DNI 13 Dental Anatomy and Oral Health Assessment Workbook Assignment sample
Reinforcing Dental Anatomy Knowledge Through Interactive Workbook By Native Assignment Help
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
DNI 13 Dental Anatomy and Oral Health Assessment Workbook
Introduction: DNI 13 Reinforcing Dental Anatomy Knowledge Through Interactive Workbook
This workbook accompanies the dental anatomy and assessment of oral health session delivered by your tutorial will consist of a series of questions and require you to research information.
You will use varying methods to enable you to complete these questions. All can be completed using either written, typed, or audio answers to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of how you support your service users within your setting. Discuss with your tutor and decide your preferred method.
This unit has six learning outcomes
The learner will:
- Know the basic structure and function of oral and dental anatomy.
- Understand the methods of dental assessments.
- Know the clinical assessments and instructions associated with orthodontics.
- Understand the changes that may occur in the oral tissues.
- Understanding the management of oral health.
- Know the medical emergencies that may occur in the dental environment.
Evidence requirements
Minimum requirement of one observation. Supporting evidence of learner understanding must be completed and provided to support performance evidence. Simulation is allowed for this unit.
Unit DNI 13: Dental anatomy and assessment of oral health (A/618/4920)
This unit focuses on knowledge of dental anatomy and oral health about assessment and treatment planning
Guided learning hours for unit DNI 13 are 29 hours.
This unit is mandatory and is not graded all criteria must be met before completion of this unit.
This unit is evidence-based and will provide underpinning knowledge in preparation for your exam at the endpoint assessment.
Relationship to GDC Learning Outcomes:
1.2, 1.1.3, 1.1.5, 1.1.6, 1.1.9, 1.2.1, 1.2.2, 1.2.4, 1.2.5, 1.5.1, 1.5.2, 1.7.2, 1.8.4, 1.9.1, 3.3, 8.1, 12.1
Relationship to Dental Standard Knowledge, Skills, and Behaviours
K25: Know and understand the importance of maintaining accurate and current patient records following legal and regulatory requirements
K26: Know and understand the principles of information governance
K30: Know and understand contributing factors that can impact oral and general health
K31: Know and understand a range of conditions that could contribute to medical emergencies
K32: Know and understand the principles of First aid in the workplace
K33: Know and understand the regulatory requirements regarding documentation of medical emergencies and first aid incidents
K34: Know and understand your competence and limitations in dealing with medical emergencies.
K5: Know and understand the basic principles of a population healthcare approach including safeguarding, oral, and general healthcare, and your duty of care
K6: Know and understand how to raise concerns as described in the current General Dental Council guidance
K7: Know and understand dental and regional anatomy
K8: Know and understand the respiratory and circulatory system

Task1
(learning outcome 1, assessment criteria1.1, 1.2,1.3, 1.4,1.5and1.6)
1. Draw a table of deciduous (primary) and permanent (secondary) dentitions. Include:
|
Deciduous |
Upper |
Roots/Cusps |
Lower |
Roots/Cusps |
Function |
Age of eruption |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permanent |
Upper |
Roots/Cusps |
Lower |
Roots/Cusps |
Function |
Age of eruption |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Name the Six stages of the tooth for
|
1. Initiation stage |
|
2. Bud stage |
|
3. Bell stage |
|
4. Cap stage |
|
5. Root and Crown Formation stage |
|
6. Maturation stage |
1. Label the following diagram of a tooth:
- Initiation stage
- Bud stage
- Bell stage
- Cap stage
- Root and Crown Formation stage
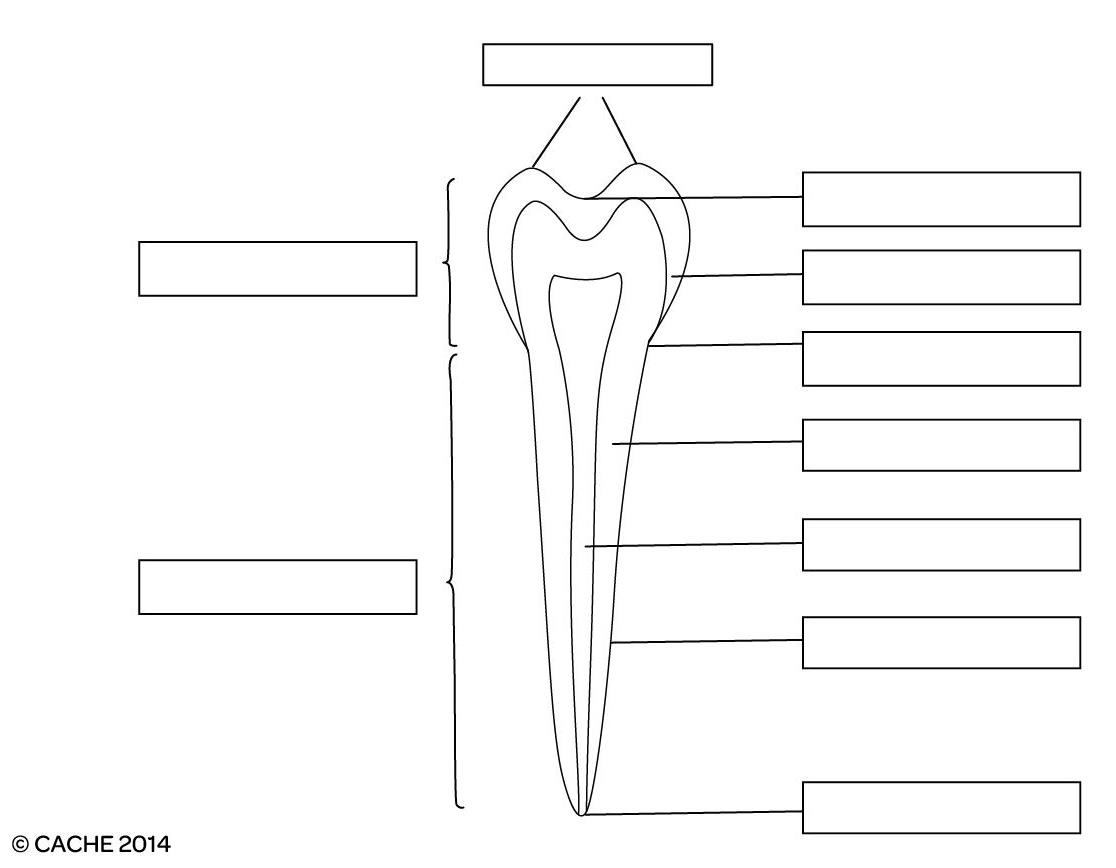
|
2. Describe the types and functions of the mineralized tissues and supporting tissues of the tooth.
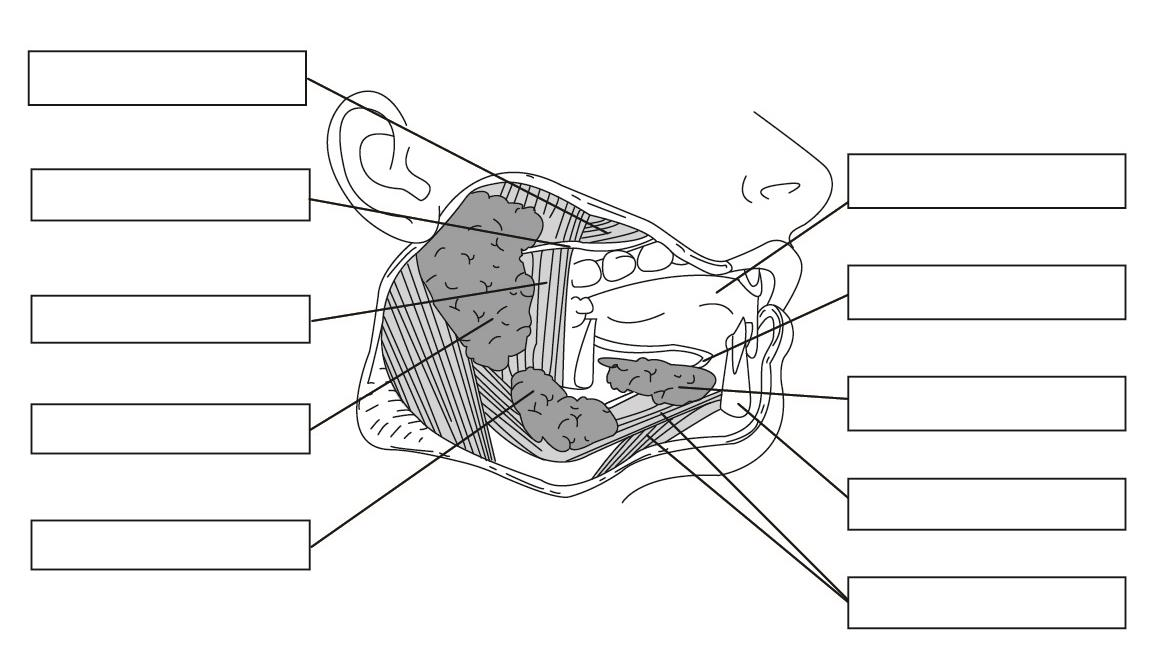
Label the muscles/salivary glands and ducts on the following diagram
3. Describe the function of salivary glands and state THREE reasons why they are important
|
The function of the 3 major salivary glands including the parotid gland, sublingual gland, and submandibular gland is to secrete enzymes, especially amylase to partially digest starch-enriched food. It also helps to keep our mouth always moist which ultimately helps to swallow the food. It also helps to protect our mouth from the invasion of harmful microorganisms, especially bacteria. |
|
1. the importance of the 3 major salivary glands is the lubricative function which helps to swallow the food as well as help in digestion |
|
2. salivary glands secrete enzymes, especially amylase enzyme which helps to digest food |
|
3. the slight acidic PH of the saliva helps to prevent bacterial invasion inside the mouth |
4. Name the following muscles of mastication:
Temporalis muscle
masseter muscle
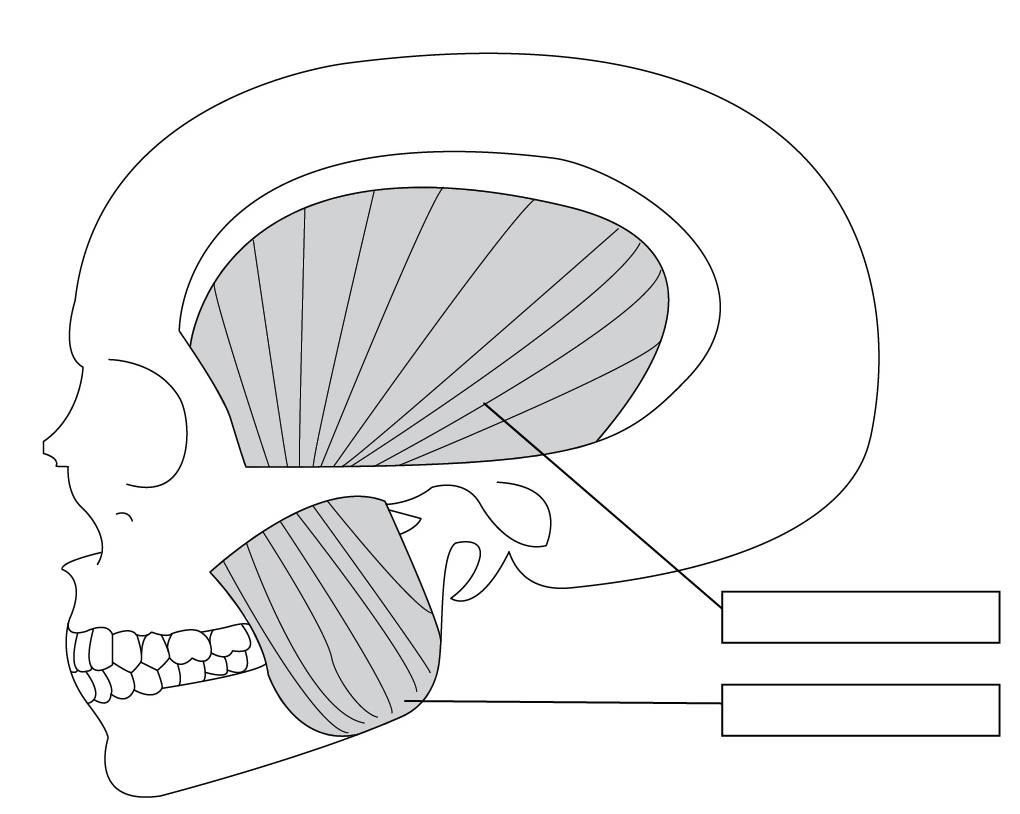
5. Name the following muscles of mastication:
Medial pterygoid muscle
Lateral pterygoid muscle
Buccinators muscle
Superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle
6. Draw a table containing the FOUR muscles of mastication and their position on the skull, ie point of insertion and point of origin and action.
|
1. The “medial pterygoid muscle” originated from the maxilla, the “medial surface of a lateral pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone”, and “Pyramidal processes of the palatine bone”. It links the two angles of the lateral pterygoid plate with the mandible to form the masseter muscle. |
|
2. The “lateral pterygoid muscle” originated from the greater wing of the sphenoid bone of the inferior head and the lateral surface of the pterygoid plate. The major function of the “lateral pterygoid muscle” is pulling the condyle out from the mandibular fossa of the head to protrude the mandible. |
|
3. Buccinator muscle originated from alveolar processes of the mandible, maxilla, temporomandibular joint, and buccinator crest. it helps to compress the cheek against the molar teeth to chew as well as swallowing of the food |
|
4. The origin of the “superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle” is from the Medial pterygoid plate and alveolar process. The function of this muscle is to contract the pharyngeal for transferring food to the esophagus. |
7. Label the following diagrams of the skull:
Nasal bone
Parietal bone
Temporal bone
Zygomatic bone
Maxilla
Mandible
Frontal bone
Coronal suture
Mental protuberance
8. Identify and label the diagram below:
Angle of jaw
Ethmoid bone
Lacrimal bone
Alveolar process
temporomandibular joint
9. Describe the movements of the temporomandibular joint.
|
Different types of movement occur in the “temporomandibular joint (TMB)” that occur in the mandibular depression as well as at the elevation level, protrusion, and lateral depression which appears on both the right as well as left sides. |
- Source and label a diagram that describes the nerves and their branches and the blood supply to the teeth and supporting structures.
The nerve that originates from the cranial nerve and supply to the teeth is the trigeminal nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and hypoglossal nerve.
However, the blood supply originates from the external carotid artery and its branches and drains at the internal as well as external jugular veins.
Task2
(learning outcome 2, assessment criteria2.1, 2.2,2.3, 2.4,2.5,2.6and2.7)
1. Describe the methods associated with two of the following and evaluate them:
Assessing and recording soft and hard tissue
Assessing and recording of periodontal conditions
Measuringpulp vitality
|
The assessing methods of the soft, as well as the hard tissue of the buccal area examination, are visual examination with the help of shining a light. Another method is Bimanual palpation where the dentist places one hand on the neck and another finger into the buccal cavity to identify the lumps from both surfaces. The dentist also takes dental photographs with the help of MRI and dental radiographs to identify any lumps in the soft or hard tissue. |
2. Oral assessment is a routine procedure performed in the dental surgery. Explain TWO of the following:
- The main purpose of an oral health assessment
- The reasons for taking photographs and radiographs when diagnosing and treatment planning
- What materials are used during an oral health assessment and why
|
The main focus of an “oral health assessment (OHA)” is to achieve the facility for transformation from a medicinal approach to a preventive approach for patient care in the long-term purposes to meet the exact requirements of respective patients. It also helps to encourage patient incrimination as well as involvement by managing OHA. However, the OHA helps to identify the suspected issues that are related to oral health as well as conditions that may be essential for clinical diagnosis by the dentist. The main reason for taking photographs as well as radiographs of both soft and hard tissue of the buccal region is to focus on the specific examination such as the presence of any kind of lumps or tumors in the tissue section which causes oral cancer in both surfaces of the oral cavity through MRI. |
3. Research the General Dental Council (GDC)principle of consent and explain how and why informed/valid consent should be obtained before any treatment is undertaken.
Task3
(Learning outcome 3, assessment criteria 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, and 3.4)
1. Explain the different classifications of malocclusion
|
The fundamental classification of malocclusion is mainly three types which are class I, class II, and class III based on the positioning of the teeth as well as the connections with the jaw bones. It is a medical term used to set the misalignment of the teeth to solve orthodontic issues. However, the different types of orthodontic issues that cause bad bites due to mismatch of the teeth with their jaws including • Crowned teeth issues • Crocked teeth issues • Protruding teeth issues • Difficulty in speech and its pattern • Difficulty in chewing • Dysfunction of the tempo mandibular joint (TMJ) |
2. List FOUR different types of orthodontic appliances used, and briefly explain their role in treatment
|
1. rubber bands or elastics The role of the use of this appliance is to fit the both upper as well as lower teeth and improve their alignment |
|
2. forces The uses of forces in the treatment of orthodontic issues such as eliminating overbites, promoting the growth of the teeth, and improving the alignment of the teeth. It is also used in jaw surgery. |
|
3. Palatal Expander It is an oral device used to open up the narrow space of the upper jaw, also used in the fittings of the roof of the mouth so that both jaws can move together |
|
4. Headgear and retainer Headgear is used to treat the overbite teeth of the patient which help to forward the upper jaw as well as the lower jaw and teeth. The retainer is a “custom-made device “which helps to correct the position of the teeth after using braces. |
3. Design a leaflet for a patient due to start orthodontic work. Explain:
- Cleaning and care of removable and fixed appliances
- What to expect (pain, other)
- Oral hygiene advice and advice about check-ups, etc.
(Please attached to your workbook)
To improve oral hygiene, the suggestive advice is to brush the teeth regularly as well as brush carefully. It also needs to focus on the use of fluoride component-based toothpaste and the bristle of the toothbrush needs to be soft. Along with this, brush the tongue. It is also required to avoid smoking or any kind of tobacco products to prevent the risk of oral cancer. It is also required to visit a dentist during any kind of dental issue.
4. Explain the dental Nurse’s role when providing support during the different stages of orthodontic assessment and treatment
|
The major role of the dental nurse is to support the patients during orthodontic issues or treatment. The nurse also helps to ensure all the dental instruments or appliances are correctly set up that are essential for the treatment as well as at the time of the post-procedure. At the time of the dental surgery, the dental nurse also assists the dentist in providing support to all the clinical procedures. The nurse also takes care of the hygiene issue of the patient after surgery to prevent cross infection as well as follow all the guidelines and policies of the clinical procedures. The nurse also helps to promote the lifestyle of the patient by ensuring their oral health as well as providing knowledge about oral health and taking care of the patient. |
Task4
(learning outcome 4, assessment criteria4.1, 4.2and 4.3)
1. Explain FOUR of the following conditions:
- Oral cancer
- Lichen planus
- Oral candidiasis
- Herpes simplextype1
- Glossitis
- Osteoporosis
- Salivary gland disorders (xerostomia)
|
1. Oral cancer- The cancer is formed in the oropharynx and oral cavity which means in the mouth, back part of the mouth, tongue, and gums. It is excess growth or tumor in the mouth that can not disappear and the symptoms are velvety white patches and bleeding (Peres et al., 2019). |
|
2. Oral candidiasis- This is a fungal means Yeast infection caused by Candida albicans that creates creamy white lesions on the tongue and the inner cheeks. Sometimes it spreads in the mouth roof. Several symptoms are taste loss, soreness, redness, and pain while swallowing. |
|
3. Herpes simplextype1- This is a transmitted disease that is spread through oral contact and causes oral herpes infection. HSV-1 also causes genital herpes. It is present in the body of those people who have antibodies of the other sub-type of Herpes Simplex (Liu et al. 2020). |
|
4. Osteoporosis- It is a condition where the bone is constantly broken down and replaced. Osteoporosis means “porous bone”. It is caused by the deficiency of bone mineral mass and density such as Calcium. Architectural deterioration happens in the structure of the bodies. |
2. Research and write a report on how aging can affect the soft and hard issues them
In the case of old people, they have receding gums because that helps create cavities on the tooth root. In old age, the mouth is dry which causes more bacterial growth and produces tooth decay. Oral cancer is also seen in older people aged 45 and above and affects the hard and soft tissues of the mouth. Ageing affects oral tissues and oral health such as oral teeth, lips, mucosa, and other associated structures. Aging creates several facial alterations and aesthetical considerations that create depression and anxiety in individuals. Aging is also caused by decreasing taste sensation and they are trying to add more taste ingredients such as salt that are also harmful to some people’s health. In the case of old people. There is the main problem with the teeth that start decaying because they are not chewing any food and do not get enough nutrients from healthy food (Zhang et al. 2021).
3. Briefly report on how four of the following medical conditions can affect the oral tissues:
- Oral cancer
- Herpes simplextype1
- HIV
- Hepatitis B
- Diabetes type 2
- Epilepsy
- Eating and digestive disorders
|
1. Oral cancer- This disease creates problems in swallowing and speaking that called dysphagia. The tissues affected by oral cancer include the oropharynx and oral cavity which means the mouth, back part of the mouth, tongue, and gums. |
|
2. Herpes simplextype1-The disease affects the gums, mouth, lips, and some other tissues. It os develops fever blisters or cold sores that are product symptoms such as painful and small blisters. It is present in the body of those people who have antibodies of the other sub-type of Herpes Simplex. |
|
3. Diabetes type 2- This specific type of diabetes creates a dry mouth known as xerostomia, which causes symptoms such as saliva that causes thrush, gum disease, and tooth decay. It causes several periodontal diseases and the main oral diseases are linked with diabetes caused by high blood sugar. |
|
4. Epilepsy- This disease affects the oral tissues with creates a dry mouth, bleeding gums, taste sense distortion, gum disease, dental caries, and soft tissue inflammation. |
Task5
(learning outcome 5, assessment criteria5.1, 5.2,5.3 and5.4)
1. Complete the table below describing the diagnosis, prevention, and management of malignant/potentially malignant lesions:
|
Malignant lesions |
Common methods as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound, and X-ray, positron emission tomography, bone scan, computerized tomography (CT) scan, and Needle Biopsy. |
The most important prevention method is avoiding smoking, Drinking alcohol, protecting against infections, regular exercise, following a healthy diet, protecting your skin, and healthy weight maintenance. |
There are several methods to control malignant lesions such as surgical treatments, “targeted drug therapy”, radiation, chemotherapy, incorporating surgery, and multimodal treatment. |
|
Potentially malignant lesions |
Common methods such as Biopsy, a new cancer device such as VELscope, OPMD slandered diagnosis, histological examination, and “Oral exfoliative cytology”. |
The common treatment method for Potentially malignant lesions are surgery that minimizes the risk of increasing tumors. Need to identify the stage, location, and type of tumor and provide therapy for the specific such as proteins and genes.
|
Need expert health care professional for predominant treatment method—scalpel excision, the laser greatly. |
|
Drugs/Medications |
Example |
Use in dentistry |
|
Analgesics |
Acetaminophen ibuprofen |
These drugs are effective for moderate pain and relieving mild pain in teeth. |
2. Completethetablebelow giving examples of the named drugs/medications and their use in dentist
|
Drugs/Medications
|
Example |
Use in dentistry |
|
Analgesics |
Acetaminophen ibuprofen |
These drugs are effective for moderate pain and relieving mild pain in teeth. |
|
Antibiotics |
metronidazole amoxicillin
|
These drugs are commonly used in the process of the adjunct of mechanical therapy, treating infected gums, dental abscesses, rosacea, and mouth infections. |
|
Anti-Viral |
valacyclovir Acyclovir
|
Valacyclovir prevent “herpes simplex virus infections” are both sub-type 1 and 2 when the dental procedure is carried out.
|
|
Anti-fungal |
fluconazole |
Prevents oral fungal infections such as candidiasis and superficial type. |
|
Tranquilisers/hypnotics |
Lorazepam Alprazolam Diazepam |
These drugs produce a long-duration anxiolytic effect for any dental surgery. |
|
Emergency drugs |
atropine midazolam metoprolol |
These drugs show Anticholinergics, Anticonvulsants, and antihypertensive effects for dental treatment. |
1. For THREE of the following areas, give TWO examples of disease and diagnosis and how they are managed:
- The oral mucosa
- Soft tissue
- Facial pain
- Facial bones
- Facial joint
- Salivary glands
|
Diagnosis |
Two examples |
Diagnosis/managed |
|
1. The oral mucosa
|
1. Behcet disease 2. Burning mouth syndrome |
is managed by using mouthwash, oral or topical corticosteroids, Immunosuppressants, and “Selective phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors”. Vitamin supplements, Saliva stimulants and substitutes, tricyclic antidepressants, benzodiazepines, and gabapentin. |
|
2. Facial joint
|
1. Myofascial Pain 2. Degenerative Joint |
A clench test, X-rays, MRI scan or CT scan, and analysis of Joint vibration. Treatment such as Arthrocentesis, arthroscopy, and “open-joint surgery”. |
|
3. Facial bones
|
1. Facial fractures
2. osteoporosis
|
Physicians check the facial impression and go through the X-rays. Drugs such as oral steroids, and surgery, prescribe some specific antibiotics. Some drugs for osteoporosis are risedronate, ibandronate, alendronate, other medications, and mineral and vitamin supplements. |
Task6
(learning outcome 6, assessment criterion6.1)
1. Identify FOUR potential medical emergencies that could take place in the surgery
|
1. Ruptured aortic aneurysm |
1. |
|
2. Aortic dissection |
2. |
|
3. Internal bleeding |
3. |
|
4. Limb ischemia |
4. |
For further tasks on medical emergencies and meeting assessment criteria 6.2, please refer to those in unit UFAEI: Firstaidessentials, which can be cross-referenced.
Learnerdeclarationofauthenticity: DNI13
I declare that the work presented for this unit/task is entirely my work.
Learner signature: Date:
For e-portfolios, a signature is not required, provided the learner has a personalized and secure login.
Reflective Account
Think about what you have learned during this unit. How has your knowledge improved and how have you applied this to your working practice? Please reflect below on the workbook you have completed by answering the following questions.
What have you learned or how has this reinforced what you already knew?
What was good about completing this workbook?
What did you find difficult?
How will your learning be used in practice?
|
How long has it taken you to complete this workbook? |
|
HRS |
|
MINS |
Click here to access top-notch assignment help provided by our Native assignment help company.
Go Through the Best and FREE Answers Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/dni-13-dental-anatomy-assessment-of-oral-health-workbook-18363
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/dni-13-dental-anatomy-assessment-of-oral-health-workbook-18363
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/dni-13-dental-anatomy-assessment-of-oral-health-workbook-18363
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/dni-13-dental-anatomy-assessment-of-oral-health-workbook-18363
- FreeDownload - 207 Times3.1 Analyse factors that influence the capacity of an individual to express consent
Introduction - Analyse factors that influence the capacity of an individual to...View or download
- FreeDownload - 780 TimesRadioisotopes Assignment Question and Answer
Introduction Radioisotopes and radiopharmaceuticals play a crucial role in...View or download
- FreeDownload - 851 TimesQuality Management in International Business: Burger King Case Study Question And Answers
Quality Management in International Business: Burger King Case Study Get free...View or download
- FreeDownload - 2081 TimesUnderstanding Safeguarding and Protection – Unit 11 Assignment Guide
Unit 11: Understand Safeguarding And Protection For students aiming to improve...View or download
- FreeDownload - 775 TimesStandard 3: Duty of Care Workbook Answers
Introduction: Duty of Care Workbook Answers in Standard 3 Get Answers to This...View or download
- FreeDownload - 914 TimesKey Answers and Explanations for Standard 9 Awareness Workbook
Standard 9: Awareness of dementia, mental health, and learning disability...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



