers are in addition to those of the customers. Future influences include social, technological, fashion, and demographic developments. Using the data from these two areas, the organization generates a lot of ideas during brainstorming sessions with various groups. The most promising concepts are picked, and concept development is started right away. Customers are employed to test the underlying assumptions. In order to draw in additional investors, Tesco's innovation team aims to spend six weeks from the initial concept to a minimum viable product.
The third element of the Tesco Corporate Innovation strategy is the support of selected outside start-up companies. Tesco has close relationships with a small number of business owners. Start-up representatives and multiple Tesco officials from various departments have brief encounters during speed dating events. There are common benefits. The executives learn about some of the most important developments, such as those in mobile technology, while the entrepreneurs receive expert advice on any topic they select from qualified managers.
According to Maurer, Tesco deals with some fierce rivalry in the retail industry for innovation that emphasize the business value for a potential investment.
the entire innovation effort is guided by the following four principles:
- Developing the concepts to meet the customer requirement
- Senior level sponsors frequently participate.
- Deadlines are set for each project, or "time boxing."
- Complete transparency within the teams.
Figure 2 Innovation in TESCO
Evaluate the range of methods for protecting innovation within organizations
The success of the multinational company depended on the recognition of innovation and the protection of those recognized innovation. Innovation can be protected with the help of intellectual property and that's why the company needs to heavily invest in intellectual property. In substantial works of person creativity are incorporated in the grouping of property recognized as intellectual property (IP) (Fraj et.al. 2015). There are plentiful ranges of intellectual possessions, as well as convinced nations are familiar with them to anecdotal degrees. The most well-known types include trade secrets, licenses, copyrights, and trademarks.
The exploitation of knowledge in addition to intellectual property rights
An Intellectual Property Right can be broken in numeral ways, which are to be selected conditional to the fauna of the Intellectual Property, the marketplace, and the worth of the Intellectual Property. The diverse modes or approaches which can be used by an Intellectual Property proprietor are copyright, patent, trademark. Direct commercialization is the exploitation of the apprehensive Intellectual Property by the proprietor itself of the corporate. The proprietor takes determination to show the fairs connections as well as reach the purchaser.
Key Intellectual Property tools
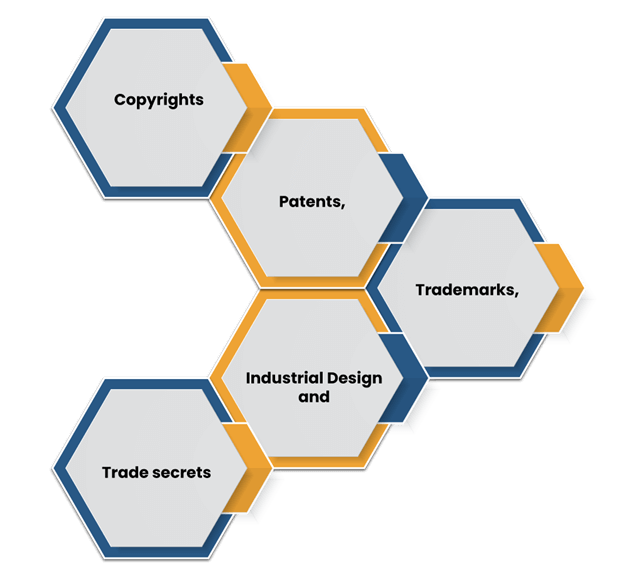
Figure 3 types of intellectual property rights
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property right which is granted by the government to the innovator of the invention. This right is provided in the exchange for the open disclosure of the discovery (Stim, 2022.). A manufactured goods or a procedure that explains a particular technical crisis constitutes a novelty. In universal, an innovation must get together the subsequent three criterions: it has to be novel, it should not be apparent, and it be required to have business applicability. To earn a patent, the owners are required to provide valuable facts and information about their innovation to the general public.
Copyright
The lawful term "copyright" is second-hand to pass on to the possession privileges that writers in addition performers have over their original workings. Original works of writing that are permanently fixed in physical or digital forms are protected by copyrights. Books, songs, audio recordings, movies, artworks, architectural works, computer code, and (in some situations) databases are among the literary or artistic writings that are protected (Bettig, 2018). Knowledge and suggestions are not sheltered by copyright; only the outline or manner of appearance is.
Industrial design rights
The orntal or artistic component of an entity is symbolized by its manufacturing mean. An industrial right for design, often recognized as a "design right" or "design patent," safeguards the aesthetic appeal of non-purely functional supplies. A design can comprise two-dimensional rudiments like prototypes, or ensign, and three-dimensional fundamentals such as the form or exterior of an entity. In general, it is what gives a thing an appealing appearance, in addition to as a product; it lifts the marketing worth of items.
Trademarks
A trademark is a representation is used to divide the goods of one corporation from the goods of other businesses. A trademark is identifiable symbol, design, or appearance which helps to distingue the good and services of one provider from another. And also helps in comparisons of two goods while making buying decision. A trademarked product may fetch a higher price in the market due to its reputation.
Trade secret
Another Intellectual property rights is trade secrete which is based on confidential knowledge which may be certified or sold. A method, technique, process, blueprint, device, shape, or gathering of knowledge that is not extensively recognized or easily ascertainable is referred to as a trade secret (Dratler Jr and McJohn, 2022). It is measured an unfair activity and violated of trade secret safety when others obtain, utilize, or disclose such secret information without permission .
Limitations of Intellectual Property in wider business environment context
In a wider business market, there are some limitations on intellectual property rights. Exploitation or violation of these rights is exercised by people, which limits the protection of innovation with the help of intellectual property. The following are the limitation of IPR:
Infringement
IPR infringement is the misuse or breach of intellectual property rights. Patent infringement occurs when the third party use, sells, and import innovation that is not authorized by the inventor. In the case of copyright, infringement takes place when a third party uses copyrighted work without the consent of the owner. The uses may be in the form of reproducing, distribution or performing work that is copyrighted (Parr, 2018). The most challenge to the patent IPR in the context of the wider environment is infringement in overseas countries. The challenge includes non-observance of infringement by WTO associate states.
Piracy
Piracy is the intentional infringement of any intellectual property right. Piracy can be done in the form of duplication of innovative work, and illegal distribution of copyrighted work. Piracy can also denote the listing or utilization of a well-known foreign brand that is not recorded in the nation or is unacceptable for the reason that the trademark is not in the use.
Counterfeiting
The terms "counterfeit" or "fake" are used to describe an imitation of a product. Consumers are misled regarding the origin and character of counterfeit goods, which hurts both the trademark owner and the public. False goods are produced, promoted, and delivered under the guise of being the real thing and coming from the real supplier (Yu et.al. 2021). Due to its link with the original goods, the counterfeit item can be offered for a higher price, which hurts sales of the real products. For products with trademarks, copying and counterfeiting original goods present significant difficulties.
Trade Secret Theft
Misuse of trade secrets is a social disobedience under central and state regulations. Stealing trade secrets can be considered a federal offense in some conditions. Industrial spying refers to the theft of trade secret facts and information that narrates about a product in foreign trade, to the financial advantage of third parties in addition to the damage to the trade secret holder.
A commercially driven business case for innovation
The business case for innovation is made to figure out how to deal with the challenges the company will experience in the UK market, and how to deal with risk and uncertainty. The innovation suggested is to Enable voice ordering, Automate tasks with robots, and eliminate checkout with grab-and-go concepts (Holliday et.al. 2017). This section of the report provides an explicit action plan for the innovation which are recommended above and used by leaders of the grocery retailers, sustained by methods to guard them in a wider environmental context. The business case for innovation captures WHY the company wants to take action on its innovation. It's generally a small, written paper that comprises the physical and elusive risks and profit of the improvement in the form of innovation. The foundation of why the innovation must be implemented and supported is also included. The action needs to be taken because this innovation has various benefits for the business but at the same time, it has some risks involved which were given above.
An action plan for successful protection of innovation in the wider business environment
The action plan includes mainly the following steps:
- Assessing the competition
- Study market trends
- Use intellectual property right
- Dealing with challenges
- Measuring the journey of innovation
The action plan starts with an assessment of the competition in the market. The biggest competitor of the new company is Tesco and Sainsbury; the company will study their innovation strategy and success with the strategy. It will lead to understanding how the company protects its innovation and what mistakes should be avoided by the company. The next step is to study market trends and how the breaches is happening, and keep an eye on the innovation of the company to protect it from such breaches. The company should purchase intellectual property rights to protect its inventions. The company will face many challenges in the protection of innovation such as infringements; it has to deal with them in legal manner.
Conclusion
The report concluded that innovation plays an important role in the success of any business including the grocery business. Tesco Plc has continuously sought out creative solutions to ensure that Tesco Plc anticipates and responds to the shifting needs of its customers. Tesco plc is currently looking for new partners to help the business generate more scalable, long-term opportunities in areas that may even be currently undiscovered and unexplored. Through constant innovation, Sainsbury's rose to become a significant UK grocery retailer in the first part of the 20th century. The largest and oldest retailer is Sainsbury. However, the company fell behind Tesco plc, its main rival, in the 1990s due to a lack of innovation and the implementation of change in its operations. The grocery sector in the UK market offers a variety of innovations. Product innovation, process innovation, and business model innovation are the three fundamental facets of innovation.
References
Amabile, T.M. and Pratt, M.G., 2016. The dynamic componential model of creativity and innovation in organizations: Making progress, making meaning. Research in organizational behavior, 36, pp.157-183.
Bilińska-Reformat, K., Kucharska, B., Twardzik, M. and Dolega, L., 2018.Sustainable development concept and creation of innovative business models by retail chains. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management.
Lončar, M., 2017. The impact of strategic management and strategic thinking approaches on business performance of companies operating in the retail industry. European Project Management Journal, 7(1), pp.85-98.
Bitterman, A. and Hess, D.B., 2021. Going dark: The post-pandemic transformation of the metropolitan retail landscape. Town Planning Review, 92(3), pp.385-394.
Fernie, J., Fernie, S. and McKinnon, A., 2018. 09 The of e-tail development logistics. Logistics and retail management: emerging issues and new challenges in the retail supply chain, p.245.
Johnson, A., 2019. How biometrics (and blockchain) could save bricks-and-mortar retail. Biometric Technology Today, 2019(3), pp.8-10.
Kahn, K.B., 2018. Understanding innovation. Business Horizons, 61(3), pp.453-460.
Lyytinen, K., Yoo, Y. and Boland Jr, R.J., 2016. Digital product innovation within four classes of innovation networks. Information Systems Journal, 26(1), pp.47-75.
Azar, G. and Ciabuschi, F., 2017. Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: The effects of innovation radicalne
Alexander, I.N., 2020. The influence of technological innovations on organization's competitive advantage: Case study on Irish food retail company (Tesco) (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin, National College of Ireland).
Tangboriboonsuk, K., 2015. Building an innovative culture in a Thai subsidiary of a multinational corporation in the retail industry: a case study of Tesco lotus.
Sainsbury, D., 2020. Toward a dynamic capability theory of economic growth. Industrial and Corporate Change, 29(4), pp.1047-1065.
Wake, D.J., Gibb, F.W., Kar, P., Kennon, B., Klonoff, D.C., Rayman, G., Rutter, M.K., Sainsbury, C. and Semple, R.K., 2020. Endocrinology in the time of COVID-19: remodelling diabetes services and emerging innovation. European Journal of Endocrinology, 183(2), pp.G67-G77.
Gault, F., 2018. Defining and measuring innovation in all sectors of the economy. Research policy, 47(3), pp.617-622.
Kroh, J., Luetjen, H., Globocnik, D. and Schultz, C., 2018. Use and efficacy of information technology in innovation processes: the specific role of servitization. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 35(5), pp.720-741.
Schaltegger, S. and Burritt, R., 2018. Business cases and corporate engagement with sustainability: Differentiating ethical motivations. Journal of Business Ethics, 147(2), pp.241-259.
Foster, J.G., Rzhetsky, A. and Evans, J.A., 2015. Tradition and innovation in scientists’ research strategies. American Sociological Review, 80(5), pp.875-908.
De Massis, A., Frattini, F., Pizzurno, E. and Cassia, L., 2015. Product innovation in family versus nonfamily firms: An exploratory analysis. Journal of Small Business Management, 53(1), pp.1-36.
Blok, V. and Lemmens, P., 2015. The emerging concept of responsible innovation. Three reasons why it is questionable and calls for a radical transformation of the concept of innovation. In Responsible innovation 2 (pp. 19-35). Springer, Cham.
Ramanathan, R., He, Q., Black, A., Ghobadian, A. and Gallear, D., 2017. Environmental regulations, innovation and firm performance: A revisit of the Porter hypothesis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 155, pp.79-92.
Ključnikov, A., Belás, J., Kozubíková, L. and Paseková, P., 2016. The entreprenurial perception of SME business environment quality in the Czech Republic. Journal of Competitiveness.
Belleflamme, P., Omrani, N. and Peitz, M., 2015. The economics of crowdfunding platforms. Information Economics and Policy, 33, pp.11-28.
Fraj, E., Matute, J. and Melero, I., 2015. Environmental strategies and organizational competitiveness in the hotel industry: The role of learning and innovation as determinants of environmental success. Tourism management, 46, pp.30-42.
Bettig, R.V., 2018. Copyrighting culture: The political economy of intellectual property. Routledge.
Dratler Jr, J. and McJohn, S.M., 2022. Intellectual Property Law: Commercial, Creative and Industrial Property. Law Journal Press.
Stim, R., 2022. Patent, copyright & trademark: an intellectual property desk reference. Nolo.
Parr, R.L., 2018. Intellectual property: valuation, exploitation, and infringement damages. John Wiley & Sons.
Yu, X., Zhang, H. and Yu, J., 2021. Luminescence anti‐counterfeiting: From elementary to advanced. Aggregate, 2(1), pp.20-34.
Holliday, C.O., Schmidheiny, S. and Watts, P., 2017. Walking the talk: The business case for sustainable development. Routledge.
university of Pittsburgh,2022. commercializing innovation (online). <https://www.innovation.pitt.edu/commercializing/commercializing-your-innovation/> (accessed on 5 December 2022).
Corpbiz, 2021. types of intellectual property rights (online).<https://corpbiz.io/learning/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-intellectual-property-rights/>(accessed on 5 December 2022).



