Dementia Care: Roles, Responsibilities, and Clinical Interventions for Healthcare Practitioners Assignment
Need assignment writing help in the UK? Native Assignment Help is your ultimate solution. Our seasoned writers possess the expertise to craft impeccable assignments that meet the highest academic standards, guaranteeing your success.
Q 1.1
The roles and responsibilities are necessary to be considered by the healthcare practitioners who are involved in giving the treatment and care of the patients. In the case of dementia patients, healthcare practitioners are required to take care of their patients as they face the prospect of vulnerability and are often subjected to self-harm. According to Mongkhon et al. (2020), the major symptoms of dementia patients have been the stage of confusion and the chances of causing self-harm. The causes and signs of the symptoms are observed above the older patients, and these patients require the care and treatment of healthcare practitioners. Healthcare practitioners who are involved in the treatment of patients who have Dementia are needed to assess their patients and need to ensure their safety and well-being of the patients. As suggested by Bethell et al. (2018), healthcare practitioners such as nurses need to ensure that dementia patients are taken care of and are subjected to continuous monitoring for 24 hours. These patients are required to be assisted with eating, bathing, dressing and other social activities.
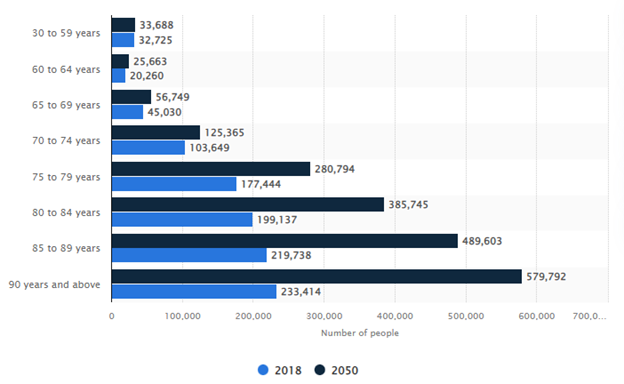
Figure 1.1: Number of dementia patients starting from 2018 and projected to 2050
The above figure shows the number of dementia patients starting from 2018 and projected to 2050. Healthcare practitioners must assess the various factors that ensure the health and well-being of the individuals suffering from the disease. Patients who have Dementia and Alzheimer's are required to be taken extra attention and care as they are vulnerable to incidents that may become detrimental to them. The doctors associated with the treatment of the patients are required to be involved in the regular assessment and analysis of the reports, which reduces the chances of hospital admittance (McGuinness et al. 2019). The doctors and nurses must do this assessment to ensure their safety. The other major initiative that needs to be taken is developing a management plan for the treatment of Dementia and Alzheimer's patients (O'Brien et al. 2019). This management is needed to address the issues of the patients, such as aggression, depression, and other behavioural changes.
Q 1.2
Professional responsibilities and accountabilities are needed to be exhibited by healthcare practitioners to ensure the safety and well-being of the patients. The doctors involved in the treatment of the patients are required to assess the various issues that will be helpful for them to address the issues of dementia patients (Handley et al. 2019). Dementia patients are subjected to issues that lead to memory loss and other major complications such as depression and self-inflicting harm. The doctors are required to assess their patients and need to start the treatment at the initial stages so as to reduce the impact of the disease (Bickford et al. 2019). In the case of dementia and Alzheimer patients, continuous assessments are required that will be helpful for reducing the impacts of the disease and helps in the formulation of plans. Healthcare practitioners are required to take care of their patients as these patients are facing the prospect of vulnerability and are often subjected to self-harm. The other major initiative which is needed to be taken is the development of a management plan for the treatment of Dementia and Alzheimer's patients.
The continuous assessment for the treatment and caring of the patients suffering from Alzheimer's and Dementia can be done through the implementation of the proper management plan. According to Ford et al. (2019), assessment leads to the development of a management plan which is required for the ensuring safety and well-being of the students. The management plan is required to secure the patients who are subjected to depression, anger, confusion and agitation (Crawley et al. 2020). The healthcare practitioners such as nurses are needed to ensure that their patients are not involved in self-infliction harm and require the 24 hours monitoring of the patient. Healthcare practitioners are required to assess the various factors that ensure the health and well-being of the individuals suffering from the disease. Patients suffering from Dementia and Alzheimer's are required to be taken extra attention and care as they are vulnerable to incidents that may become detrimental to them (Swann et al., 2020). The doctors associated with the treatment of the patients are required to be involved in the regular assessment and analysis of the reports, which reduces the chances of hospital admittance.
Q 2.1
The main inclusion criteria of an individual are identified as needs which are mitigated with the healthcare professionals for the management of the needs of an individual. The patient with special needs raises requirements for individual needs (Heger et al. 2019). The individual needs of the patients are listed in the below section;
- Quality of life is a need which helps to analyse rehabilitation and analysis of side effects.
- Psychological impact assessment of the identified illness
- The behaviour of the patient affecting the disease
- Assessment of social care
- Educational intervention helps to promote self-care and improve healthcare (Midtbust et al. 2018)
The above-mentioned area is needed for an individual, which is modified with the presence of special and chronic health issues. Patients with dementia are identified with special needs, as behavioural and psychological changes are identified in those patients (Yousaf et al. 2020). The changes in behaviour and aggressive behaviours change their healthcare needs. An individual with dementia get support from healthcare based on their needs, and those are listed below;
- ADLs (Activities of daily living) such as eating, mobility etc.
- IADLs (instrumental activities of daily living) such as meal preparation, financial and medical management
The mentioned care is given to the patient who has suffered from dementia where management of quality of life is needed as that is identified as the need of an individual. The social needs of the patient are also included in the healthcare needs of the patient, where specialities are needed to boost their self-esteem to improve their social position. The healthcare needs of an individual include “physical, developmental, mental, sensory, behavioural, cognitive and emotional impairment”(Heger et al. 2020). Those needs need to be fulfilled under the medical management of health issues such as special health situations such as dementia. Healthcare needs an individual treatment process and control along with the prevention of health issues (Yousaf et al. 2020). Therefore, the professional needs to analyse the actual health issues and related complications in an individual with a specialised case of health. In the case of dementia, the healthcare needs are identified with special areas.
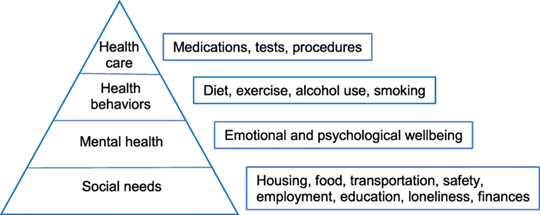
Figure 2.1: Healthcare needs
“Controlling a patient's life”is the main healthcare need of a patient with dementia, and during this process, the specialist needs to give personal space to the patient. As the healthcare needs, the nurses or specialist needs to identify needed time and activities which are needed to be developed for the quality care process (Midtbust et al. 2018). Besides, the basic need of the patient in primary healthcare needs of an individual need to be covered to improve the quality of care. “Environmental health needs”and “Health enhancement”are two main areas which are needed to meet and improve by a health professional (Aspe.hhs.gov, 2022). In addition, "basic needs, preventative service and necessary medical needs"are some other healthcare needs that are identified in an individual. Effective quality health care services are completed with the use of those needs to improve the health issues of an individual. Therefore, the identified health care needs include the background and situation of the person who has suffered from the present health situation.
Q 2.2
The healthcare practitioners, such as doctors and nurses, are required to understand the clinical treatments and interventions that are required to ensure the safety and well-being of the patients. The safety and well-being of the patients are done through the interventions of the doctors and nurses, and they need equal participation (Holmes et al., 2020). As in the case of the treatment and care of dementia patients, the patients suffer from complications that lead to loss of memory and other complications such as self-inflicting harm. The major clinical intervention for the treatment of dementia patients is memory training and physical exercise, and the training of social stimulation. Patients suffering from Dementia and Alzheimer's are required to be taken extra attention and care as they are vulnerable to incidents that may become detrimental to them. According to Davies et al. (2020), the doctors associated with the treatment of the patients are required to be involved in the regular assessment and analysis of the reports, which reduces the chances of hospital admittance. Memory training and physical exercise are required to improve the health status of the patients and ensure their improvement in their mental health and well-being, which leads to making the patients memory conscious.
The other major clinical intervention that is required for the treatment of dementia patients is training in social stimulation.Dementia patients are subjected to the conditions such as depression, anger, behavioural changes and other major issues that lead to self-inflicting harm (Faulkner et al., 2021). This clinical intervention needs to be undertaken by the healthcare practitioners such as nurses who ensure the health and well-being of the patients. Healthcare practitioners are required to assess the various factors that ensure the health and well-being of the individuals suffering from the disease. Social stimulation is done by helping older patients to participate in social gatherings and ensuring they meet with other individuals. The older patients who are made to interact with other individuals are being subjected to mental well-being, which is helpful for the reduction of the incidences of Dementia. The care institutions are made to ensure that the patients are involved in social interactions, which ensures that they are not facing depressive issues.
Q 2.3
The clinical activities that have been identified for the treatment of the patients are memory training and learning exercises and training of social stimulation with respect to dementia patients. The healthcare practitioners, such as doctors and nurses, are required to understand the clinical treatments and interventions that are required to ensure the safety and well-being of the patients. The safety and well-being of the patients are done through the interventions of the doctors and nurses, and they need equal participation. Healthcare practitioners are required to involve in the interventions of memory training and learning exercise in which the patients are subjected to learning the issues and topics which are related to patients' earlier life and other major important topic that is required to be remembered. The nurses working on caring for the patients are required to be involved with the patient's family, which will be helpful for the initiative of memory training. Patients suffering from Dementia and Alzheimer's are required to be taken extra attention and care as they are vulnerable to incidents that may become detrimental to them. As in the case of the treatment and care of dementia patients, the patients suffer from complications that lead to loss of memory and other complications such as self-inflicting harm. Thus the clinical intervention ensuring the memory rollback is required that will ensure the improvement in the psychological aspects of the patient.
The other major clinical intervention that is considered is the training of social stimulation, which is done by the active participation of the nurses and the family members of the patient. Dementia patients are subjected to the conditions such as depression, anger, behavioural changes and other major issues that lead to self-inflicting harm. These issues and conditions can be addressed by this clinical intervention as the patient will be subjected to meeting with the individuals and boosting the societal factors of the patients. Healthcare practitioners are required to assess the various factors that ensure the health and well-being of the individuals suffering from the disease. The practitioners are involved in the interaction of the patients and assessing the various issues that the patients face. The older patients who are made to interact with other individuals are being subjected to mental well-being, which is helpful for the reduction of the incidences of Dementia. The care institutions are made to ensure that the patients are involved in social interactions, which ensures that they are not facing depressive issues. Healthcare practitioners are also needed to get involved in other ways of intervention, which will ensure the improvement of the patients, such as the medication treatment and management of the behavioural stages of patients.
Reference
Bethell, J., Pringle, D., Chambers, L.W., Cohen, C., Commisso, E., Cowan, K., Fehr, P., Laupacis, A., Szeto, P. and McGilton, K.S., 2018. Patient and public involvement in identifying dementia research priorities. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 66(8), pp.1608-1612.
Bickford, B., Daley, S., Sleater, G., Hebditch, M. and Banerjee, S., 2019. Understanding compassion for people with dementia in medical and nursing students. BMC Medical Education, 19(1), pp.1-8.
Britton, E., Kindermann, G., Domegan, C. and Carlin, C., 2020. Blue care: A systematic review of blue space interventions for health and wellbeing. Health promotion international, 35(1), pp.50-69.
Burns, D., Dagnall, N. and Holt, M., 2020, October. Assessing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on student wellbeing at universities in the United Kingdom: A conceptual analysis. In Frontiers in Education (Vol. 5, p. 582882). Frontiers Media SA.
Crawley, E., Loades, M., Feder, G., Logan, S., Redwood, S. and Macleod, J., 2020. Wider collateral damage to children in the UK because of the social distancing measures designed to reduce the impact of COVID-19 in adults. BMJ paediatrics open, 4(1).
Davies, N.G., Kucharski, A.J., Eggo, R.M., Gimma, A., Edmunds, W.J., Jombart, T., O'Reilly, K., Endo, A., Hellewell, J., Nightingale, E.S. and Quilty, B.J., 2020. Effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 cases, deaths, and demand for hospital services in the UK: a modelling study. The Lancet Public Health, 5(7), pp.e375-e385.
Faulkner, J., O’Brien, W.J., McGrane, B., Wadsworth, D., Batten, J., Askew, C.D., Badenhorst, C., Byrd, E., Coulter, M., Draper, N. and Elliot, C., 2021. Physical activity, mental health and well-being of adults during initial COVID-19 containment strategies: A multi-country cross-sectional analysis. Journal of science and medicine in sport, 24(4), pp.320-326.
Ford, E., Rooney, P., Oliver, S., Hoile, R., Hurley, P., Banerjee, S., van Marwijk, H. and Cassell, J., 2019. Identifying undetected dementia in UK primary care patients: a retrospective case-control study comparing machine-learning and standard epidemiological approaches. BMC medical informatics and decision making, 19(1), pp.1-9.
Handley, M., Bunn, F. and Goodman, C., 2019. Supporting general hospital staff to provide dementia sensitive care: A realist evaluation. International journal of nursing studies, 96, pp.61-71.
Heger, I., Deckers, K., van Boxtel, M., de Vugt, M., Hajema, K., Verhey, F. and Köhler, S., 2019. Dementia awareness and risk perception in middle-aged and older individuals: baseline results of the MijnBreincoach survey on the association between lifestyle and brain health.;BMC public health,;19(1), pp.1-9.
Holmes, E.A., O'Connor, R.C., Perry, V.H., Tracey, I., Wessely, S., Arseneault, L., Ballard, C., Christensen, H., Silver, R.C., Everall, I. and Ford, T., 2020. Multidisciplinary research priorities for the COVID-19 pandemic: a call for action for mental health science. The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(6), pp.547-560.
McGuinness, L.A., Warren‐Gash, C., Moorhouse, L.R. and Thomas, S.L., 2019. The validity of dementia diagnoses in routinely collected electronic health records in the United Kingdom: a systematic review. Pharmacoepidemiology and drug safety, 28(2), pp.244-255.
Midtbust, M.H., Alnes, R.E., Gjengedal, E. and Lykkeslet, E., 2018. Perceived barriers and facilitators in providing palliative care for people with severe dementia: the healthcare professionals’ experiences.;BMC health services research,;18(1), pp.1-10.
Mongkhon, P., Fanning, L., Lau, W.C., Tse, G., Lau, K.K., Wei, L., Kongkaew, C. and Wong, I.C., 2020. Oral anticoagulant and reduced risk of dementia in patients with atrial fibrillation: a population-based cohort study. Heart Rhythm, 17(5), pp.706-713.
O’Brien, R., Goldberg, S.E., Pilnick, A., Beeke, S., Schneider, J., Sartain, K., Thomson, L., Murray, M., Baxendale, B. and Harwood, R.H., 2018. The VOICE study–A before and after study of a dementia communication skills training course. PloS one, 13(6), p.e0198567.
Skivington, K., Matthews, L., Simpson, S.A., Craig, P., Baird, J., Blazeby, J.M., Boyd, K.A., Craig, N., French, D.P., McIntosh, E. and Petticrew, M., 2021. A new framework for developing and evaluating complex interventions: update of Medical Research Council guidance. bmj, 374.
Swann, O.V., Holden, K.A., Turtle, L., Pollock, L., Fairfield, C.J., Drake, T.M., Seth, S., Egan, C., Hardwick, H.E., Halpin, S. and Girvan, M., 2020. Clinical characteristics of children and young people admitted to hospital with covid-19 in United Kingdom: prospective multicentre observational cohort study. bmj, 370.
Yousaf, K., Mehmood, Z., Awan, I.A., Saba, T., Alharbey, R., Qadah, T. and Alrige, M.A., 2020. A comprehensive study of mobile-health based assistive technology for the healthcare of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD).;Health Care Management Science,;23(2), pp.287-309.



