Global Strategy Simulation Report
1.0 Introduction: Global Strategy Simulation Report
Explore our comprehensive assignment help services for tailored academic excellence.
By analyzing and implementing relevant business strategies while taking into account their effects and limitations, the company has established long-term competitive advantages. Speed Cycle was given to a business that makes high-quality bicycles for adults, children, and mountaineers. It designs, customizes, and sells them. Their product is designed to work in a variety of street conditions. India, China, Brazil, and South Africa are the four markets that they have expanded into. An organization's name is very much addressed in the event that it lines up with the mission and vision of the organization, which assumes a significant part in the development of the market. Additionally, it conveys your message to your intended audience. Speed Cycle is a UK-based cycling company that was started by members of the Red Two team. It sells smart bikes, mountain bikes, and folding bikes and has locations all over the world in Brazil, South Africa, China, and India battling major competitors in the industry. The report is focused on businesses, focusing on the key factors that influenced decision-making, adapting to internal, external, and industry-specific business environments, and putting strategies into action. It clearly demonstrates the difficulties the company faced while implementing the strategy.
1.1 Ansoff Matrix for the growth strategy
The Ansoff model aids corporate marketers in identifying opportunities to "penetrate" into new markets or develop new products and services to boost revenue. The four elements of Ansoff's matrix that the "Speed Cycle" used are as follows: product development, market expansion, market penetration, and then diversification. This can boost sales and profits by implementing the four strategies he it employs in business. Companies use the Ansoff Growth Matrix, a business tool, to forecast and evaluate their growth strategies. The company has implemented a strategy for expanding into existing markets through market penetration (Clarissia, 2019). The organization has accomplished this by taking on savvy estimating techniques while offering the greatest bikes that can speak to clients and increment pieces of the pie. The Company is a UK-based business that has expanded into China, India, Brazil, and South Africa. A company needs a growth strategy in order to evaluate how well its work is progressing toward its objectives. This aids employees and executives at Speed Cycle in maintaining focus and coordination. The business was able to launch the same product in multiple nations thanks to this strategy. Through advertisements, sponsorships, direct marketing, and social media campaigns, the company reached a variety of demographics. The introduction of new products into existing markets is one component of product development strategies.
There are also disadvantages to the Ansoff growth strategy. One of the greatest disadvantages of the Ansoff framework is that it overlooks contenders (Weiwei, 2021). This matrix only depicts the strategy taking into account the company's markets and products. However, competitors exist for each and every market and product in the real world.
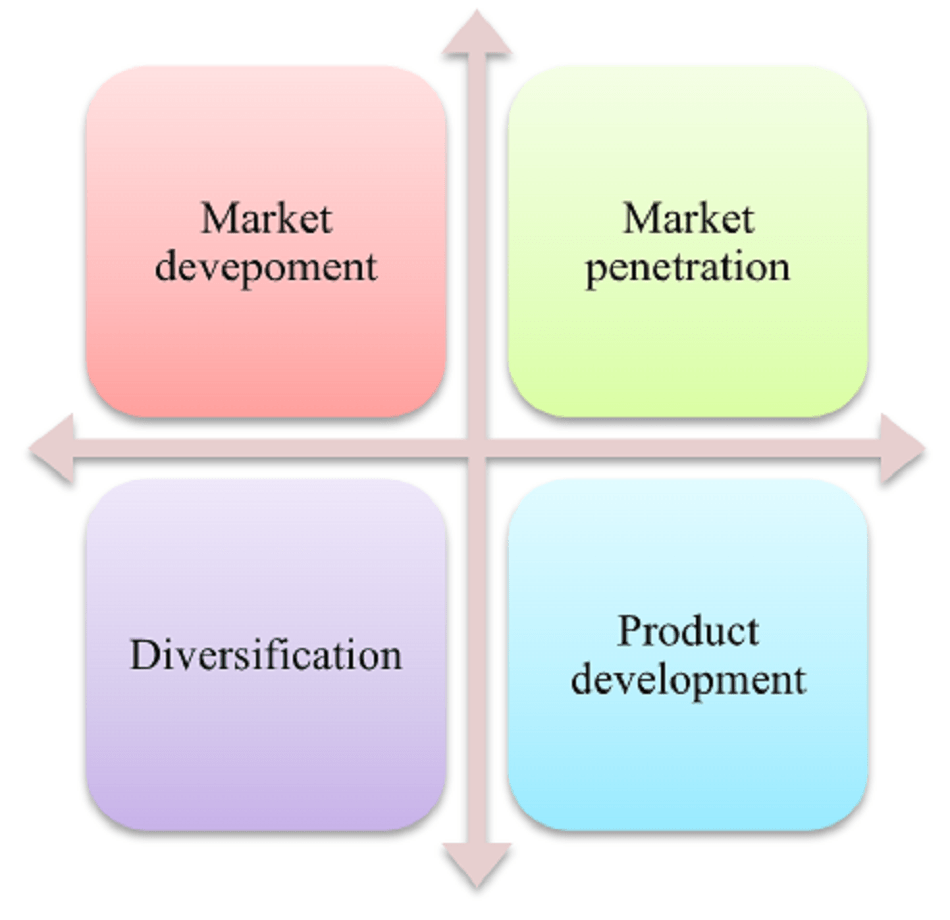
Figure 1: Ansoff Matrix
1.2 Mission, Vision, and Targets
The company's vision (Speed Cycle) is related to the mission of the company, whereas the company's mission outlines the organization's norms and values.
Mission: The goal of the business known as Speed Cycle is to produce the most affordable, durable, and comfortable bicycles available on the market while also producing the best bicycles of lightweight quality.
Vision: The Company’s goal is to become the leading bicycle manufacturer across the globe.
Targets: The Company targets to reach at least 5 million sales of bicycle by 2030. This target can only be achieved by providing customers with the best quality bicycles at affordable prices. This will also aid to gain more new customers for the company.
2.0 PESTLE Framework
Marketers use a framework or tool called a PESTEL analysis to look at and keep track of the external marketing environment and macro-environmental factors that have an impact on an organization, business, or industry (Vallati and Grassi, 2019). The PESTLE framework was used by the company to examine the economic, legal, social, political, technological, and environmental aspects of the external environment of the company before investing in Brazil, South Africa, India, and China and putting product improvement strategies into action to gain a competitive advantage on a global scale. It will aid in the analysis systematically all those factories that will impact the business.
2.1 Political Factors
At the time of expanding the business across the globe, it is usually that different countries will have some differences in perspective of political factors. They too will have some similarities that will be in favour of the company Speed Cycle. The establishment of Speed Cycle in China, India, Brazil, and South Africa will support each nation's market policy as well as the development of international trade relationships, tax policy, labour, and environmental laws. China employs an effective strategy to maintain low raw material costs. Additionally, investors can reduce labour costs, which is beneficial to businesses.
2.2 Economic Factors
The country's economic conduction is directly related to its growth. The speed cycle will raise interest rates, exchange rates, and income in addition to having a significant impact on every nation's business and retail distribution profits. Speed Cycle will also encourage each nation's interest rate control, tax policy, and spending by the government. Since labour costs are so low in China, many reputable businesses prefer to hire workers there. Additionally, the cost of hiring skilled workers from this nation is significantly lower than that of other nations. GDP in China is high. This indicates that citizens of the nation also have significantly higher buying power. Investors see China as a lucrative market as a result, .Pproperty prices are rising alongside China's alarmingly high rate of inflation. The economic expansion could slow down in the future, which could slow it down.
2.3 Social Factors
The prevalent beliefs and attitudes of the population will play a role in the Speed Cycle's social and cultural effects in each nation. This has an effect on population growth by providing sufficient cycles for flexible movement to each location and age range cycles for age distribution. Marketers will be particularly affected by these effects, which will have direct effects on their understanding of customers and their motivations. The population is large, and approximately 90 percent of it is literate (Praharsi et al. 2022). As a result, businesses can hire employees and skilled workers at lower costs. One reason labour costs are low is that there is a large population. Choices and preferences change with people's lifestyles. Businesses are also beginning to notice shifts in social behaviour and shopping habits as the urban lifestyle takes over a large portion of the country.
2.4 Technological Factors
The company is all aware of the ways in which our product marketing is affected by recurring shifts in the technological landscape. Speed Cycle will concentrate on innovative methods for producing goods and services, disseminating goods and services, and communicating with the target market. Especially important will be the creation of a new model each year to keep up with technological advancements. Additionally, China is developing methods to motivate people to concentrate on growth-enhancing innovations. In order to improve production, these guidelines are beneficial to both domestic and international businesses. A significant portion of the population prefers to shop online rather than in stores because of the country's excellent technical support.
2.5 Environmental Factors
The development of electric bikes (made by Speed Cycle) will be eco-accommodating, and it has turned into a significant component to consider in accomplishing its natural space and conveying a practical item to limit contamination. Businesses can follow these countries' guidelines for Production ethics and the environment. The following aspects have increased as a result of profits and production being reduced. There are environmental issues in China. These include wWater pollution, landfills, biodiversity loss, nuclear waste, an increase in the emission of greenhouse gas emission, threats to the quality of the air, not properly managing plastic waste, etc. The nation has established some business guidelines. It aims to safeguard production environmental standards. It might build the expense of creation and diminish the benefit.
2.6 Legal Factors
The Speed Cycle project's establishment in each nation will affect the legal system by producing or manufacturing long-lasting bicycles that promote health and safety, equality of opportunity, product labeling, and product safety. Social media platforms and their use in other countries are subject to restrictions from the Chinese government. Reduced profits and revenues as a result of direct investment or, if they use reputation in a way that harms the brand and reputation of the company, then they may face fines and lawsuits. Speed Cycle requires knowledge of what is and is not permitted in these nations for a successful trade. Foreign companies are also restricted in their ability to invest in China. It might make it harder for multinational corporations to invest in that nation's market. Some laws require sellers and buyers to verify online contracts, but there are none. E-commerce site transactions may be much riskier online.
3.0 CSR Strategy
The all-encompassing strategy employed by businesses and donors to plan, implement, and evaluate their CSR initiatives is known as CSR strategy. It includes specific focus areas, the design of the program, strategies for promotion and communication, and methods for evaluation. There are four nations where Speed Cycle operates as an organization: South Africa, India, Brazil, and China (Bian et al. 2021). The company is committed to giving back to society in order to support the communities that surround our business because we are aware that our presence in these locations improves their economic well-being. It is significant. Through corporate social responsibility, this can be accomplished. This includes the societal expectations that businesses must meet at any given time in terms of money, law, morality, and charity.
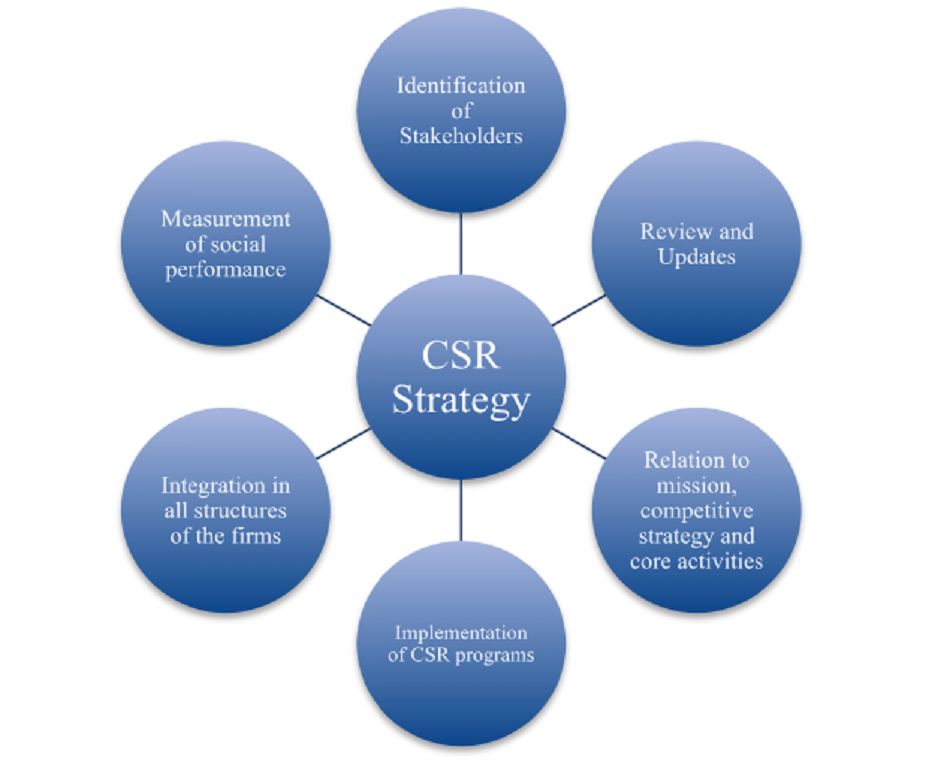
Figure 2: CSR strategy
Businesses are able to assume social responsibility for themselves, through the self-regulatory business model known as, stakeholders, and the general public "Corporate Social Responsibility" (CSR). Businesses are able to be aware of their impact on society because of corporate social responsibility as a whole, encompassing the economy, society, and environment, also referred to as corporate citizenship. A company that is committed to “corporate social responsibility” (CSR) does what it normally does to help society and the environment rather than harm them. Speed Cycle intends to make the most of the communities in which it operates and its dedication to the nations to which it exports and sells its goods. Speed Cycle has established a foundation to deliver twenty-five free bikes annually to the four nations in which they have their headquarters (ElAlfy et al. 2020). Additionally, Speed Cycle will commit to supplying selected hospitals in its four operating nations with medical supplies. Additionally, they intend to soon include additional CSR projects in the program. The company hopes to be able to support and give back to the communities in which they operate in unique ways and assist the less fortunate in achieving their objectives through our partnerships with those communities.
4.0 Porter Five Forces Model
By identifying and evaluating the five competitive forces that shape each industry, “Porter's Five Forces” is a model that assists in determining its strengths and weaknesses. To ascertain corporate strategy and industry structure, five forces analysis is frequently utilized. Porter's model can be used to improve a company's long-term profitability and comprehend the level of competition in an industry.
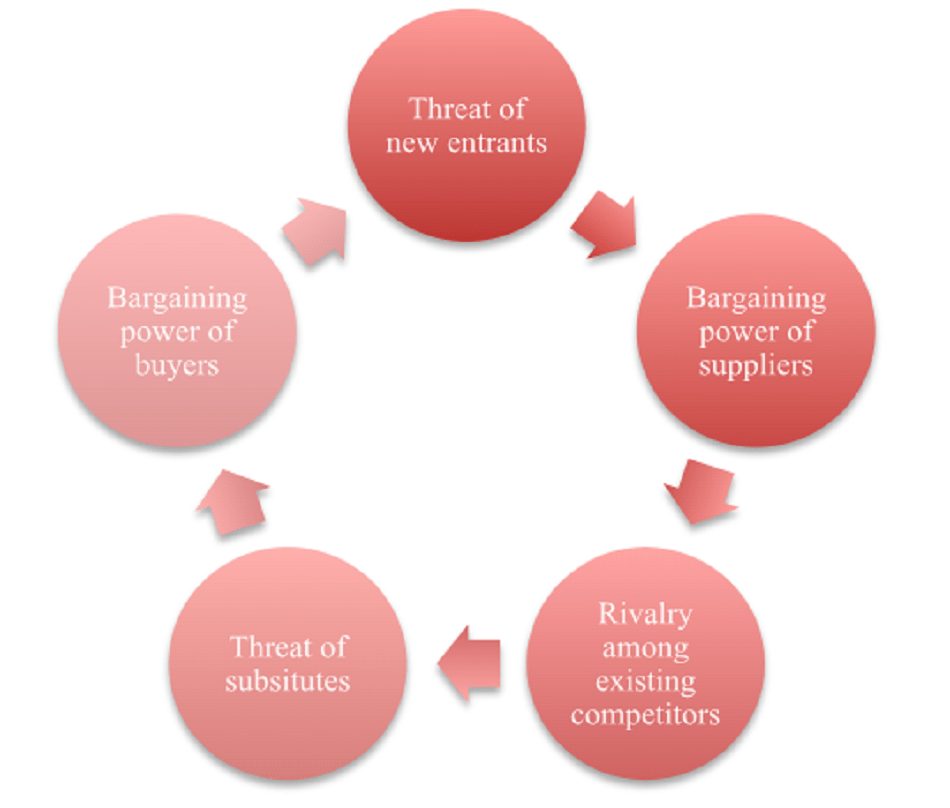
Figure 3: Porter Five Force Model
4.1 Competitive Rivalry
The first of the five forces isare the number of competitors and their capacity to devalue a business. The more similar your competitors' products and services are, the weaker your business will be. Both buyers and suppliers look for corporate rivals who might be able to provide better deals or lower prices (Bruijl and Gerard, 2018) On the other hand, businesses charge higher prices and have more control over the conditions necessary to boost sales and profits when competition is low. Lifecycle, Nimble, and Dragon Cycles Limited, among others, compete with Speed Cycle in the market where it operates. These contenders might influence Speed Cycle’s piece of the pie and deals.
4.2 The threat of Entry
The power of new competitors also has an effect on a company's power. The likelihood that an established business will lose ground increases faster and for less money, a competitor can enter a business's market and become a formidable rival. Since incumbents can charge more and get better deals in industries with high barriers to entry, and also in terms of suppliers. and supplier terms are. Due to the industry's low barrier to entry, more new players have entered the market. However, there are a few things that prevent the newcomer from gaining an advantage with because of the his existing competitors. Speed Cycle. Government policies, high capital requirements, access to distribution channels, product marketing strategies, etc.
4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The next aspect of Porter's model is the ease with which suppliers can raise their input costs. The cost, the uniqueness of the key inputs, and the number of suppliers businesses switching suppliers all have an impact on this. An industry's dependence on a single supplier increases with the number of suppliers. Speed Cycle operates in a market with numerous rivals and few suppliers (Kieltyka et al. 2022). There are five of his suppliers at the moment: SA Prodovski, Henderson Ltd., Schneider Gmbh, Hong Kong Ltd., and Kansas Inc. Each of these providers has its own unique selling points, which can drive up the cost of preliminary services. Speed Cycle switches to a limited number of suppliers, but in order to meet their customers' production needs, Speed Cycle must partner with suppliers who are cost-effective, produce high-quality goods, and deliver on time.
4.4 Bargaining Power of Buyers
One of the five forces is a customer's ability or level of power to lower prices. In a multi-company, multi-customer industry, customers have lower switching costs to switch to other competitors if they do not get value or satisfaction from their purchase. This is influenced by one of the five forces is a customer's ability or level of power to lower prices. The business has, the significance of each one, and the amount of money it takes to find new markets or customers for its products. SpeedCycle must therefore ensure that their bikes are of high quality, long-lasting, and reasonably priced. Continuous research and development to keep ergonomics at the forefront of innovation in order to increase market share, and investments in promotional and marketing strategies should also be increased and put into action.
4.5 Threat of Substitutes
Substitution is the primary focus of the final force, the fifth one. Alternatives or administrations that can be utilized instead of an organization's items or administrations represent a danger. Prices can rise and favourable terms can be obtained by businesses that are responsible for the production of goods or services that are no comparable substitutes. Consumers might have the choice not to purchase the company's goods if there are better alternatives, reducing the company's power. Customers can easily switch to other products like motorcycles, automobiles, and buses for commuting in the area where Speed Cycle operates (MacLeod et al. 2021). Additionally, the pricing power of Speed Cycle and other competitors in the market is diminished because these alternative products can be purchased domestically or imported at lower prices.
5.0 Marketing Communication
The communication mix includes every tool that the company can use for communicating with its customers. The communication mix elements are responsible for conveying the message to their target customers. These elements will aid in increasing the revenue of the company and simultaneously mitigates the risks of miscommunication.
|
Factors |
Brazil |
China |
India |
South Africa |
|
Price |
160 |
155 |
155 |
160 |
|
Budget |
3000 |
4000 |
4000 |
3000 |
|
Communication mix |
Direct marketing |
Direct marketing |
Sales promotion |
Sales promotion |
|
E-commerce |
Social media |
Social media |
Social media |
Social media |
Table 1: Communication in the marketing
The above table shows the marketing communication of Speed cycle. The table provides information regarding the price, budget, e-commerce, and communication mix for different countries like Brazil, India, China, and South Africa (Piao et al. 2020). The price of the product for India and China is the same which is 155 and for Brazil, and South Africa it is 160. For the communications mix, the company uses direct marketing for Brazil and China. For India and South Africa, they use sales promotion.
6.0 Recommendations
The company must invest a large percentage of profit in improving the products. This will attract the attention of the customers. As the company is across the globe, there it is important to maintain the reputation of the company along with building healthy relationships. It can only be achieved by providing good training to their staff and making them understand to deal with the customers. The company should also adopt and implement new strategies for innovative ideas and it also mitigates the risk. By adopting the strategies, the company will be able to sustain the customers whether they are existing ones or new, and they will able to keep them for the long run. Furthermore, the company should also analyse the risk on the regular basis to provide seamless performance and products to the customers.
7.0 Conclusion
From the study, it can be concluded that Speed Cycle has penetrated the globe. The market has gained a huge share in India, China, South Africa, and Brazil. There are various frameworks that has been adopted by the company for examining different factors that affect the company. Though the company is dynamic it has not gained the topmost rank. The competition was able to gain a significant competitive advantage in the market thanks to efficient supply chain management that met consumer demand. The recommendations have been suggested for the improvement of the business in a better way.
Reference List
Journals
Angelini, M.L. and García-Carbonell, A., 2019. Developing English speaking skills through simulation-based instruction. Teaching English with Technology, 19(2), pp.3-20.
Bian, J., Liao, Y., Wang, Y.Y. and Tao, F., 2021. Analysis of firm CSR strategies. European Journal of Operational Research, 290(3), pp.914-926.
Bruijl, D. and Gerard, H.T., 2018. The relevance of Porter's five forces in today's innovative and changing business environment. Available at SSRN 3192207.
Clarissia, M.S., 2019. A study on Ansoff Matrix Technique: As a growth strategy and an adaptive learning technique adopted in the leading brand of products. Journal of Composition Theory, 12(9), pp.1494-1506.
Currie, C.S., Fowler, J.W., Kotiadis, K., Monks, T., Onggo, B.S., Robertson, D.A. and Tako, A.A., 2020. How simulation modelling can help reduce the impact of COVID-19. Journal of Simulation, 14(2), pp.83-97.
ElAlfy, A., Palaschuk, N., El-Bassiouny, D., Wilson, J. and Weber, O., 2020. Scoping the evolution of corporate social responsibility (CSR) research in the sustainable development goals (SDGs) era. Sustainability, 12(14), p.5544.
Garcia-Muiña, F.E., González-Sánchez, R., Ferrari, A.M. and Settembre-Blundo, D., 2018. The paradigms of Industry 4.0 and circular economy as enabling drivers for the competitiveness of businesses and territories: The case of an Italian ceramic tiles manufacturing company. Social Sciences, 7(12), p.255.
Guo, Z., Zhou, D., Zhou, Q., Zhang, X., Geng, J., Zeng, S., Lv, C. and Hao, A., 2020. Applications of virtual reality in maintenance during the industrial product lifecycle: A systematic review. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 56, pp.525-538.
Kieltyka, L., Hiep, P.M., Dao, M.T.H. and Minh, D.T., 2022. Comparative analysis of business strategy of Hung Thinh and Novaland real estate developers using McKinsey matrix. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Growth Evaluation, 3(1), pp.175-180.
Lee, D.S., Fahey, D.W., Skowron, A., Allen, M.R., Burkhardt, U., Chen, Q., Doherty, S.J., Freeman, S., Forster, P.M., Fuglestvedt, J. and Gettelman, A., 2021. The contribution of global aviation to anthropogenic climate forcing for 2000 to 2018. Atmospheric Environment, 244, p.117834.
MacLeod, M., Arp, H.P.H., Tekman, M.B. and Jahnke, A., 2021. The global threat from plastic pollution. Science, 373(6550), pp.61-65.
Nguyen, B.H., German, R., Trovão, J.P.F. and Bouscayrol, A., 2018. Real-time energy management of battery/supercapacitor electric vehicles based on an adaptation of Pontryagin's minimum principle. IEEE transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(1), pp.203-212.
Piao, S., Wang, X., Wang, K., Li, X., Bastos, A., Canadell, J.G., Ciais, P., Friedlingstein, P. and Sitch, S., 2020. Interannual variation of terrestrial carbon cycle: Issues and perspectives. Global Change Biology, 26(1), pp.300-318.
Praharsi, Y., Hardiyanti, F., Puspitasari, D., Akseptori, R. and Maharani, A., An Integrated Framework of Balance Scorecard-PESTLE-Smart and Green Port for Boosting the Port Performance.
Rodriguez-Gomez, S., Arco-Castro, M.L., Lopez-Perez, M.V. and Rodríguez-Ariza, L., 2020. Where does CSR come from and where does it go? A review of the state of the art. Administrative Sciences, 10(3), p.60.
Sturgeon, T.J., 2021. Upgrading strategies for the digital economy. Global Strategy Journal, 11(1), pp.34-57.
Tyukhtenko, N.A., Makarenko, S.M. and Oliinyk, N.M., 2018. Increasing competitiveness of the enterprise by improving logistic strategy of distribution of production and supply of raw materials. Науковий вісник Полісся, 2(2 (14)), pp.56-63.
Vallati, M. and Grassi, A., 2019, July. AI to Facilitate Legal Analysis in the PESTLE Context. In Proc. Emerging Technology Conference (EMiT) (pp. 66-68).
Weiwei, L., 2021. Analysis of Ansoff Growth Strategy: a Case of Chinese Yunnan Baiyao Company. Industrial Engineering and Innovation Management, 4(2), pp.1-6.



