UK Banks' Risk Management During COVID-19 Pandemic
Native Assignment Help provides assignment help to assist students in research, writing and proofreading process.
Chapter 1: Introduction - Risk Assessment of UK Banking Sectors During COVID
1.1 Introduction
The banking system in the UK was affected by the pandemic situation in covid-19. Risk assessment of the banking sector in 5 different banks: Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds, Natwest, and Santander were concerned about this condition and took action to improve the situation. Considering the system and the experience of the banks and their financial outcomes, exercise and differential activities in the risk management program. The economic implementation supports the recovery of the respective function in the banks. Analysis of the management system of finance and generated the measurement structure of the UK’s banks.
Capital of the banking assets and their structure for social improvement established the technologies or services for the cooperating society. Analysis of the performance and the risk factors to carry out the situation of certain measurement methods for the risk management operated for the economic background.
1.2 Background of Study
Financial reports were conducted for the analysis of the bank's condition and approach in the pandemic situation and management team for the performance in the risk management and statistical measurement for indicating the increasing strategies and chosen measurement methods for the potential structure development .For this research report made the comparison in the risk management terms and 5 different banks. Maintained the rules and limitations for supportive economy build-up. Different types of income statements and financial statements with ratios measurement and also market price measurement for the 5 banks were Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds, Natwest, and Santander, and collected previous years' data and pandemic year’s data for the analysis relevant structure development for the risk management. Reflects the return policies in the banking system and the influenced performance for the regulation services in the financial approaches also.
1.3 Research Aim
The natural aim of the research work focused on the financial management system of the UK’s banks in the covid-19 pandemic situation. The methods for the analysis and measurement of the risk management structure of the selected 5 banks and the entire study recognized the development condition during the pandemic situation in the UK for the banking sector. Around the financial condition of the monitoring, the risk and response were generated by the management system and internal environment of the banks associated with the standard and correct performance of the economic growth. In the research, the aim defines the technologies and methods used for financial development and risk management structure to enable the impactful improvement of the financial condition in the UK’s banking sectors.
1.4 Research Objective
- To enhance the development through risk management in the banking sector.
- To create economic growth and financial conditions in the UK.
- To determine the banking sector with efficiency development with a great management system.
- To conduct the selected 5 banks in the UK, conditions, and approaches to deal with the pandemic situation during and after covid-19.
- To evaluate growth structure in the banking sectors and connection needed more sufficient with banking and social system to the development.
- To generate the implication for the Uk’s banking opportunities outlines and successful for the risk factors analysis.
1.5 Research Questions
- What is the connection between financial risk management and banking sectors?
- Which aspect of risk management was followed for the banks in the UK?
- How efficient are technologies to collect and analyze the data for risk management?
- How can I determine the structure of risk management in a bank?
1.6 Research Hypothesis
H0: Significance connection between risk management and banking sectors.
H1: Between the risk management and banking sectors had a great and important significant connection.
H2: Between the risk management and banking sectors had no significant connection.
H0: Efficient technologies were to collect and analyze the data for risk management
H1: Efficient technologies were important for the collection and analyzing the data for risk management.
H2: Efficient technologies were not important to collect and analyze the data for risk management.
1.7 Research Rationale
This study investigated the analysis part of the banking sectors and financial growth and alternative structure from the perspective of the banks and the features of the demanding the connection of the stabilities in the banking performance and system for the impactful 5 banks represented the related analysis parts conducted and dealt with the risk management structure also. Respectively forecasted the structure and risk management with GDP increasing procedure conducted.
1.8 Research Significance
There was an evaluated significance for the research work development and financial conditions for the application structure for the banking sector recognized their work and policies for the society. Strong relationship management for the risk factors and appropriate methods used in the banking structure like specific analysis, gap analysis, credit risk management, liquidity risk management, market risk management, and interest rate risk management. Performance of the 5 banks in the financial condition of the UK, provided the potential activities for the research work conducted and factors of the risk management associated with the effective production of the banks and environment contracts involvement. Principle of the credit risk management arising the legal approaches in the banks and conducted the research work assessment liability effects also.
Research Framework

Figure 1: Research framework
1.9 Conclusion
Financial sectors for the investors and the considering the development of the risk management factors and analyzing the data for the effectiveness specified. Guidelines for the research work conducted and solving the issues and supportive nature for all elements in the research objectives targeted for the development. Increasing the experience compounded the impactful forwarded concepts for society. Figure out the structure of the development of the financial condition of the banks and generate the risk factors for the management and directly connected to the pandemic situation for the positions in the UK and their economic situation in the financial field. Ensuring the public for the financial condition is enhanced for investment purposes and global projections for the risk management opportunities in the pandemic situation also. Focused on the estimated structure of the growth and faced many challenges for the impactful significant activities provided by the bank’s financial system.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
The chapter of the literature review defines the information from the different types of journals and articles adopted and discusses their elements in the related topic. Relevant factors in the risk management analysis for the banking sector in the UK and choose the 5 banks and collect their system also. Crucial structure for providing issues in the research work and connected to the perception of the research question and research objectives also. Similar actions for the selected topic in the different strategies to follow and studies the previous condition to deal with the problems and dependent on the structure of the helpful information or theories connected to each other for the entire research work.
2.2 Empirical Study
As per the author Wang et al.2021, the study identified the impact of a given behavior character on financial markets during COVID-19. This study is explained with quantitative data. The data information has been collected from primary sources. Also, the author collected the survey questionnaire (Wang et al.2021). The researcher adopted sampling with 337 respondents' information. The questionnaire section was self-administered. This was mainly based on a 7 points large scale. Discussing the analysis, the technique of SEM has been adopted. For the determination of the variables, the path analysis and CFA were carried out.
According to the authors Ozil and P.K., 2022, the research paper examined the company on the pre-provisions earning and loan loss provisions during the pandemic situation. The positive effect moved for the different variables. The variables also indicated proof of smoothing in income (Ozil and P.K., 2022). The findings declared that the loan loss provision converted into a V-shaped property in the COVID-19 situation. In 2020, the Loan loss provision touched its highest level during the second stage pandemic situation and declined in all quarters. Making a positive relationship in the situation of pandemic quarters. Indicated the evidence of smoothing income. The individual bank described that “three of the four systemic banks” executed higher income graph charts during the pandemic quarters.
As per the author Henry, and J.2020, the researched paper discussed the banking system on stress tests of the central bank for the UK. This was published shortly approaches at the beginning of the strategies of the banking sector development. Evaluated the structure for the banking sector in the risk management structure to be improved and the possibilities for the measurement policies of the data and models for the analysis of financial condition during the covid-19 situation and after the time also.
According to Zaharievet al.2020, the function of the bank system and the interaction policies in the stable information for maintaining the respective management and the nature of the subjective decision-making transformation with the operations of the monetary savings and performance of the applications in the administrators and status of the deposit connection of the system. Resources for the economic stages in the related field confirmed the situation in the pandemic situation and for the established liquidity factors of the bank.
According to Matos et al.2021, Estimated the undertaken efforts in the banking system and economic impactful subjective in the “long-run and short-run” markets in the financial monitoring procedures and conducted the generating financial strong attachment and social distance maintained for associated the fundamentals approaches and the banking system also evaluated. Integrity for the systematic values and the impactful investment plans in the pandemic situation is also covered in the objective management plans.
Non-financial risk in Risk Management
Financial risks are thrown back into the financial position. It is reflected on the different bank’s balance sheets and gives the result from their risk factor activity. The bank operation (systems and processes) helps to arise the non-financial risks. Similar risks are also faced by many companies that are outside the financial sector. Every bank was taking a financial risk and generating profit from this pandemic situation. It is related to misconduct, operational challenges, technology, etc. The top banks globally lost near about $ 200 billion in operational trouble, legal action, and damages. 19 incidents obtained losses near about $2 billion each, other 68 incidents gave losses resulting from more than $ 120 million. The reputational damage was hardly affected by the bank department model. Non-financial risks arise for some issues. These are:
Conduct Risk: It indicates the behavior of the bank employees who are passed throw in the losses section
Reputational Risk: It is the potential loss which is caused for the damage of firm’s reputation
Cyber Risk: It is similar to IT Risk, which identifies the losses due to security branches.
Operational Risk: The operational Risk is part of the Non-Financial Risk
Compliance Risk: It is related to Governance risk management. It is managed by putting a price tag on the failures of the bank rules as well as Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory Risk: It is possible losses to the change in the regulation and law.
Risk factor influencing in the bank performance
Some of the important operational risk factors, liquidity risks, credit, and market are affected the bank's performance. Making the connection between employee performance and flexible work arrangements. Every bank sector adopted flexible work arrangements which are more identified the better performance in every banking sector. It can utilized to make the objectives and facility of the effectiveness of all employees in the working place. The pandemic situation is made shocked throughout the world. It has been generate for the economic crisis, massive social and human. Identifying the risk factors is needed for the effects of countermeasures in the banking sector. It made the incident rates of all potential risk factors all over in the world. The author made the GWR model which identify the four factors: "monthly consumption, urban population, distance from the capital area, and the number of health workers". Among the other model, it was performed the best for identifying the variation in the pandemic situation. He examined the incidence rate, which was an r2 value of 79%.
Here are the three main key elements for managing the risk strategy:
- Taking the risk approach and also focused the high risk areas and finding the resources area.
- Implementing and developing the all programmer for mitigation and manage the risk management.
- Performed regularly in the scheduled basic of the risk assessments.
2.3 Theories and Models
The selected research theory for the study describes the research topic with the factors impactful on the related study. Risk management structure and their addressing theories are discussed in the efforts in the banking sector. Prioritizing the risk assessment for the developing stages in the knowledge and system with the quality and the solution for the management assurance for the research work. Specifically interpreted the data and analyzed them properly connected to the understanding purpose of the outcomes of the banking activities and generalized the impactful features in the theoretical approaches.
Effective management for the systematic and accepting of the developing models was required for expressing the structure of the actual decision and recognizing the connection with the improvement. Difficulties with the particular models or methods created the dependent features in the operating system of risk management possibilities with the measurement structure also included in the procedure.
Comparison in between financial risk analysis between HSBC, Barclays, NatWest, Lloyds, and Santander
It has been determined that HSBC and Barclays will serve as the basis for this investigation. The respective companies' “2019 to 2020” fiscal years should be utilized to compare their banking institutions. To correctly appreciate how both businesses have offered financial solutions to their clients, it is crucial to properly determine the business results throughout that calendar year, given the circumstances. Net interest margin, or NII, for HSBC bank for the semesters of 2020 was $27.6 (Billion), which is a reduction of $2.9 Billion compared to its previous fiscal year, so the year 2019. As a result, it is possible to say that the Net income for HSBC had decreased by about 9.5%. On the other hand, Santander enjoys a monopoly in practically all of its traditional markets. Throughout Germany, Spanish, Portuguese, Italy, and other countries, this is ranked well for mortgages and marketing services. With only a 10% market share in the form of savings, its merger with Partnership and Bradford places it as the 3 banks in the UK. With only a 60-year client representative background, it is among the banks in LATAM that has the longest historical strong brand.
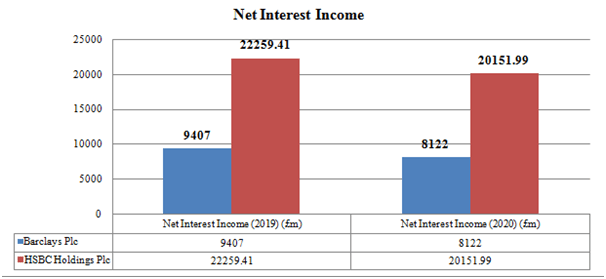
Figure 2: Net interest income between HSBC and Barclays bank
On the contrary, interest expense declined by over $12.9 again for the 2020 fiscal year, and it was $41.8. . As a result of lower median bond yields, loan revenue has fallen by 24%. The financial items' net profit, which was held for trade or managed using the fair valuation, has, on the contrary hand, decreased by $0.6 and now includes a loss of $0.3 (Million) from the sale of the assets. Its restructuring scheme is to blame for the entire issue. It may be concluded from this discourse that HSBC Bank's net revenue or costs can be calculated at their fair impairment losses. Experts who can help with the project claim that this net income or expenditure can be calculated using the assets and debts of the insurers along with the necessary derivative contracts. Conversely, it is found in nine countries, including Mexico, and Chile, that hold significant economic roles in the region's big economies. Due to the fact that it acquired Monarch, it also has a respectable presence in the US.
Consequently, HSBC's income trend is effective and profitable when compared to Barclays. The greater NII assessment shows that HSBC has indeed been conducting business profitably and has better investment performance than Barclays Plc. However, because savers are in more use than loans, Banks' NII margins are smaller because the company isn't able to make enough money from its equity capital assets. On the other side, the bank aims to achieve an immediate post-Rote of 13% to 15%, about this in line with its European counterparts, and a reduced CET-1 coverage of 11% to 12%.
The phrase "Net Investment Income" is examined to determine the financial viability of banks and other financial network operators. It represents the discrepancy between both the income generated by the company's investment holdings and the cost-of-service commitments. In light of this, Net Investment Income would be regarded as the key quarterly earnings indicator that would characterize the lenders' development as crucial and natural inclination through the revenue earned from investing resources in the context of economic analysis of both HSBC and Deutsche bank and comparing them.
According to the aforementioned graphic display, Banks reported net interest profits of £9407 million in 2019; this figure dropped to £8122 billion in 2020. On the contrary, it really was evident that NatWest NII assessment was £22259.41 in 2019 and had dropped to £20151.99 billion during 2020. It is discovered by examining the NII of the two banks (Lloyds, and Santander) reveals, for both Santander and HSBC, the assessment of net interest earnings has fallen in 2020. If you pay close attention, however, it can be noticed that Lloyd’s net rate of return was valued higher in each of the subsequent years compared to NatWest.
2.4 Literature Gap
All the adopted research articles for the literature review chapter conducted and focused on the chapter of the essential provided the impactful features and the theoretical analysis and the models approach for the development of the compacted values in the financial risk management factors in the pandemic situation and the financial condition.
2.5 Conceptual Framework

Figure 3: Conceptual framework
2.6 Conclusion
After completing the entire chapter of the literature review very clear observations for the impotence of this chapter in the critical research analysis paper and generated a lot of things to connect for the informative suggestion. The adopted selected variables is for the crucial role to play the significant approaches and the resources categories. Developing the approaches for the bank and utilizing the perception of the banks and maintaining the significance created the theoretical analysis and the models also activated for the demonstrating the structure of the development.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Introduction
Discussed the concept is of the UK in the banking sector related to risk management in the financial background of the covid-19 pandemic situation. The effectiveness of the financial approaches and value of the strategies and the measurement relationship relies in the descriptive method to use in the research work. Research structure and management procedure with the analysis activities performance for the effectiveness created. Perspectives of the research approaches and the objectives in the different sources and connected methods followed for the related studies. Research questions and their hypotheses are also related in this methodology chapter. UK-based bank’s activities in the covid-19 stages and also correct methods for the appropriate uses in the research design process also.
Collected the data and their analysis methods are also included in the chapter. Research strategies and ethics are to be maintained for the great and informative interaction created with the general perspective. Activities for the research purpose and collected data from the different6 types of the source also generated the structure of the methodology. Determine the interest margin in the pandemic situation and the respective services of the banks towards the society and the reduction values created the business results for the UK financial condition improved in these stages.
3.2 Research Philosophy
The previous structure of the business strategies for the banking sector development generated the forms of the savings approaches and collected data for the analysis purpose in the research philosophy and compared the whole development stages also (Comunian, and England, 2020). It defines the investigation purpose and experience of the descriptive approaches for the influence created and the perception also connected to the research work. Fulfilling the structure of the research philosophy and data analysis for the significant work attached to the concepts of the research. The movement of the research structure and the conceptual activities also promoted the philosophical purpose in the research development and created the contribution of the understanding of the values also. The aspects of the research and financial movement of the banking sector generated the total revenue structure in the analysis process of the risk management issues.
Phenomena for the research condition refer to the concerned values about the subject of the research and controlled the philosophical thoughts and ideas for the research work development. Individual activities for the research categories observed and provided the best contribution to the sensitive issues in the research situation. Dynamic approaches for the development stages in the research approaches and the methodological concepts are also included in the situation of the research subject.
3.3 Research Approach
Generated the values in the research work activities conducted in the approaches to be maintained properly for the research approaches contributed. The classification of the activities and the condition with the several changes in the research programs are more useful and more significant for the subject topic in the research purpose. Interesting the research objectives with the selected approaches for the development of the conditions in the descriptive data analysis methods for the research purpose. Financial risk management of the banks and taking actions during the condition of the covid-19 issues (Ozili, 2020). And addressed the descriptive methods to use the specific issues in the research subject and relevant practices for the involvement situation in the sufficient selected plans of the research work.
The approaches for the research work generated and the entire research perspective also conducted the strategies and take the approaches for more identified perspective measurement with the great approaches in the research activities. Involvement of the perspective structure in the approaches purpose conducted for the combination of the data and general issues also be specified in the conducted values and potential work also.
3.4 Research Design
A similar condition of all selected banks in the research subjects faced and analyzed the risk management structure during the pandemic condition. All the evaluated analysis procedure and experiment values in the data collection procedure and design were made for the research work. Selected measurable research subjects and regulated the descriptive analysis for the research activities. Associated the requirements for the research work and properly design the research procedure and all steps to be followed properly, calculating the selected data for the research work. Contains the designs and the subjective methods were included in the descriptive methods and values of the research work generated the connection of the subject also.
Preferable variables in the measurable factors also indicate the structure of the research design and the flexibility of the cultivated procedure of the analysis (Sundleret al. 2019). Experiments for calculating the subjective data and research activities in the data management situation for the financial risk management of the banking sectors. Research work designs definition of the changes and the positive approaches in the research aspects. Correct information and the methods used for the research design purpose and generated the structure of the research conducted “step by step” also.
3.5 Research Ethics
Research work in this project activities followed more ethics to conduct the practical solution of theoption and multiple procedures for the improvement of the concepts also. Standard applied ethics for research development created the essential and systematic study for the banking sector. Risk management structure in the research work analysis for the particular ethics to follow. Application of the business and the banking sector in the research work generated the development aspects and the directed engaging ethics with correct descriptive analysis of the data (Dicanio, and Montesi, 2020). Effective structure for the ethics conducted the development purpose in the proposed activities. Informative data for the research work generated the banking sector risk management analysis.
3.6 Method of Data Collection
The descriptive methods used for the different types of sources gathered data or information. Research for developing the data collection methods for the conducted different types of journals, articles, and previous survey reports for the research subjects generated and the studies for the analysis also connected in the descriptive procedure. Meaningful requirements for the research data collection method focused on observation and the importance of subjective values in the research work (Atmowardoyo, 2018). Conceptual systems in the dynamic approaches and the perception ways also cultivated the descriptive method in the research function. The source in the different types with the public reaction and the relevant survey report collected for the study and during the covid-19 situation in the UK’s banking sector faced risk management in the financial stages.
From the various literature reviews, newspapers were also included in the data collection procedure in the descriptive method. Generated the collection of the data in the descriptive method to used, all the significant descriptive suggestion refers to the economic and the financial stability with the risk management factors.The effectiveness of the collected data and they are used for the research purpose are also connected to the informative descriptive approaches for the research work. Evaluated the research work using the descriptive methods in a unique and updated research work development for the created fundamental sources in the research activities.
3.7 Method of Data Analysis
Considering collected information from the different kinds of resources and explained them for the research analysis. Logically analysis for the development data is equally effective in the data analysis possibilities. Highlighted the research work and involves the discussion part of the related studies. Entirely the preparing activities the measurement technologies. A direct combination of the research work and data analysis purpose gained the numeric condition of the explanation with the appropriate descriptive method to use (Alamo et al. 2020). Addressed the preparing attachments of the data related to the measurement elements in the transforming procedure also. The descriptive method was used for the data collection and the carried out the significant approaches in the research work. Contains in the research analysis procedure made the sampling data from the different sources arranged the interpreting technologies and the applied measurement structure improved the data analysis categories. In the UK financial risk management of the selected bank and during covid-19 and the post-pandemic situation explained the problem and addressed strategies followed for generating a good framework structure for the increasing development. Applied technologies for preparing data and the scale for the measurement connected each other. Connected the approaches in the research data analysis with the measurement properly.
3.8 Conclusion
This methodology part of the research activities defines the structure of the research function according to the approaches and the creative features in the research work. Specific analysis with the appropriate method to use developing the research structure more significant for the society and the business activities. Investigation for the expanded values in the research concepts and the experiments source in the research procedure also. Collected the methodology with experiment the descriptive method and practical significance in combining the outcomes of the research work. Approaches were in the research procedures through the significant process also. Research design and strategies and ethics were also contained in the research methodologies chapter more useful and informative. Risk management analysis in the UK’s banks during the covid-19 condition and post the condition also. Various types of features in the research methodology with sufficient outcomes for research work. Demonstrated the structure of the research approaches and the planning structures for the values for increased in the methodology chapter also.
Chapter 4: Analysis and Findings
4.1 Introduction
This chapter presents the research findings on determine the financial risks and the performance of UK banks during Covid-19. Thisstudy conducted on 5 selected UK banks’ financial data over a period of 5 years based on secondary data published in their respective websites. Statistical techniques and analysisapplied to the collected datato measure the risks and performances of banks during COVID-19.
4.2 Risk Measurement
4.2.1Credit Risk Measurements:
Credit risk is the risk of economic loss caused by the counterparty’s failure or default at the time of debtrepayment on the agreed date. Credit rating is the measurement technique used to analyze the performance of banks (,2021) Council of Europe
The following table simplified the ratings from 2017 -2021 also the actions accordingly to the ratings with previous years. These ratings are collected from Moody’s website.The rating scale has two categories, investment grade (AAA/Aaa to BBB-/Baa3)indicates low to moderate risk and speculative-grade(BB/Ba1 toD/Ca) indicatesa higher level of risk (Peresetsky et al., 2008).
There is a relationship between the credit premium and rating, the higher rating company can get higher debtand the lower rating of the company will have low creditworthiness. The credit rating expresses creditworthiness and financial health. Defaults and unpaid loans reduce the banks’ credit ratings (Corporate Finance Institution Team, 2022).
|
Ratings |
2017 -Action |
2018 -Action |
2019 -Action |
|||
|
HSBC |
- |
- |
Aa2 |
New |
Aa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
|
BARCLAYS |
Baa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
Baa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
Baa3 |
DOWNGRADE |
|
LLOYDS |
- |
- |
Aa3 |
New |
Aa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
|
NATWEST |
- |
- |
Baa3 |
New |
Baa2 |
Upgrade |
|
SANTANDER |
Aa2 |
NEW |
Aa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
Aa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
|
Ratings |
2020 -Action |
2021 -Action |
||
|
HSBC |
Aa3 |
DOWNGRADE |
Aa3 |
DOWNGRADE |
|
BARCLAYS |
Baa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
Baa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
|
LLOYDS |
Aa3 |
DOWNGRADE |
Aa3 |
AFFIRMATION |
|
NATWEST |
Baa2 |
AFFIRMATION |
Baa1 |
Upgrade |
|
SANTANDER |
Aa3 |
DOWNGRADE |
Aa3 |
AFFIRMATION |
From the table, in period (2017-2019) ratings are Affirmed and upgraded, only one bank is downgraded. Later during covid-19(2020-2021), the ratings of banks are comparatively downgraded, which shows the bank’s credibility towards the loan payments and performances. Moody’s assigns ratings based on financial strength and deposits (Moody’s Investment Services, no date); This study shows the ratings downgraded during covid-19. Investors and customers preferred to save money for survival instead of paying loans and investments during covid situation made changes in banks’deposits, Income levels,and bank size that caused changes in overall performances and ratings.
4.2.2Market Risk Measurement:
Market risk is the risk of losses on financial investments caused by adverse price movements and volatility (European Banking Authority, no date). Market risk arises from the low investment of investors in the market. The customers who were buying stocks regularly stopped buying (Azarenkova et al. 2018). This happened due to more concentration on savings. During the covid-19 people try to save money because of medical treatment and managing their necessary requirements of the day. This lowered huge investments in the market, and banking sectors were unable to generate more funds and loans.
In this study, Regression was applied to measure beta for 5 fiscal years prior to and during covid, and thehistorical data used to measure Beta, and daily retunes were taken as intervals and against FTSE All shares as the market index to regress.
|
Regression Analysis-BETA |
||
|
FY17 & FY18 |
FY19, FY20&FY21 |
|
|
BARCLAYS |
1.00 |
1.68 |
|
HSBC |
1.08 |
1.02 |
|
Lloyds |
0.70 |
1.45 |
|
NatWest |
0.88 |
1.32 |
|
Santander |
-5.50 |
0.15 |
Beta is a measurement of risk, the historical prices of all the above stocks have regressed with FTSE all share price index, and the beta calculated. “The beta (β) of an investment security (i.e., a stock) is a measurement of its volatility of returns relative to the entire market” (Corporate finance institute,2022).
“Beta coefficient (β) interpreted as follows,
β =1 exactly as volatile as the market
β >1 more volatile than the market
β <1>0 less volatile than the market
β =0 uncorrelated to the market
β <0 negatively correlated to the market” (Corporate finance institute,2022).
From the table, FY17&FY18(Before Covid-19)
- High beta, HSBC with more than 1 (1.082) means more volatile than the market and has returned 108% of what the market has returned over the period.
- Low beta, the Beta for Barclays, Lloyds, and NatWest is < 1 (0.99,0.70, and 0.88) which is less volatile than and comparatively fewer returns than the market given.
- Negative beta, Santander has negatively correlated with market returns.
From the table,FY19, FY20&FY21(During Covid-19),
- High beta, Barclays, HSBC, Lloyds, and NatWest are having a beta of more than 1 (1.68,1.02,1.45&1.32) means more volatile than the market and have returned 168%,102%,145% & 132% of what the market has returned over the period.
- Low Beta, Santander has a beta <1 (0.14) means the volatility is less, and comparatively returns are also than the market returns.
(London stock exchange, no date) At end of the year 2019, the FTSE All-share index fell from 4132.71(Feb 21, 2020) to 2837.05(Mar 20, 2020) in a brief period, later it plunges back to its previous position in (Apr2021).
The huge volatility caused due the shareholders selling their shares at the initial stage of covid-19 was bearish, after the market fluctuation from the timeof the vaccination invention the market started acting bullish.High volatility gives high returns at elevated risk and low volatility gives low returns at lower risk.
4.2.3 Interest Rate Risk Measurement:
“Interest rate risk is the exposure of a bank’s current or future earnings and capital to adverse changes in market rates. This risk is a normal part of banking and can be an important source of profitability and shareholder value; however, excessive interest rate risk can threaten banks’ earnings, capital, liquidity, and solvency” (FDIC, no date).
Value-at-Risk (Var):
Var is a statistical tool used to measure the extent of loss or riskiness of afinancial institution over a specific period. Banks determine the probability of losses in their portfolios and used it to measure the level of exposure by applying to specific positions or a whole portfolio. This study involves in historical simulation method applied to banks’ 5 years daily returns.
|
VAR(P) |
A.VAR (95) |
B.VAR (99) |
||
|
BANKS/Financial Years |
FY17 & FY18 |
FY19, FY20&FY21 |
FY17 & FY18 |
FY19, FY20&FY21 |
|
BARCLAYS |
-2.51% |
-3.69% |
-3.53% |
-7.19% |
|
HSBC |
-1.67% |
-3.00% |
-2.79% |
-5.09% |
|
LLOYDS |
-1.69% |
-4.08% |
-2.81% |
-7.42% |
|
NATWEST |
-2.20% |
-3.83% |
-4.09% |
-2.58% |
|
SANTANDER |
-0.48% |
-0.67% |
-2.51% |
-2.58% |
Var gives an amount that could lose on a portfolio and calculates an estimated loss amount on a portfolio position over a holding period with a given confidence level.
In this Study, Var applied at two confident levels (Var at 95% and Var at 1%) considering them as two scenarios which mean,
- Scenario - Var (95)
Confidence level:
Var at 95% means, 95 % Confident that the maximum one-day loss will not exceed the expectedloss.
Minimum loss level:
Five percent chance that the loss will exceed the expected loss.
- Scenario - Var (99)
Confidence level:
Var at 99% means, 99 % Confident that the maximum one-day loss will not exceed the expected loss.
Minimum loss level:
One percent chance that the loss will exceed the expected loss.
Banks usethe var technique to estimate loss levelfor a specific period, the expected loss amount will function asa buffer or capital amount that banks keep aside, Banks will use this amount to make up the losses if anything happens to the bank portfolio.
Before covid period (FY17 & FY18), levels of both Var 5% and Var 1% lies between (-0.48% to -4.09%)
- Var (95) has a 5% of chance to lose Barclays (-2.51%), HSBC (-1.67%), Lloyds (-1.69%), NatWest (-2.20%), and Santander (-0.45%). Barclayshas a 5% chance to lose more than 2.51% of its portfolio in a single day.
- Var (99) has a 1% of chance to lose Barclays (-3.53%), HSBC (-2.79%), Lloyds (-2.81%), NatWest (-4.09%), and Santander (-2.51%). NatWest has a 1% chance to lose more than 4.09% of its portfolio in a single day.
During the Covid-19period (FY19, FY20&FY2), levels are between (-0.67% to -7.42%).
- Var (95) has a 5% of chance to lose Barclays (-3.69%), HSBC (-3.00%), Lloyds (-4.08%), NatWest (-3.83%), and Santander (-0.67%). Lloyds has a 5% chance to lose more than 4.08% of its portfolio in a single day.
- Var (99) has a 1% of chances to lose Barclays (-7.19%), HSBC (-5.09%), Lloyds (-7.42%), NatWest (-2.58%), and Santander (-2.58%). Lloyds has a 1% chance to lose more than 7.42% of its portfolio in a single day.
This study shows clearly That the chances of the expected loss in a single day of the portfolio during Covid-19 are comparatively higher than before covid period.
4.2.4Liquidity Risk Measurement:
Managing liquidity is especially importantfor a bank to cover the difference in future cash inflows and outflows, the degree of uncertainty on these differences are higher in the banking industry (Banque de France,2008).Liquidity risk is the risk of being unable to convert a position in a timely manner at a reasonable price. (Joe Wirija,2020) at the start of 2020, the market was gone up all-timehigh, but the pandemic hit the market and the lockdowns created unexpected disruption in the economy, making everyone see low sales and liquidity risk drastically increase.
(EngTiffany,2014)High-Quality liquid assets are Level 1, Level 2A, and Level 2 b. (Level 1= Reserve balance requirement, 85% of Level 2A assets, 50% of Level 2B assets)
|
LCR |
FY17 |
FY18 |
FY19 |
F20 |
F21 |
|
BARCLAYS |
154% |
169% |
160% |
162% |
168% |
|
HSBC |
142% |
153.8 |
150.20% |
142.70% |
138.40% |
|
LYODS |
125% |
128% |
137% |
126% |
135% |
|
NATWEST |
140% |
158% |
152% |
165% |
156% |
|
SANTANDER |
120% |
133% |
142.20% |
152% |
172% |
Source: Bank websites (Annual Reports)
As per Basel norms, LCR should be 100%, That means HQLA should be equal or greater than the net cash flows over 30-day stress period.
From the table, the Liquidity coverage ratio is> 100 by all the selected banks for all 5 years. It shows three banks’ (HSBC, Lloyds, and Santander) LCRsdeclined at the peak of the covid-19 period (FY 2020).
Descriptive Analysis:
Afterconducting different techniques Beta, Var, Credit rating, and Ratings during Covid-19 and prior years to measure the risks.
Credit rating: The bank performances such as bank deposits and bank sizes reduced during the pandemic which causes the downgraded of bank ratings.
Beta: Due to lower investments and selling shares at higher volumes at the time of the pandemic causes high volatility in the market.
Var: Var method is used to determine the expected loss; this study shows that the expected rate of loss is huge at the time of the pandemic.
LCR (Liquidity coverage ratio): During Covid-19 the LCR declined comparatively to before covid-19.
To overcome the losses the banks have taken measurements that are briefly discussed below.
(Catherine Casanova and Bryan Hardy,2021)COVID-19 has broughta sudden haltto economic activity,whichmade to take a swift and strong reaction taken by monetary fiscal, and prudential authorities.
Two mechanisms it has implemented to increase the flow of bank credit, enhancing lending capacity and providing incentives to the banks.
Enhancing lending capacity:to increase capital capacity, the policy measures haveloosenedthe balance sheet restrictions,reducing measuring constraints on the riskiness of banks, and capital ratios. Implemented the moratorium to distress the borrowers from missed payments and releasedbuffers to free up the restrictions on the usage of capital.
Incentives to banksto increase lending: programs like “funding for lending “which allows banks funding at low cost and conditions to use them.
4.3 Summary
The main purpose of this research is to investigate the distinct types of risks and the techniques used to determine banks’ financial performance during covid-19, and the banks can enhance their financial performance by following the measurements and regulatory disciplines. The regulatory policies helped in enhancing the capital capacity that maximized the performance of banks.
Reference list
Journals
Alber, N. and Dabour, M., 2020. The dynamic relationship between FinTech and social distancing under COVID-19 pandemic: Digital payments evidence. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 12(11).
Azarenkova, G., Shkodina, I., Samorodov, B. and Babenko, M (2018). The influence of financial technologies on the global financial system stability. Investment Management & Financial Innovations, 15(4), p.229.
Catherine Casanova, Bryan Hardy and Mert(2021) Covid-19 policy measures to support bank lending BIS Quarterly Review Central banks’ response to Covid-19 in advanced economies
Diab, A.A., Metwally, A., AlZakari, A.M. and Fazal, A., 2022. Banks’ concurrent risks during the COVID-19 pandemic: A road map for risk officers and risk management. Journal of Risk Management in Financial Institutions, 15(2), pp.161-170.
Dicanio, A. and Montesi, G., 2020. Banking System in Time of Covid-19: A Reverse Analysis on Loss Absorption Capacity, Lending to the Economy and Market Valuation. CASS Business School, City, University of London, preliminary draft (confidential).
Dinu, V. and Bunea, M., 2022. The Impact of Competition and Risk Exposure on Profitability of the Romanian Banking System During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Competitiveness, 14(2), pp.5-22.
EfstathiaKoulouridi, Sameer Kumar, Luis Nario, Theo Pepanides, and Marco Vettori(July 2020) Managing and monitoringcredit risk after theCOVID-19 pandemic.
El-Chaarani, H., Ismail, T.H., El-Abiad, Z. and El-Deeb, M.S., 2022. The impact of COVID-19 on financial structure and performance of Islamic banks: a comparative study with conventional banks in the GCC countries. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences.
Elnahass, M., Trinh, V.Q. and Li, T., 2021. Global banking stability in the shadow of Covid-19 outbreak. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 72, p.101322.
George S. Oldfield (2020) AnthonyPlace of Risk Management in Financial Institutions Santomero95-05-B.
Grondys, K., Ślusarczyk, O., Hussain, H.I. and Androniceanu, A., 2021. Risk assessment of the SME sector operations during the COVID-19 pandemic. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(8), p.4183.
Hamad, H.A., Qader, K.S., Gardi, B., Abdalla, P., Hamza, D. and Anwar, G., 2021. The essential variables to consider before investing in financial markets during Covid-19.
Henry, J., 2020. Banking system stress testing and COVID-19: A first summary appraisal. Journal of Risk Management in Financial Institutions, 14(1), pp.7-24.
Joe Wirija (2020) Principles of Measuring and Managing Liquidity Risk.
Koulouridi, E., Kumar, S., Nario, L., Pepanides, T. and Vettori, M., 2020. Managing and monitoring credit risk after the COVID-19 pandemic. Risk and Resilience, 31.
Li, X., Xie, Y. and Lin, J.H., 2021. COVID-19 outbreak, government capital injections, and shadow banking efficiency. Applied Economics, 53(4), pp.495-505.
Margaret Woods and Kevin Dowd (2009). Financial Risk Management for Management Accountants.
Matos, P., Costa, A. and da Silva, C., 2021. On the risk-based contagion of G7 banking system and the COVID-19 pandemic. Global Business Review, p.09721509211026813.
Miković, N., 2022. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on trends in the European banking sector. Trendovi u poslovanju, 19(1), pp.59-68.
Najaf, K., Subramaniam, R.K. and Atayah, O.F., 2022. Understanding the implications of FinTech Peer-to-Peer (P2P) lending during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment, 12(1), pp.87-102.
Ozili, P.K., 2022. Bank income smoothing during the COVID-19 pandemic: Evidence from UK Banks. In The New Digital Era: Other Emerging Risks and Opportunities (Vol. 109, pp. 127-139). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Peresetsky, Anatoly; Karminsky, Alexander (2008) : Models for Moody's bank ratings, BOFIT Discussion Papers, No. 17/2008, ISBN 978-952-462-925-6, Bank of Finland, Institute for Economies in Transition (BOFIT), Helsinki,
Riadi, S.S., Hadjaat, M. and Yudaruddin, R., 2022. Bank Concentration and Bank Stability during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Emerging Science Journal, 6, pp.262-274.
Sakyi, K.A., Saidi, L. and Rolls, D.W., 2022. Theoretical Review of Macro-Environment of Banks-Generic Approach to Risk Management and Paradigm Shift in Banking Practices Post-COVID-19-Perspectives from Zambia. Management, 1(06), pp.1-29.
Shad, M.K., Lai, F.W., Fatt, C.L., Klemeš, J.J. and Bokhari, A., 2019. Integrating sustainability reporting into enterprise risk management and its relationship with business performance: A conceptual framework. Journal of Cleaner production, 208, pp.415-425.
Tsuji, C., 2022. Stock Return Jumps and Tail Risk Assessment: The Case of European Non-Euro Banking Sectors. International Business Research, 15(5), pp.1-53.
Uchehara, I., Hamma-Adama, M., Obiri, K.A., Jafarifar, N. and Moore, D., 2020. Impacts and risk management of COVID-19 pandemic on real estate supply chain. International journal of real estate studies, 14(S1), pp.41-53.
Virglerova, Z., Dvorský, J., Kozubikova, L. and Cepel, M., 2020. Perception of non-financial risk determinants in SMEs in Visegrad countries. OeconomiaCopernicana.
Wang, F., Zhang, R., Ahmed, F. and Shah, S.M.M., 2021. Impact of investment behaviour on financial markets during COVID-19: A case of UK. Economic Research-EkonomskaIstraživanja, pp.1-19.
Zahariev, A., Prodanov, S., Radulova, A., Zaharieva, G., Pavlova, M., Angelov, P., Ismailov, T., Aleksandrova, A. and Marinova, K., 2020. The Bank Insolvency: from Lehman Brothers to Covid-19 (international remarks and national peculiarities). Economic and Social Developments (58), pp.44-59.
Council of Europe development bank (no date),CEB Risk Management Disclosure Report
Finance train (no date), Calculating Beta Using Market Model Regression (Slope)
EBA(no date),Market, counterparty and CVA risk.
Corporate finance institute, (2022) Beta The volatility of returns for an investment, relative to the market.
London Stock Exchange (no date): FTSE All shares
FDIC (Federal deposit insurance corporation, no date) Interest Rate Risk
Banque de France (2008) Financial stability Review. SPECIAL ISSUE LIQUIDITY
Eng, Tiffany (2014), Office of the comptroller of the currency



