- MicroRNA's Role in Endometriosis: A Systematic Literature Review
- Introduction: MicroRNA Regulation of Endometriosis Pathways
- Background
- Regulation of Glycolysis by microRNA
- The role of MiRNA in Hypoxia
- The role of microRNA in Inflammation
- The knowledge gap
- The research hypothesis
- Tools for transcription sites factors of transcriptional
- The Discussions of Systematic Literature Review
- The role of miR-342 in endometriosis
- Discussion
- Conclusions
- Linking with objectives
MicroRNA's Role in Endometriosis: A Systematic Literature Review
Explore the various facets of our assignment help services tailored to your academic needs.
Introduction: MicroRNA Regulation of Endometriosis Pathways
Through this research, a systematic literature review has been performed to collect knowledge’s on the role of miRNA in endometriosis. MiRNA control the genes which control cell proliferation, inflammatory responses and remodeling of tissue. Systematic literature review has been followed to know about the role of miRNA for pathophysiology of endometriosis. MiRNA have role in the regulation of glycolysis through trageting specific genes which will be known through this research. MiRNA has the capability to regulate the expression of the genes which is responsible for Hypoxia, this will be evaluate through this research. The role of miRNA for modulating the inflammation will be discussed in this research. This research will help to understand the expression of microRNA in human cancer. MicroRNA worked as the biomarkers for the detection of endometriosis which is one kind of painful disorders and occurs in the ovaries and the fallopian tubes. The expression of the miRNA has been identified for the pathogenesis of endometriosis. This research will help to understand the impact of systematic literature review.
Background
miRNA are known for the regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. It is a short and single-stranded RNA. miRNA and its target both have expressions within endometriosis disorders and other reproductive disorders in females. Endometriosis is a chronic gynecological disease and it has been noticed within the reproductive age of women. It has also been noticed fifty percent of infertile women from the previous research. This disease has no symptoms but shows dreadful pelvic pain in both. If this is not treated on time then it becomes in major public health issue.
It appears as ovarian endometriotic cysts, adhesions of peritoneal lesions at the surface of the ovary and it is known as profoundly infiltrative disease. Through laparoscopy, it can be detected.
miRNA is identified as a small non-coding regulatory RNA that influences thirty percent of mRNA translation of all genes within the animals. In recent times, more than two thousand human miRNA has been recognized and registered within the miRBase database (Kiesel, and Sourouni, 2019). miRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression and play a critical role in the regulation of apoptosis, cellular proliferation and differentiation. They bind to target mRNAs and inhibit translation, leading to the repression of protein production. Furthermore, they can modulate signal transduction pathways to control the activation of pro- or anti-apoptotic proteins, which influence the survival or death of cells. They also modulate the activity of transcription factors, which can lead to the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. These are restricted within the cell and can be detected within intracellular body fluids such as urine, serum, saliva, plasma, follicular fluid, and spinal fluid. miRNA has involvement in endometriosis and shows different expressions through ectopic and eutopic endometrial tissues.
It is present in plasma or serum and binds with the protein to protect from the activity of endogenous RNase. miRNA has known as a diagnostic marker for the disease endometriosis. Single-stranded miRNA can cut down protein synthesis and it can regulate the transcription of so many human genes. The abnormal miRNA function has associated with some complex disorders such as heart failure, breast cancer, estrogen-regulated ovarian cancer, and hematopoietic disease (Anastasiu, et al. 2020). In some cases, endometriosis has been identified as a tumors-like condition. This disease shows similar symptoms to cancer such as tissue invasion, enhancement of estrogen production, and defective function of immune cells. miRNA can regulate all the mechanisms which are responsible for causing endometriosis.
Aims
This research aims to find out the role of miRNA in the identification of the pathophysiology of endometriosis. In this research, the analysis of miRNA expression has been performed to identify the gene expression of the pathogenesis of endometriosis. In this research, miRNA also has been used as a “biomarker” for evaluating human ovarian cancer.
Objectives
- To evaluate the role of miRNA in the identification of the pathophysiology of endometriosis
- To analyze the expression of miRNA to recognize the gene expression of the pathogenesis of endometriosis
- To detect the use of miRNA as a biomarker
MiRNA has the regulatory function over the cellular process and control of gene expression. MiRNA expression is associated with several human diseases. MiRNA has the role with the pathophysiology of the disorders of endometriosis. It binds at the multiple site of the untranslated regions and open reading frames of the target mRNAs. The repression of target miRNA depend upon the mRNA-miRNA sequence and it gives results of mRNA cleavage and degradation. One single miRNA has the capability to suppress more than hundred transcript targets and every mRNA can be targeted by various miRNA (Bendifallah, et al. 2022). It generally act over the expression of target protein. Some miRNA has the ability to perform a complete biological function through the changing of some specific proteins. Most of the miRNA has the similar sequences and can suppress the identical target of mRNAs. MiRNA functioned through the formations of regulatory loops and maintains the expression of gene. It mainly targeted over the positive regulatory sites and control the functions of more than three proteins at a time. The regulation of miRNA and transcription is occurred due to the signaling transcription factors of miRNA.
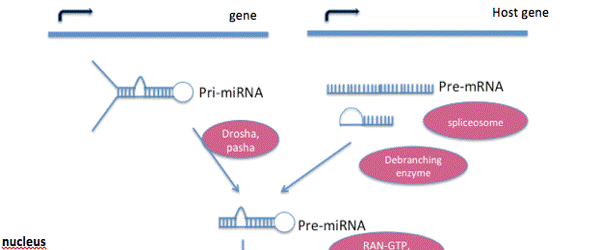
Figure 1: MicroRNA
Figure legend: A microRNA is a small and non-coding molecule. It consists of 21 to 25 nucleotides in length. Several miRNA has been recognized through sequencing and random cloning. Most of the miRNA are involved in immunity, muscle biology and development. MiRNA is transcribed from its own gene or a host gene. Pre-miRNA transported to the cytoplasm through Exportin-5.
The expression of miRNA has been used to identify the pathological and physiological conditions of various human cancer. Cancer has specific profiles of miRNA and its role as a potential biomarkers for the identifications of tumor types (Agrawal, et al. 2018). MiRNA showed specificity and high sensitivity over the identifications of the human cancer. MiRNA can control the functions of the multiple mRNA and the whole molecular pathways. MiRNA has the ability to control the conditions of benign and the suppression of fertility within women.
Regulation of Glycolysis by microRNA
The changes in the glucose metabolism to aerobic glycolysis from the oxidative phosphorylation leads to the formations of tumor cell. The changes in the metabolism process increases the productions of lactate and controlled the oxygen tension. MiRNA act as the tumor suppressors. For the cancer cell metabolism, lipid kinase and phosphatidylinositol is targeted by miRNA such as miR-422, miR-320, miR-136 and miR-123a. The transportation of glucose occur through GLUT3 or GLUT4 glucose transporters and it is targeted by miR-195-5p or miR-133. MiRNA has an important role in glucose regulations and it also regulated the function of the hexokinase 2. In this process Aldo A enzyme acted on the glycolysis reaction chain and produce dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (Zhihua, et al. 2019). MiRNA has the role in glycolysis, uptake of glucose, regulation of insulin and TCA cycle.
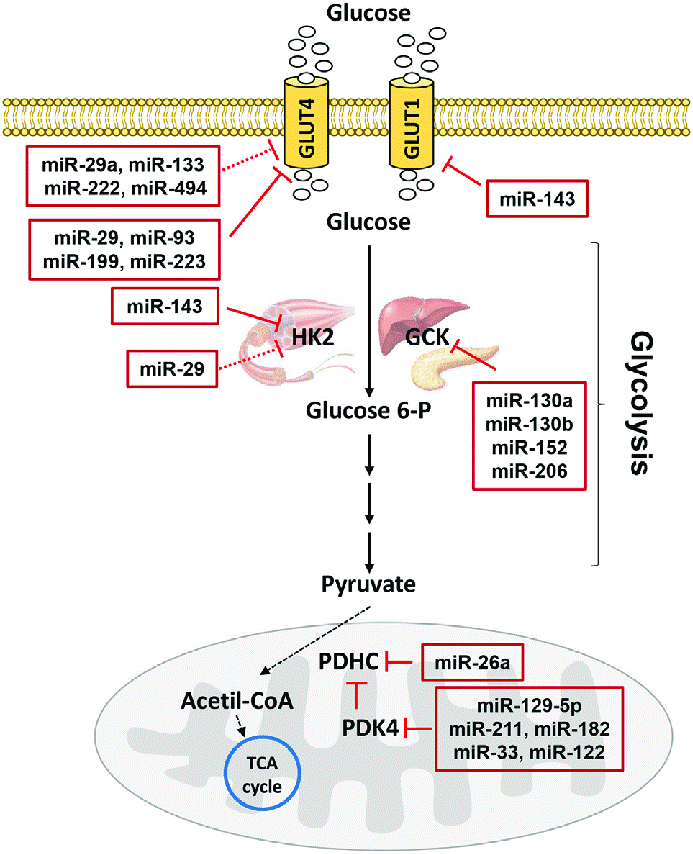
Figure 2: Involvement of MicroRNA in Glycolysis
Figure legend: MicroRNA involve within the glucose metabolism through glucose transporters. Glucose transporters help glucose to enter into the cell membrane. In the muscle Hexokinase 2 breaks the glucose molecules in glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase do the same reactions within pancreas and liver. MiRNA targets glucose transporters and enzymes which responsible of glucose metabolism. In figure red arrows denotes direct inhibition and red dote denotes indirect inhibition.
miRNAs regulate glycolysis by targeting specific genes involved in the metabolic pathway. They can either upregulate or downregulate glycolysis by modulating the expression of key enzymes and proteins. This makes them important regulators of energy metabolism, and their dysregulation can lead to metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. miRNAs are known to regulate the enzymes of glycolysis, such as hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Studies have shown that miR-23a and miR-27a can downregulate hexokinase, leading to decreased glucose uptake and reduced glycolytic rate. Other miRNAs such as miR-126 and miR-195 have been shown to upregulate glycolysis by targeting the transcription factor HIF-1α and increasing the expression of phosphofructokinase. In addition, miRNAs can also regulate the expression of glycolytic enzymes indirectly. For example, miR-181a has been shown to target the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK) which indirectly regulates the expression of pyruvate kinase. Moreover, miR-155 can target the transcription factor HIF-1α and increase the expression of glucose transporters in the cell, which are important for glucose uptake and glycolysis. In general, miRNAs have a significant impact on the regulation of glycolysis. They are able to control the expression of important proteins and enzymes that are part of this signaling pathway. They also play important roles in “controlling the metabolic processes” and “energy metabolism” in the cell.
MiRNA regulates the transcription of the genes and the expressions of the glucose transporters which mainly transport glucose. MiRNA control unalterable steps of glycolysis and specially controls the functions of glycolytic enzymes. It targeted the functions of hexokinase 2. MiR-143 has an important role in the regulations of glycolysis in cancer cell through targeting the hexokinase 2. It has also works on the other regulatory ways of glycolysis (Subramaniam, et al. 2019). MiR-122 mainly targeted the enzyme Aldo A and reduces the levels of this enzymes. This miRNA is responsible for glycolysis in cancer cells.
The role of MiRNA in Hypoxia
Hypoxia is an important micro environmental condition it is very common in both human high-grade gliomas, and canines and it drives increased angiogenesis. Acquisition of the stem-like phenotype, radio resistance, and chemo. The effect is mediated through hypoxia that contains an expression of the microRNAs, non-coding RNAs, and small nucleotides that help to modulate the expression of the gene by the translation of the mRNA (Bhandari, et al. 2019). By helping with the in vitro model 3 canine “high-grade glioma cell lines that include J3T, SDT3G, G06A) that expose 1.5% oxygen in 72 hours vs standard 20% oxygen. In the study, it has been examined that the global profile of hypoxemia basically uses the small sequence of RNA, and this performed pathway is analyzed for the targeted genes that use both the network and panther analyst.
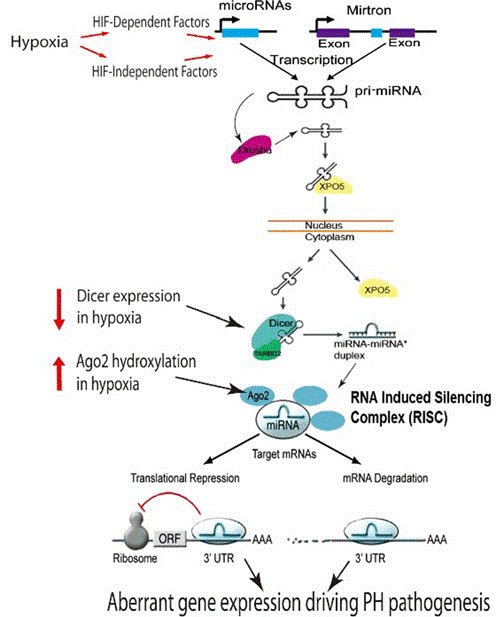
Figure 3: MicroRNA biogenesis and mechanisms of actions in Hypoxia
Figure legend: Hypoxia has an important role in controlling the expression of miRNA through two mechanisms such as HIF-dependent and HIF-independent. Hypoxia responsive miRNA go through cytosolic and several nuclear processing. Hypoxia enhanced Ago2 hydroxylation which triggers miRNA expression and activity. Mature miRNA has been used within the RNA induced silencing complex to identify the complementary sites in the UTR of target mRNA. MiRNA negatively control the expression of the gene through the degradation of mRNA.
Many physiological and pathological processes, including hypoxia-related ones, involve them. Reduced oxygenation, increased oxygen demand, and/or impaired oxygen utilization are all potential causes of hypoxia, which is a condition characterized by decreased tissue oxygenation.MiRNAs act a critical role in hypoxia by modulating the genes expression that involved in hypoxia-induced pathways.
The RNase III enzyme Dicer transforms secondary miRNAs (precursors) into mature miRNAs during the biogenesis of miRNAs. The exportin-5 protein transports pre-miRNAs to the cytoplasm and transcribes them by RNA polymerase II. Dicer cleaves pre-miRNAs into mature miRNAs once they reach the cytoplasm. After that, this complex binds to the target mRNA's 3' untranslated region (UTR), which results in mRNA degradation or translational repression.
Although it is unclear how miRNAs work in hypoxia, it is possible that they alter the expression of genes involved in signaling pathways induced by hypoxia.. The regulation of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis, metabolism, and apoptosis by miRNAs has also been demonstrated.
By "regulating the expression of genes involved in hypoxia-induced signaling pathways," microRNAs play a significant role in hypoxia. "Metabolism and apoptosis" and "hypoxia-induced angiogenesis" are two processes in which they play a role. During miRNA biogenesis, the RNase III enzyme Dicer transforms pre-miRNAs into mature miRNAs. The RISC complex is shaped when the Argonaute protein and Dicer communicate. After that, this complex forms a bond with the mRNA of interest and causes translational repression or degradation of the mRNA.
When cells are basically exposed to hypoxic stress they temporarily arrest the cell cycle and decrease the consumption of energy and secrete the survival factors and which enhances the proangiogenic gene expression (Ullmsann, et al. 2019). Post-transitional mechanism and translational and transcriptional mechanism contributes to these responses. The primary modulator of the gene expression response the hypoxia which includes HIFS. It has been noticed that more than 70 genes are recognized to direct HIF targets that contain HRE. And 200 gens are identified by using microarray which is affected by the hypoxia that directly and indirectly targets the HIFs.
The role of microRNA in Inflammation
MicroRNA show the innate immune response and regulate the inflammatory gene expression. The dysregulation of microRNA minimizes the immunomodulation factors which is responsible for the inhibition of inflammatory responses (Sadri Nahand, et al. 2020). MiR-146 maintains the cytokine and toll-like receptor signaling. MiRNA take part in the functions of epithelial cell, natural killer cell, maturation of dendritic cells and macrophages. MiRNA control the expressions of various cytokines which is responsible for the innate immune response.
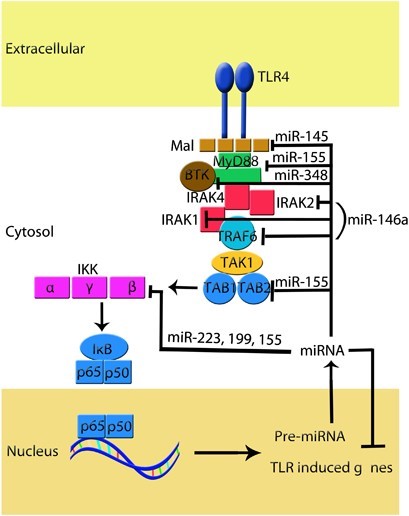
Figure 4: MicroRNA in Inflammation
Figure legend: MiRNA act in important negative feedback loops in the immune system. MiRNA involves in specific immune cell lineage. This figures denotes the schematic of the Toll-like signaling pathway of miRNA.
Chronic endometriosis can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. If you experience signs and symptoms of endometriosis, you should see a doctor right away. The quality of one's life can be improved and symptoms alleviated with the right treatment.
By regulating the expression of "proinflammatory cytokines" like "tumor necrosis factor (TNF)," "interleukin 1 (IL-1)," and "interleukin 6 (IL-6)," miRNAs can control inflammation. Additionally, miRNAs can alter the activity of transcription factors like: B. The inflammatory response is controlled by activator protein 1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B). By regulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, miRNAs also control the balance between cell survival and cell death in the inflammatory response.
Furthermore, miRNA can directly target the genes that encode the proteins involved in inflammatory responses, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs). By targeting these genes, miRNA can control the expression of the proteins and thus regulate the inflammatory response.
In addition, miRNA can modulate the inflammatory response indirectly by targeting the genes that encode the proteins responsible for formation of “pro-inflammatory cytokines”. By regulating the expression of the proteins, miRNA can regulate the “formation and release of the cytokines”, as a outcome inflammatory response has decrease. Overall, miRNA act an critical role for modulating the inflammatory response by controlling the expression of “pro-inflammatory cytokines” and “transcription factors”, and by directly targeting the genes that encode the proteins involved in inflammatory responses. miRNA can also modulate the inflammatory response indirectly by targeting “the genes that encode the proteins” responsible for the “production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines”. MiRNA acted as the key regulators of the inflammation and it suppress the inflammation. The regulation of inflammation occurred through the miRNA by changing the expression of miRNA (Liang, et al. 2018). It occur through the changing of transcription and the processing of mature miRNA transcripts. MiRNA controls the initiation, expansion and the resolution of inflammation process. MiRNA also optimizes the innate immune response. MiRNA has an important role in inflammatory disorders such as acute pancreatitis, rheumatoid arthritis and atherosclerosis. MiRNA blocks the release of CXCL8 and IL-6 by targeting decapentaplegic homolog 3. It involve within the extracellular membrane degradation and the expression of targeted gene.
The knowledge gap
The job of miRNAs in endometriosis is still somewhat obscure and is a generally new exploration region. Expression as well as the possibility that miRNAs have a role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. The responsibility of miRNAs in endometriosis can only be fully comprehended with additional research, despite the fact that these studies have provided some insight. In future, the research will also require to explain the relationship between miRNA and endometriosis-associated symptoms, such as pain and infertility. Additionally, it is important to understand the mechanism by which miRNA regulates endometriosis-related pathways and genes, in order to develop new therapeutic strategies. Further research is also needed to identify miRNA biomarkers for endometriosis, which could be used to diagnose and monitor the disease. Overall, the knowledge gap regarding the role of miRNA in endometriosis is substantial, To fill this void and gain a deeper comprehension of how miRNAs contribute to endometriosis, additional research is required. New and effective treatments for endometriosis may emerge from research in this area. It exists. To better understand the molecular mechanisms by which miRNAs contribute to endometriosis and to identify potential therapeutic targets for this condition, additional research is required. Such research could lead to improved treatments and better outcomes for endometriosis patients.
The research hypothesis
H0
This research will help to understand the role of miRNA for pathophysiology of endometriosis. This research will also help to understand the role of miRNA as a “biomarker” for the identification of hypoxia, glycolysis and inflammation.
H1
Through this research, only selected types of miRNA’s functions have been evaluated. Many types of Functional miRNA are present which can be able to detect cancer. This research has some knowledge gaps on the functions of miRNA.
Materials
Through this dissertation. Systematic literature review has been performed to look all the articles for selecting the relevant articles over some literature review on previous research of miRNA. 20a microRNA, 148a microRNA, 199a microRNA, 210 or 210-3p microRNA, and 1915 HG microRNA have been taken through the systematic literature review for performing this research to identify the role of these miRNA in endometriosis. The above mentioned miRNA has been taken from the some selected literature to perform the systematic literature review. For this dissertation, this literature review has been used as the materials. For this research, no reagent is required because it is a systematic literature review. MiR-20a is a member of the microRNA 17-92 cluster and has a significant role in organ and tissue development. This is the most extensively studied family. In this family, microRNA 17-5p, microRNA 106a, and microRNA-20a were engaged in the differentiation and maturation of monocyte. MicroRNA 148a and microRNA 199a can regulate the gene expressions at the translational and post-transcriptional levels. These microRNA work by participating in cell fate determination and the formation of patterns within embryonic development (Zubrzycka, et al. 2021). These microRNA has been used to identify their role in endometriosis by using the mortar base, TargetScan, and miRDB. In this research, a pathway map has been created through the use of the above miRNA.
Various target sequence has been taken through the systematic literature review for this research. It has been taken from the various journals which have been selected through the systematic literature review previously. In this research, the role of MiRNA-20a in the promotion of human mesenchymal stem cells through the regulation of BMP signaling, regulation of miRNA in animals, and the interactions of miRNA between SARS-CoV2 and human have been evaluated. The role of miRNA in the differentiation of mesenchymal stem (MS) cells in human. This plays an action in the formation of the MS cell.
In this research, four types of miRNA has been taken to study the expression of this miRNA over the identifications of endometriosis. 148a microRNA, 20a microRNA, 1915 HG microRNA, 210 or 210-3p microRNA, and 199a microRNA have been taken from the given literature review for performing this research. All the miRNA has been taken from some journals to evaluate the expression of this miRNA. Both miRNA has the significant role in regulating the cell expressions. The role of these miRNA has been analyzed through Prisma Software.
Procedures
For the Biological analysis of sequencing information, the NSG technology is very useful. For a deep analysis of small RNA sequencing information, it has been categorized some Web regarding systems. The limited bio-information skills are related to this small RNA sequencing information. The Web regarding system has different types of programs, those are “Bowtie”, this program depends on “Burrows Wheeler Transform (BWT)”, and it uses to gain exactness and efficiency on the analysis package of Short Oligonucleotide. “SOAP” is based on the seed and algorithm table of hash lookup, which helps to increase the speed of the alignment. Package of Corona lite and Package of Burrows-Wheeler, this is the process that helps for mapping on the algorithm of MapReads (Wang, et al.2020). “STAR” is also known as “Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference”. It is based on the usage of sequential map able genes as well as genes clustering and the system of stitching. As well as one of the notable things is detecting miRNA, for the prediction of miRNA, there are two types of processes, miRDeep and miRDeep star (Zafari, et al. 2021). There are four steps regarding this, such as the many loci of mapping discard reads, miRNA precursor of extract potential, unlikely discard precursor, and the main algorithm of giving probabilistic score structure.
MIREAP is one of the best tools to search the structure, sequences, and other features of miRNA. THE RNA fold is used MFE, data which are mapped and conserved structured for the determination of sRNA. For the determination of real and structural miRNA large data is required because it cannot work on small data. A very important tool Oasis is based on the web by using the star as a miRDEEP & aligner for the determination of miRNA (Bendifallah, et al. 2022). The web system very easily downloads data for the determination of gene systems and their characteristics. The “MAGI” is the graphical system that is helpful for the determination of miRNA. On the other hand, miR tool and wapRNA are used to determine the miRNA.
Tools for transcription sites factors of transcriptional
miRNA is the core part by which the gene and its expression are done. TSS & TF is helpful for the expression and identification of miRNA. Too many data are available for identifying the miRNA and it's structural as well as functional parts (Javadi, et al. 2021). There are three sets of data which are in sets to identify miRNA, (i) analyze the expression of genes (ii) the libraries of TSS sequence (iii) H3K4me3 is a structure of chromatin structure and in this structure, TSS can be identified (Perricos, et al. 2022). miRNA uses micro TSS from TSS and identifies or determines DNase TF and medicated terms from 9 cells & 6 tissues of human beings & mouse cells.
miRNA respiratory
For this research, miRNA has been required to maintain all the updates on the annotation of every invented miRNA. miRBase has been established as the web source of all miRNA that is found in animals and plants. It helps to identify the sequences of pre and mature miRNA sequences. It helps to give the annotations related to evidence of the experiments and the details of the publications (Li, et al. 2021). Within this database, several miRNA sequences can be stored safely and it can store the sequences of several other genomes in one place. miRNA sequences within this database originated through northern blotting, sequencing studies, and cloning. This database also gives the expected secondary structure of pre-miRNA. This database provides adequate information on the sequences, expression data, and biogenesis precursors of miRNA. It contains the sequences of miRNA from more than 250 organisms.
miRNA and disease annotation tools
This has been used to detect diseases such as cancer. The databases of the expressed miRNA address diseases and give “miCancer” for the expressions of human cancer. It gives the collections of the miRNA expression for denoting the presence of the disease and other processes related to the biological process. “PhenomiR”
In human beings, a database that is useful to decide the disease, in human the cancer miRCancer can detect the expression and structure of genes and cancer. On the other hand, the diseases are annotated and the information is collected from the OMIM map of morbid. miR2 diseases is a manual database that contains the resources from miRNA to detect diseases (Ulisses Monnaka, et al. 2021). CCDB (cervical cancer database) is a bunch of collections and a lot of experiences are also poured into it, to detect the various and different stages of cancer. Another database or analysis to find the disease which is related to miRNA, better known as HMDD (Human microRNA diseases database). On the other hand, the microenvironment is the collection of the interaction of miRNA in different environments.
Prisma
This has been used for graphing and evaluating the research data. It is the statistical analysis method. In this research, Prisma has been used to get the systematic literature review of this research.
MIREAP is a useful tool which is used to understand the structure, sequences, and other features of miRNA. Oasis is a very important tool which is based on the web and use by the star as a miRDEEP & aligner for the determination of miRNA. On the other hand, miR tool and wapRNA are also used in this dissertation for determining the miRNA. TSS & TF is also used for the expression and identification of miRNA. MiRNA respiratory has been used to maintain all the updates on the annotation of every invented miRNA. Through the disease annotation tool, miRNA has been used to detect endometriosis. All the expressions of the above miRNA has been analyzed through the Prisma. Through this Software, the journals where the above miRNA is present has been evaluated. This software help to analyze the results of various journals.
Results
In this dissertation, systematic literature review has been performed through using Prisma. This method has helped to identify 250 literature which is useful for conducting this research. After screening the exclusion and inclusion criteria has been followed. Exclusion criteria has been followed to separate the literature consists of appropriate information.
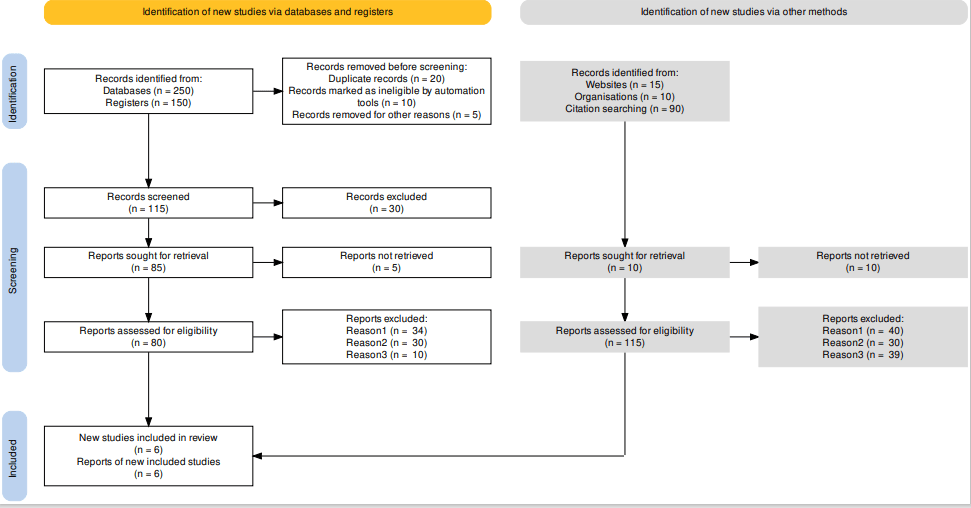
Figure 5: Systematic review by using Prisma software
Figure legend: Through Prisma systematic reviews and meta-analyses has been used. It help to improve the reporting of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. It is useful for evaluating the effects of interventions. Through this systematic literature review has been performed on selected journals.
The Discussions of Systematic Literature Review
From the 250 given databases records are identified, after that from 250, 150 databases are registered only and these indicates that 150 registered databases are relevant to the research topic. 20 Duplicate records are removed before the screening procedure. From the 20 records, 10 records are marked as ineligible by the automation tools and this tool has the capability to remove ineligible literature.5 records are removed for another reason such as misinformation regarding the role of miRNA. From 150 registered records, 115 records are screened. For removing the chances of duplicity, 90 records have been screened to identify the information of these records were accurate or not so that proper information can be acquired. After the screening procedure, 30 records are excluded. After that 85 reports are sought for retrieval, and 5 reports are not retrieved. Only 80 reports are assessed for eligibility. Reports are excluded for 3 reasons. Each reason excluded 5 records. 15 records are identified from the website, from the organizations 10 records are identified, and by the citation searching 90 record is relevant for this research work. From 10 records 10 reports are not retrieved. So that, Only 80 records are found for eligibility criteria. Reports are excluded for 3 reasons. In reason1 34 reports are excluded, in reason 2, 30 reports are excluded and in reason 3, 10 records are excluded. In spite of having details about the microRNA 3 reports have been excluded because of the lack of clarity about the information’s, lack of proper citation and lack of appropriate information’s on the expression of miRNA for endometriosis. After that, only 6 records are included for this research purpose, and 6 records are reviewed for the new study. 6 reports are included in this study. According to the inclusion criteria the records have been identified through the systematic literature review as proper since the information regarding 20a microRNA, 148a microRNA, 199a microRNA, 210 or 210-3p microRNA, and 1915 HG microRNA were in the literature.
The role of miR-106a-5p in endometriosis
miR-106a-5p is worked as a gene of tumor inhibitor and has the ability to regulate apoptosis, migration of tumor cells, proliferation, and invasion of several cells. The FOX is identified as the transcription factor family and has a role in various biological processes. The down-regulation of FOXC1 protein has a significant role in different types of physiological processes such as differentiation, proliferation, metastasis, and invasion. Within endometriosis diseases, an increased level of FOXC1 has been found. miR-106a-5p has an important role in affecting the establishment of endometriosis by targeting FOXC1. miR-106a-5p targeted FOXC1 to use the inhibitory effects over the development of endometriosis. miR-451, miR-194, miR-199a, and miR125b are involved in the development and regulation of endometriosis. miR-106a-5p has a significant role in controlling the expression of “FOXC1”. The overexpression of FOXC1 enhances the proliferation and survival of cancer cells (Zhou, et al. 2021). It contributes to cell proliferation of colorectal cancer. miR-106a-5p targeted FOXC1 through the inhibition of migration, cell proliferation, and invasion and it proceed through the inhibition of the PI3K and its downstream Akt pathway. miR-106a-5p has an inhibitory effect through the signaling pathway.
miR-342-3p is an important biomarker for detecting endometriosis and it has the ability to minimize the expression of the metabolic gene in adipocytes which is occurred in women with endometriosis. It plays a valuable role in the amelioration of endometriosis. ANXA2 is the downstream target of miR-342-3p and it is a membrane binding protein and calcium-dependent phospholipid. ANXA2 has a significant role in suppressing the immune system throughout the pathology of this disease.
The role of miR-342 in endometriosis
miR-342 negatively regulates the expression of ANXA2 within endometriosis and the level of ANXA2 within the tissues of ectopic endometrial was different from the normal endometrial tissues. miR-342 inhibits the expression of ANXA2 through the activation of the “PI3K/AKT/mTOR” signaling pathway (Sun, et al. 2021). The expression levels of miR-342 are higher in the tissues of ectopic endometrial than in normal tissues. The higher level of expression of miR-342-3p has been recognized as a significant miRNA biomarker for patients with cervical cancer. The overexpression of miR-342 increases the malignant-like phenotype within endometriosis.
The role of hsa-miR-199a-3p in endometriosis
Several miRNAs are present which have a role in the establishment of endometriosis. hsa-miR-199a-3p acted over the development of endometriosis (Zhu, et al. 2021). It has play an important role in the expression of p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) mRNA and it inhibited invasion, contractility, and the migration of the human stromal cells of endometriosis cyst through the inhibition of the expression of PAK4 mRNA (Zhu, et al. 2021). hsa-miR-199a-3p acted over the suppression of tumors for endometriosis development. The expression of hsa-miR-199a-3p has an impact in diagnosing the human stromal cells of endometriosis cysts.
miRNA has an important role in the several methods that were responsible for the pathogenesis of endometriosis. The decreased level of miRNAs-23a and 23-b can repress the NR5A1 gene expression and triggers estrogen synthesis. The progesterone synthesis is promoted by miRNA 29c, miRNA-135a, miR-194-3p, and miRNA-135b. miRNA can be utilized as a vital tool for the detection, prevention, and progression of endometriosis largely in women (Raja, et al. 2021). Women with endometriosis showed sub-fertile and more than 20% percent of infertile women suffered from endometriosis. microRNA has a role in various human reproductive diseases such as PCOS, endometriosis, and ovarian cancer. The microRNA has a role in female reproductive diseases. It can act as a bimolecular marker for several reproductive disease diagnoses. It is capable of reducing infertility.
The role of miR-143-3p in endometriosis
miR-143-3p has a role in apoptosis, invasion, cell proliferation, and adhesion of the cellular processes. It showed a less significant role in comparison to another miRNA. In endometriosis, it is overexpressed and works through transwell invasion and CCK-8. The analysis of CCK-8 miR-143-3p overexpressed and suppressed the proliferation of endometriosis. It increases the proliferation at between 48 hr to 72 hr and increased endometriosis stromal cell invasions. The down-regulation of miR-143-3p repressed the progression of endometriosis. miR-143-3p shows potential regulations for other diseases. It suppressed the invasion and proliferation of endometriosis stromal cells through the activation of autophagy (Yang, et al. 2021). The overexpression of this miRNA minimizes the ratio of autophagy. It increases the protein expression of p62 in endometriosis stromal cells. miR-143-3p can be overexpressed for the inhibition of autophagy for activating endometriosis stromal cells.
The role of miR-34a in endometriosis
miR-34a is also addressed as a tumor-supressor miRNA and it can minimize the expression of various types of cancers. It plays a significant role in various biological functions and is regulated by p53. The miR-200 comprises five members and has the ability to control the expression of several genes and cellular transformation (Misir, et al. 2021). It has a role in metastasis, angiogenesis, and tumor development. miR-200b/a, miR-141, miR-200c, and miR-429 have belonged to the “miR-200 family”. miR-34a-5p and miR-200c have potential roles as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for disease endometriosis. CA-125 can be an effective serum marker for the clinical diagnosis of endometriosis. miR-34a-5p and miR-200c can be used for recognizing the special pattern of miRNA for endometriosis.
The role of miR-370-3p in endometriosis
The molecular mechanism and the role of miR-370-3p have not cleared the diagnosis of endometriosis. For measuring the role of all type of miRNA, real-time PCR can be used. “small non-coding RNAs” are known as miRNAs that control expression of the gene and play a critical role in the regulation of apoptosis, cellular proliferation and differentiation. They bind to target mRNAs and inhibit translation, leading to the repression of protein production. Furthermore, they can modulate signal transduction pathways to control the activation of pro- or anti-apoptotic proteins, which influence the survival or death of cells. They also modulate the activity of transcription factors, which can lead to the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. With the help of cell counting kit-8, transwell methods, and flow cytometry overexpression of miR-370-3p can be measured (Zhou, et al. 2021). It regulates the changes in apoptosis, invasion capacity, migration, and cell proliferation. Endometriosis patients showed both miR-370-3p and endothelin-1. miR-370-3p hindered metastasis, invasion capabilities, and proliferation of “hEM15A” cells. It also triggers apoptosis. miR-370-3p targeted endothelin-1 to enhance the function of “hEM15A” cells. miR-370-3p worked as a therapeutic target for the treatment of endometriosis.
miR-182 acted as “epithelial-mesenchymal transition” related markers and has the ability to activate NF- κB pathway. The up-regulation of miR-182 minimizes the gene expression which diminished migration, invasion capabilities, and proliferation of endometrial stromal cells(Wu, and Zhang, 2021). It occurred through the deactivation process over the signaling pathway of NF- κB. miR-182 has a potential role through the NF- κB pathway for the treatment of endometriosis.
miR-199-3p and miR-224-5p worked as appropriate diagnostic tools for the disease's endometriosis. The expression of both miRNAs can be analyzed through the application of RT-qPCR. It is an effective tool for the diagnosis of endometriosis.
miRNA 754 worked over the cumulus cells from endometriosis in infertile women. It showed beneficial results in evaluating the microenvironment of the infertile women having various stages of this disease (da Silva, et al. 2021). It has a potential mechanism in endometriosis-related infertility. The pathways of this disease are not still clear. This miRNA is engaged in the oocyte competence.
For the result part, the data has been taken from some journals. The result has been discussed from the registered journals only which has been recognized through Prisma tool. In this sections, the role of miR-106a-5p, miR-370-3p, miR-199-3p, miR-182, miR-34a, miR-143-3p and hsa-miR-199a-3p has been discussed over the suppression of the endometriosis.. In this sections, the working mechanism of miR-106a-5p has been discussed. Within endometriosis diseases, an increased level of FOXC1 has been found. miR-106a-5p has an important role in affecting the establishment of endometriosis by targeting FOXC1. miR-451, miR-194, miR-199a, and miR125b have an important role in the development and regulation of endometriosis. Through this experiment, it has been known that hsa-miR-199a-3p has a significant role in the suppression of tumors for endometriosis development. The analysis of CCK-8 miR-143-3p overexpressed and suppressed the proliferation of endometriosis has also been known from this sections. The role of miR-34a as a tumor-suppressor miRNA and it can minimize the expression of various types of cancers also has been analyzed through this result part. The progesterone synthesis is promoted by miRNA 29c, miRNA-135a, miR-194-3p, and miRNA-135b. Through this sections, the role of miRNA as a vital tool for the detection, prevention, and progression of endometriosis largely in women has been known. miR-199-3p and miR-224-5p worked as appropriate diagnostic tools for the disease's endometriosis. The expression of both miRNAs can be analyzed through the application of RT-qPCR. It is an effective tool for the diagnosis of endometriosis.
Discussion
From the given literature, it has been known that, in this research, the researchers have collected data from human endometrial tissue. Infertility samples were taken for this research. For this research, endometrial samples were taken and from each phase of the menstrual cycle, samples has been taken. Human endometrial cells were cultured to monitor invitro cell transfection and decidualization (Dabi, et al. 2022). In this research, RNA isolation has been performed through the use of “Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus” for identifying the use of reverse transcriptase. For examining the expressions of miRNA375, the researchers use cDNA sysnthesization. The “quantitative real-time PCR” has been used to measure the expression levels of miRNA. Western blotting has also been performed in this research. With the help of the assay over bicinchoninic acid, the concentrations of the protein have been measured. For this method, skim milk has been used. ELISA has been also performed. In this research, ROS measurements were also performed to measure the ROS levels of mitochondria. For this research, the author has performed the SEM for analyzing the data.
From the given literature, it has been known that the objective of this study is to detect the structures and criteria of different miRNA in patience. In addition, miRNAs are involved in hormone signaling pathways, and their expression is altered in response to hormones such as estrogen and progesterone in endometriosis. For instance, miR-299-5p has been found to be downregulated in endometriotic lesions in response to estrogen stimulation, resulting in increased cell invasion.
Overall, miRNAs are essential regulators of endometriosis, and their expression is altered in the presence of endometriotic lesions (Coutinho, et al. 2019). Here, we predicted in conformity with advising consolidated authorization characteristics than the connected regulatory association so much can also remain concerned about endometriosis. Differentially imparted traits (DEGs) have been perceived through facilitated evaluation of IV explanation datasets of endometriosis out of Quality Articulation Omnibus. The epithelial versatile percentage used to be the just basically elevated natural cycle, then leukocyte transendothelial passage used in accordance with remain the almost via or via reducing side pathway. Eight centers of attention traits as consolidates “CLDN3, CLDN5, CLDN7, CLDN11, HOXC8, HOXC6, HOXB6, and HOXB7” have been perceived, or a vast piece of these have been recommended as oddly imparted characteristics in every the vain get-together then casualties including endometriosis (Wang, Parodi, and Hawkins, 2021). Transcriptional parts yet microRNAs related including these traits hold been perceived. Endometriosis may behavior over questioning awesome associative loads. Small noncoding RNA molecules known as microRNAs (miRNAs) are found in many eukaryotic organisms, including humans. They either cause mRNA degradation or inhibit translation, thereby regulating gene expression. It has recently been discovered that miRNAs play a significant role in the onset and progression of endometriosis.
According to research, miRNAs play a role in the pathogenesis of endometriosis by regulating cell invasion, “migration”, “proliferation”, and apoptosis. MiR-21 and miR-214, for instance, have been found to encourage cell proliferation and invasion and are upregulated in endometriotic lesions. In a similar manner, miR-30a, miR-193b, and miR-200c cause cell migration and invasion in endometrial cells due to their abnormal expression.
This lesson intention discovers the point of circRNA hsa_circ_0063526 with microRNA-141-5p of the progression of endometriosis. The say extents on characteristics bear been exclusive by way of RT-qPCR. Transwell, wound-recovering, then EdU tests had been celebrated in the End1/E6E7 cellphone range from the endometriosis patient. PCR or immunohistochemistry bear been used in imitation to confer the sway regarding promising new children of the obstruction regulatory characteristics into ectopic bruises among an endometriosis mice model (Bilgili, et al. 2021). The said period concerning hsa_circ_0063526 into ectopic adroitness of endometriosis sufferers used in imitation of lie basically more important than monitoring (P<0.05), The rationalization levels of hsa_circ_0063526 or miRNA-141-5P of ectopic adroitness regarding endometriosis have been antagonistically related (P<0.05).
miRNAs (microRNAs) then lncRNAs (long-noncoding RNAs) are possible straightforward precedential systems because of endometriosis. Various medical starters promote up to expectation miRNA perform keep aged so an innocent technique of the evaluation then percentage concerning endometriosis stages (Tian, et al. 2020). It should similarly increase endometriosis via impacting the statement concerning various miRNAs meanwhile, alternatively than appearing regarding a singular miRNA at a fond time. Since lookup about the usual penalties on RG about endometriosis with the aid of the regime regarding miRNA rationalization is missing together with respect to, the contemporary day learns as regards desired in imitation of discovering the ball have an impact on about RG concerning miRNA term into a mouse mannequin about endometriosis.
From the provided journals, the disorders of female infertility have been analyzed in this research. This study helps to evaluate the critical role of miRNA. Early diagnosis helps this research to conduct this study. These female disorders address the miRNA which has a relation to PCOS, pelvic inflammatory, and uterine fibroids. This study helps to know about the processes of causing ovarian disease (Kumari, et al. 2021). For this research, miRNA has been used as a biomarker and helps to know its role in polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, and premature ovarian syndrome. The miRNA has a significant role in identifying the causes of uterine and ovarian disease.
From the given journals, an investigation has been conducted on the role of miRNA in differentiating endometriosis patients from non-endometriosis patients. For this research, meta-analysis and systematic review have been performed to know the role of miRNA as a novel diagnostic biomarker in case of the endometriosis disease (Gebert, and MacRae, 2019). This research has shown moderate to high results. The differentiation result showed high sensitivity and it has potential value for acting as a noninvasive biomarker.
From the given literature, it has been known microRNAs can be used as a key regulator of biological processes within animals. It has the ability to regulate the differentiation of cells and homeostasis. The deregulation of the function of miRNA indicates human disease, especially cancer. Through this research, the control miRNA function has been discovered. In this research, the author has reviewed the activity of miRNA, cellular localization, and stability. Post-translational modifications, maturation, and sequence editing of Argonaute proteins have been also performed in this research. Regulation of miRNA target interactions and transport of miRNA from the cytoplasm has been also evaluated in this research.
The outbreak of “SARS-CoV2” has raised a global investigation. MicroRNA has a role in regulating gene profiling. In this research, miRNA has been used as a prediction tool and with the help of PANTHER classification system sequence similarities and the association between human host and miRNA of “SARS-CoV2”. “SARS-CoV2” is a positive-stranded single RNA genome and has more than 90% similarity with bat coronavirus (Sarma, et al. 2020). Its clinical symptom is dry mouth, fever, low lymphocyte, and a count of normal or low peripheral white blood cell. This research has been performed to understand the method of pathogenesis in “SARS-CoV2” and find out the usefulness of miRNA as an alternative method. From the previous research, it has been known that miRNA has several roles in regulating apoptosis, proliferation, development, fat metabolism, stress response, and tumorigenesis.
The miRNA is short in length and has the ability to control the expression of the post-transcriptional genes. On this topic, any research has not been conducted previously. Through this research, the identifications of the effective and potent targets have been performed to activate the interactions between the host-pathogen. For this research, in-silico-related methods have been followed which has a significant role in studying the role of the human miRNA over “SARS-CoV2”. For this research, the genomes have been gathered from various geographical locations to recognize the notable host miRNA targets. This research will help to identify the relationship between the host and the pathogen. This research will give a strategy for antiviral activity and also help to evaluate the interactions network.
For conducting this research, the viral genome was examined for hairpin-like structures of miRNA through the “Vmir visualizer”. All viral hairpin fragment has been lined up with microRNA and recognized as target miRNA. Through the RNA hybrid tool, a favorable hybridization has been performed between viral miRNA and target microRNA. The output of this hybridization has been classified with regard to pattern and pairing energy. With the help of an online tool Mature Bayes, the mature miRNA has been recognized from the sequences of pre-miRNA (Zhang, et al. 2021). The potent miRNA has been also selected through this research. For predicting the pre-miRNA secondary structure, the RNAfold web server has been used. To evaluate the biological process, cellular components, and the molecular function of the targeted genes, PANTHER classification system. This research will help to recognize the role of the necessary genes for the replication and survival of the virus within the host cytoplasm.
Through this study, the involvement of genes within the condition of the pathogen has not been monitored. The identification of the novel miRNA, “SARS-CoV2” has been used as the initial aim of this research. In this research, some ZIKA miRNA has also been identified which have a relation to cell communication, regulation of the immune system, and the process of the cell cycle. Through this research, the author has predicted more than twenty viral miRNA against the human genome. In this research, the author has used several bioinformatics tools for conducting this research (Schoolmeesters, et al. 2019). The author has suspected that miRNA has an important role in evaluating the relationship between the host and the pathogen. In this experiment, hsa-mir-147b, hsa-mir-1-3p, and has-mir-325 have been found which helped to recognize the virus “SARS-CoV2” miRNA.
Based on acquired data, the author has established a method of “SARS-CoV2” through the use of miRNA. After entering into the cytoplasm of the host cell, “SARS-CoV2” discharges its gnomic RNA and uses the host system for its existence and replications. This research does not provide enough evidence over the identifications of miRNA for evaluating more details on the viral replication process.
The author has performed this research to understand the role of microRNA in the development of cardiac and skeletal muscle. MicroRNA is non-coding RNA and was recently determined. It can negatively control the expressions of the gene through the degradation of target mRNA and translational repression. It has been monitored that miRNA can show tissue-specific manner and can be exhibited within skeletal and cardiac muscles. In this research, the author has set focused on the role of miRNA in muscle development (Klemmt, and Starzinski-Powitz, 2018). Existing evidence has illustrated that muscle miRNA has a significant role in the control of muscle proliferation and the process of differentiation. In the case of muscle specification and early myogenesis, miRNA does not play a significant role. If miRNA does not work properly then the muscle-related disease has occurred e.g cardiac hypertrophy. Mutation in the target site of miRNA within the myostatin gene triggers the down regulations of the targeted protein. For this research, miRNA has been used as a regulator of muscle biology and will be used as novel therapeutic targets for muscle-related diseases in humans.
In their journal, they describe the critical role the functional profiling reveals for miRNA in the differentiation of the Mesenchymal stem cells of humans. Mesenchymal stem cells are based on therapeutic strategies in the injured tissue. The human MS cells are isolated from the bone marrow and these MS cells are differentiated by the osteogenic pathway. The determination of the cell-fate regulation is not understood. This report helps to recognize the role of microRNAs, the regulator of gene expression through inhibit the translation process and stimulating the degradation process of the mRNAs. For conducting this research they employed inhibitors of miRNA for evaluating the action of miRNA in the previous osteogenic differentiation of the mesenchymal stem cells of humans (Marí-Alexandre, et al. 2019). They innovate that -27a, miR-148b, and -489 are very essential for regulation. MiR-489 and miR-27a are down-regulated whereas miR-148b is up-regulated. The modulation of the miRNA initiated when the absence of another kind of external factor restored the osteogenic potential in the human MS cells.
The “mesenchymal stem cells” of humans are categorized as non-hematopoietic type cells. Adult bone marrow is derived from the “human mesenchymal stem cells” and then isolated the cell and then expand into the culture. These cells are differentiated and form different kinds of tissues that include cartilage, bone, other tissues, adipose, tendon, etc. the specific kind of tissue differentiation in the “human mesenchymal stem cells” is the multi-stage process. In this process, each step is associated with a specific type of marker. The early diagnosis is accompanied by the enhancement of the activity of the alkaline phosphate and induction of the specific type of biomarkers that include SPP1. MiRNAs regulate the appearance of the genes through the inhibition of the translation and prompt the degradation of the mRNA. For conducting this research hundreds of miRNAs have been identified by the experiment. These miRNAs regulate 30% of the protein-coding genes from the genome of humans. It highlights the significance of the expression of the gene. This study indicates the involvement of the miRNA in the various cell fates like a muscle, and neural. The current methodology recognizes miRNA and its focuses on the miRNA level in the cell type. The expression of the miRNA is vary within the cell. The role of the miRNA in osteogenesis obtain by the screening of the miRNA, and it modulates the endogenous level of the miRNA during“human mesenchymal stem cells” osteogenesis. In this research study -27a, hsa-miR-148b, -489 regulate the cell fates of osteogenesis. It has been found that specific miRNA affects cellular differentiation (Huang, et al. 2019). To determine the resulting miRNA regulates the differentiation of the osteogenesis. The activity of the alkaline phosphate makes osteogenic differentiation. It adjuncts the activity of the miRNA that induced the differentiation of the hMSC in the absence of the other stimuli. It rescues the osteogenic potential by alternating the activity of miRNA. The biological function of miRNA is unknown in cell proliferation, and molecular regulation. The death of the cells has been demonstrated. The critical regulatory factors are miR-148b, -489, and -27a. It affects cellular physiology. Human -27b, and miR-27a differ from the 2 nucleotide position. MiR-27b and miR-148 are excluded in the future research process. The expression -148b and miR-27a changed and they are correlated with the osteogenesis differentiation. The expression of the miR-489 was recognized very low level in the MS cells. The miR-125b and miR-26a play a crucial role in the regulation of the “osteogenic differentiation” in the human cell. And ST2 cell of the mouse. These 3 miRNAs play an important role in the osteogenic differentiation of the mechyamal cells of the bone marrow of humans. This analysis predicted the gene from the kidney, bone, and liver by the alkaline phosphatase. This data is suggested 2 miRNAs that regulate the upstream of SPP1 and APL. RUNX, PPIB, and Spp1 expressions were determined by the branched DNA assay. This GAPDH is used in the housekeeping gene expression for normalization purposes. Functional profiling plays a critical role in miRNA in the differentiation of the stem cells of humans.
According to the author, the mesenchymal stem cells, the osteogenic process is a very complex process. It is regulated by numerous factors that include microRNAs. In this research study, the preliminary data shows the endogenous expression of miR-20a. During osteogenic differentiation The endogenous miR-20a increase. The other expressions are3 obsolete. They regulate BMP4, BMP2, Osx, OPN, and OCN (Xu, et al. 2018). It elevated the adipocyte markers, and osteoblast antagonists, Crim1, and Bambi are downregulated. MiR-20a plays a significant role in osteoblast differentiation. In their research study, they showed that miR-20a was promoted in the osteogenic differentiation through the upregulation of the “BMP/Runx2 signaling”. For conducting this research they analyze bioinformatics and predict PPARy, Crim1, and Bambi. Here in this research PPRAy act as a negative regulator. That help to regulate BMP/Runx2 signal. Crim1 and Bambi play an antagonistic role in the BMP pathway. Quantitative RT-PCR and western blot methods are used during this examination. This assay enhanced crim1, PPARy by the specific kind of siRNAs. They concluded that miR-20a plays osteogenesis in the human mesenchymal stem cells in the co-regulatory pattern by the PPARy, Crim1, and Bambi.
The role miRNA has been evaluated through the given journals. The role of microRNA in the development of cardiac and skeletal muscle has been discussed in this sections. MiRNA has an important role in evaluating the relationship between the host and the pathogen and it has been also discussed in this sections. In this sections, the functions of miRNA has been discussed through various journals. The regulation of miRNA also has been discussed here.
Conclusions
Introduction
Through this research, the role of miRNA as a “biomarker” for the discovery of the disease endometriosis has been evaluated. Endometriosis is a systematic disease. Due to this disease, women reproductive-aged face several issues related to chronic pelvic pain, subfertility, and painful periods. More than forty types of miRNA were present for a diagnosis of this disease. Only a few miRNAs can be expressed as the control for endogenous miRNA. miRNA participated in pathological processes such as angiogenesis, migration, and cell proliferation. This research will help to evaluate the systematic review of the role of miRNA in the treatments of endometriosis (Staicu, et al, 2020). Endometriosis has similarities with reproductive disease and can spread into other distant organs. This research will help to know about the risks of endometriosis and also help to know that this disease can increase the risks of developing other types of cancer in the human body. The data has been measured through the use of Prisma software and it helps to analyze the role of miRNA in the disease endometriosis. The abnormalities of miRNA also enhance the occurrence of various types of cancers in the human body. This research has significant value for understanding the role of different types of miRNA in the treatment of endometriosis.
Linking with objectives
The role of miRNA in the identification of pathophysiology of endometriosis
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are little noncoding RNAs that can control quality articulation. They are involved in cell growth and differentiation, the immune system, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis, among other physiological processes.
From the different research study it has explained miRNAs are dysregulated in endometrial tissues from patients with endometriosis. By targeting mRNA molecules for degradation or translational repression, miRNAs can control gene expression.miRNA dysregulation in endometriosis can lead to the altered expression of target genes, which can lead to the abnormal growth of endometrial tissues.
From the different research study it has explained miRNAs may also it is associated in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis. Endometriosis is often associated with the inflammation which is very critical, which can lead to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Different researchs have shown that miRNAs are associated in the regulation of cytokine production, miRNAs play a role in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis.
Furthermore, miRNAs associated in the development of “endometriosis-related pain”. Endometriosis is involve the chronic pelvic pain, which can be difficult to treat. MiRNAs act as an onset of endometriosis-related pain, as studies have demonstrated that miRNAs regulate pain pathways.
In conclusion, miRNAs play crucial performanmce in the “pathophysiology of endometriosis”. miRNA dysregulation can lead to the altered expression of target genes, which can lead to the abnormal growth of endometrial tissues. In addition, miRNAs may be involved in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis and the development of endometriosis-related pain. As such, miRNAs may be useful for the identification of endometriosis and the development of new therapies.
The expression of miRNA to identify the gene expression of the pathogenesis of endometriosis
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are little noncoding RNAs that can control quality articulation. They are involved in cell growth and differentiation, the immune system, inflammation, and disease pathogenesis, among other physiological processes.
From the different research study it has explained miRNAs are dysregulated in endometrial tissues from patients with endometriosis. By targeting mRNA molecules for degradation or translational repression, miRNAs can control gene expression.miRNA dysregulation in endometriosis can lead to the altered expression of target genes, which can lead to the abnormal growth of endometrial tissues.
From the different research study it has explained miRNAs may also it is associated in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis. Endometriosis is often associated with the inflammation which is very critical, which can lead to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Different researchs have shown that miRNAs are associated in the regulation of cytokine production, miRNAs play a role in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis.
Furthermore, miRNAs associated in the development of “endometriosis-related pain”. Endometriosis is involve the chronic pelvic pain, which can be difficult to treat. MiRNAs act as an onset of endometriosis-related pain, as studies have demonstrated that miRNAs regulate pain pathways.
In conclusion, miRNAs play crucial performanmce in the “pathophysiology of endometriosis”. miRNA dysregulation can lead to the altered expression of target genes, which can lead to the abnormal growth of endometrial tissues. In addition, miRNAs may be involved in the inflammatory process associated with endometriosis and the development of endometriosis-related pain. As such, miRNAs may be useful for the identification of endometriosis and the development of new therapies.
Detection of ovarian cancer through the use of miRNA as a biomarker
MiRNA (microRNA) is a “small non-coding RNA molecule” that is control the expression of the gene at a “post-transcriptional level”. They have been studied extensively and have been found to be altered in various cancer types, including ovarian cancer. MiRNA molecules are able to bind to mRNA, leading to either the degradation or inhibition of gene transcription, thus resulting in changes to protein production. It is basically use as a biomarkers for recognize the ovarian cancer cells.
Identifying miRNA molecules that are specifically associated with ovarian cancer is essential for the development of an effective miRNA-based biomarker. This research recognize the m-RNA cells of upregulated in ovarian cancer samples. “These miRNAs, including miR-145, miR-125b-2, and miR-223”, are known to be involved in the “regulation of cell cycle”, apoptosis of the cells, and tumor progression of the cell, respectively. These miRNAs can be used as “biomarkers for the early detection of ovarian cancer”, allowing for the implementation of early intervention strategies. In addition to the identification of miRNAs that are associated with ovarian cancer, the development of a miRNA-based biomarker requires validation of the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the biomarker. This can be done through the use of various analytical methods, such as quantitative PCR. By testing a panel of miRNAs in a set of ovarian cancer samples, the ability of these miRNAs to differentiate ovarian cancer from benign tumors can be determined. Once a miRNA-based biomarker can be used in combination with other clinical and imaging tests to provide a more accurate diagnosis. It can also be used to assess treatment response and detect disease recurrence, thus allowing for timely interventions. Overall, miRNA-based biomarkers are a promising tool for the detection of ovarian cancer. By identifying miRNAs that are specifically associated with ovarian cancer and validating their accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, a reliable and effective miRNA-based biomarker can be developed for the early detection of ovarian cancer.
Future perspectives
Endometriosis is a disease of reproductive age and can be diagnosed with the help of laparoscopy. In the current scenario, miRNA has been discovered to use as a modulator for gene expression. From the previous research, it has been known that miRNA has a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases and is preferred as the potential biomarker for endometriosis. miRNA has an important role as a representative of various diseases and it delivers more information about the diseases during the study of the expression of various mRNA. miRNA work as effective biomarkers for various post-translational modifications and structure of the protein.
miRNA has originated as a powerful regulator of gene expression and it can be used for various investigations of various diseases. This help this systematic review to complete timely. In this research, the isolation of miRNA triggers big challenges in endometriosis research. In the future, it should be applied with a new tool for the isolation of miRNA. miRNA can be successfully isolated by following LCM technique and this isolated miRNA will give high results within the analysis process. For future perspectives, the isolation and analysis process should be performed on specific cells of the endometrium and lesions. The study of endometriosis needs a highly standardized sample of miRNA and the phenotype data of the endometriosis patients.
The data of endometriosis patients should be collected related to the history of past endometriosis surgery, hormone treatment, and through the features of the menstrual cycle. The data handling process should be improved for conducting the systemic review of miRNA in endometriosis (Vishnubhatla, 2020). The harmonized data collection will be beneficial for future research on this topic. This will open new possibilities for performing a large-scale study on this topic and it will also enhance the liability of future findings. This will also help to define the important role of miRNA in endometriosis pathogenesis which was not previously covered. The use of miRNAs for endometriosis has recently been gaining traction as a potential therapeutic approach. By preventing the translation of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), miRNAs, which are “small noncoding RNAs”, are able to maintain the expression of the gene. As a result, certain proteins involved in pathological processes like inflammation and angiogenesis may be suppressed. miRNAs have been proposed as a potential treatment for endometriosis due to their ability to alter gene expression.
Initial research has demonstrated the potential of miRNAs to suppress the expression of genes involved in endometriosis-related processes. For example, MMPSs suppress the breakdown of extracellular matrix and this is control by mIR-21.This could lead to a reduction in inflammation caused by endometriosis. Similarly, miR-145 has been demonstrated to suppress the expression of “vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)” which has involvement in the establishment of “new blood vessels”, thus potentially leading to a decrease in endometrial lesions.
Despite the promising initial research, there is still much to be done in order to fully understand the potential of miRNAs for the treatment of endometriosis. For example, further research is needed to determine the effectiveness of miRNA-based therapies in vivo. Additionally, the mechanism of action of miRNAs in endometriosis needs to be fully elucidated in order to develop better-targeted therapies. Finally, more studies are needed to identify the potential side effects of miRNA-based therapies.
In conclusion, there is a great deal for the application of miRNAs for the treatment of endometriosis. However, more research is required to fully comprehend the safety and efficacy of miRNA-based therapies. Mirna therapeutics' in vivo efficacy, miRNA mechanisms of action in endometriosis, and potential side effects should therefore be the primary focus of research. MiRNAs may be a safe and effective treatment option for endometriosis, according to additional research.
Conclusion
This research has been performed through a systematic review of the role of miRNA in endometriosis. For conducting this research, the data on the role of miRNA has been taken from various journals. With the help of journals, the role of various kinds of miRNA has been evaluated. miR-20a is one of the known miRNA which played a significant role in the development of human organs and tissue. This research helped to evaluate the role of miR-20a in monocytic cell differentiation and maturation. The role of miR-148a and miR-199a in negative regulation over the post-translational has been discussed through this research. miRNA has several roles in the regulation of protein-coding genes of the human genome has been analyzed. From the existing journal, the role of miRNA in the determination of muscle and neuronal cells has been evaluated. This research will help to know the role of various types of miRNA in detecting the disease endometriosis. The systematic review of miRNA on endometriosis help to perform the comparison of various types of miRNA which regulate and inhibit ovarian cancer.
Reference
Journals
Agrawal, S., Tapmeier, T.T., Rahmioglu, N., Kirtley, S., Zondervan, K.T. and Becker, C.M., 2018. The miRNA mirage: how close are we to finding a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in endometriosis? A systematic review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), p.599.
Agrawal, S., Tapmeier, T.T., Rahmioglu, N., Kirtley, S., Zondervan, K.T. and Becker, C.M., 2018. The miRNA mirage: how close are we to finding a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in endometriosis? A systematic review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), p.599.
Anastasiu, C.V., Moga, M.A., Elena Neculau, A., Bălan, A., Scârneciu, I., Dragomir, R.M., Dull, A.M. and Chicea, L.M., 2020. Biomarkers for the noninvasive diagnosis of endometriosis: state of the art and future perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(5), p.1750.
Azam, I.N.A., Wahab, N.A., Mokhtar, M.H., Shafiee, M.N. and Mokhtar, N.M., 2022. Roles of microRNAs in Regulating Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis. Life, 12(9), p.1321.
Azam, I.N.A., Wahab, N.A., Mokhtar, M.H., Shafiee, M.N. and Mokhtar, N.M., 2022. Roles of microRNAs in Regulating Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Endometriosis. Life, 12(9), p.1321.
Aziz, N.B., Mahmudunnabi, R.G., Umer, M., Sharma, S., Rashid, M.A., Alhamhoom, Y., Shim, Y.B., Salomon, C. and Shiddiky, M.J., 2020. MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer and recent advances in the development of microRNA-based biosensors. Analyst, 145(6), pp.2038-2057.
Bast, R.C., Lu, Z., Han, C.Y., Lu, K.H., Anderson, K.S., Drescher, C.W. and Skates, S.J., 2020. Biomarkers and Strategies for Early Detection of Ovarian CancerEarly Detection of Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 29(12), pp.2504-2512.
Bendifallah, S., Dabi, Y., Suisse, S., Delbos, L., Poilblanc, M., Descamps, P., Golfier, F., Jornea, L., Bouteiller, D., Touboul, C. and Puchar, A., 2022. Endometriosis Associated-miRNome Analysis of Blood Samples: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics, 12(5), p.1150.
Bendifallah, S., Suisse, S., Puchar, A., Delbos, L., Poilblanc, M., Descamps, P., Golfier, F., Jornea, L., Bouteiller, D., Touboul, C. and Dabi, Y., 2022. Salivary MicroRNA Signature for Diagnosis of Endometriosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), p.612.
Bilgili, G., Verdi, H., Zeyneloglu, B.H., Tohma, Y.A. and Atac, F.B., 2021. The Role of miRNA in Endometriosis.
Chen, S.N., Chang, R., Lin, L.T., Chern, C.U., Tsai, H.W., Wen, Z.H., Li, Y.H., Li, C.J. and Tsui, K.H., 2019. MicroRNA in ovarian cancer: biology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic opportunities. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(9), p.1510.
Chen, Z., Guo, X., Sun, S., Lu, C. and Wang, L., 2020. Serum miR-125b levels associated with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) development and treatment responses. Bioengineered, 11(1), pp.311-317.
Coutinho, L.M., Ferreira, M.C., Rocha, A.L.L., Carneiro, M.M. and Reis, F.M., 2019. New biomarkers in endometriosis. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 89, pp.59-77.
da Silva, L.F.I., Da Broi, M.G., da Luz, C.M., da Silva, L.E.C.M., Ferriani, R.A., Meola, J. and Navarro, P.A., 2021. miR-532-3p: a possible altered miRNA in cumulus cells of infertile women with advanced endometriosis. Reproductive BioMedicine Online, 42(3), pp.579-588.
Dabi, Y., Suisse, S., Jornea, L., Bouteiller, D., Touboul, C., Puchar, A., Daraï, E. and Bendifallah, S., 2022. Clues for Improving the Pathophysiology Knowledge for Endometriosis Using Serum Micro-RNA Expression. Diagnostics, 12(1), p.175.
Gebert, L.F. and MacRae, I.J., 2019. Regulation of microRNA function in animals. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, 20(1), pp.21-37.
Grayson, K., Gregory, E., Khan, G. and Guinn, B.A., 2019. Urine biomarkers for the early detection of ovarian cancer–are we there yet?. Biomarkers in cancer, 11, p.1179299X19830977.
Huang, X., Zhong, R., He, X., Deng, Q., Peng, X., Li, J. and Luo, X., 2019. Investigations on the mechanism of progesterone in inhibiting endometrial cancer cell cycle and viability via regulation of long noncoding RNA NEAT1/microRNA‐146b‐5p mediated Wnt/β‐catenin signaling. IUBMB life, 71(2), pp.223-234.
Javadi, M., Rad, J.S., Farashah, M.S.G. and Roshangar, L., 2021. An insight on the role of altered function and expression of exosomes and microRNAs in female reproductive diseases. Reproductive Sciences, pp.1-13.
Kiesel, L. and Sourouni, M., 2019. Diagnosis of endometriosis in the 21st century. Climacteric, 22(3), pp.296-302.
Klemmt, P.A. and Starzinski-Powitz, A., 2018. Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of endometriosis. Current women's health reviews, 14(2), pp.106-116.
Kolanska, K., Bendifallah, S., Canlorbe, G., Mekinian, A., Touboul, C., Aractingi, S., Chabbert-Buffet, N. and Daraï, E., 2021. Role of miRNAs in normal endometrium and in endometrial disorders: comprehensive review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(16), p.3457.
Kumari, P., Sharma, I., Saha, S.C., Srinivasan, R. and Minhas, P., 2021. Diagnostic potential of differentially regulated microRNAs among endometriosis, endometrioid ovarian cancer, and endometrial cancer. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics, 17(4), p.1003.
Laganà, A.S., Garzon, S., Götte, M., Viganò, P., Franchi, M., Ghezzi, F. and Martin, D.C., 2019. The pathogenesis of endometriosis: molecular and cell biology insights. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(22), p.5615.
Li, L., Guo, X., Liu, J., Chen, B., Gao, Z. and Wang, Q., 2021. The role of miR-27b-3p/HOXA10 axis in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Annals of Palliative Medicine, 10(3), pp.3162-3170.
Li, M., Peng, J., Shi, Y. and Sun, P., 2020. miR-92a promotes progesterone resistance in endometriosis through PTEN/AKT pathway. Life sciences, 242, p.117190.
Loginov, V.I., Pronina, I.V., Burdennyy, A.M., Filippova, E.A., Kazubskaya, T.P., Kushlinsky, D.N., Utkin, D.O., Khodyrev, D.S., Kushlinskii, N.E., Dmitriev, A.A. and Braga, E.A., 2018. Novel miRNA genes deregulated by aberrant methylation in ovarian carcinoma are involved in metastasis. Gene, 662, pp.28-36.
Maier, I.M. and Maier, A.C., 2021. miRNAs and lncRNAs: potential non-invasive biomarkers for endometriosis. Biomedicines, 9(11), p.1662.
Marí-Alexandre, J., Carcelén, A.P., Agababyan, C., Moreno-Manuel, A., García-Oms, J., Calabuig-Fariñas, S. and Gilabert-Estellés, J., 2019. Interplay between microRNAs and oxidative stress in ovarian conditions with a focus on ovarian cancer and endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), p.5322.
Márton, É., Lukács, J., Penyige, A., Janka, E., Hegedüs, L., Soltész, B., Méhes, G., Póka, R., Nagy, B. and Szilágyi, M., 2019. Circulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated miRNAs are promising biomarkers in ovarian cancer. Journal of biotechnology, 297, pp.58-65.
McAlarnen, L.A., Gupta, P., Singh, R., Pradeep, S. and Chaluvally-Raghavan, P., 2022. Extracellular vesicle contents as noninvasive biomarkers in ovarian malignancies. Molecular Therapy-Oncolytics.
Misir, S., Hepokur, C., Oksasoglu, B., Yildiz, C., Yanik, A. and Aliyazicioglu, Y., 2021. Circulating serum miR-200c and miR-34a-5p as diagnostic biomarkers for endometriosis. Journal of Gynecology Obstetrics and Human Reproduction, 50(4), p.102092.
Moga, M.A., Bălan, A., Dimienescu, O.G., Burtea, V., Dragomir, R.M. and Anastasiu, C.V., 2019. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis and endometriosis-related ovarian cancer—An overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), p.735.
Moga, M.A., Bălan, A., Dimienescu, O.G., Burtea, V., Dragomir, R.M. and Anastasiu, C.V., 2019. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis and endometriosis-related ovarian cancer—An overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), p.735.
Moga, M.A., Bălan, A., Dimienescu, O.G., Burtea, V., Dragomir, R.M. and Anastasiu, C.V., 2019. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis and endometriosis-related ovarian cancer—An overview. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), p.735.
Ni, L., Tang, C., Wang, Y., Wan, J., Charles, M.G., Zhang, Z., Li, C., Zeng, R., Jin, Y., Song, P. and Wei, M., 2022. Construction of a miRNA-Based Nomogram Model to Predict the Prognosis of Endometrial Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(7), p.1154.
Penyige, A., Márton, É., Soltész, B., Szilágyi-Bónizs, M., Póka, R., Lukács, J., Széles, L. and Nagy, B., 2019. Circulating miRNA profiling in plasma samples of ovarian cancer patients. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(18), p.4533.
Perricos, A., Proestling, K., Husslein, H., Kuessel, L., Hudson, Q.J., Wenzl, R. and Yotova, I., 2022. Hsa-mir-135a Shows Potential as A Putative Diagnostic Biomarker in Saliva and Plasma for Endometriosis. Biomolecules, 12(8), p.1144.
Raja, M.H.R., Farooqui, N., Zuberi, N., Ashraf, M., Azhar, A., Baig, R., Badar, B. and Rehman, R., 2021. Endometriosis, infertility and MicroRNA's: A review. Journal of Gynecology Obstetrics and Human Reproduction, 50(9), p.102157.
Rekker, K., Tasa, T., Saare, M., Samuel, K., Kadastik, Ü., Karro, H., Götte, M., Salumets, A. and Peters, M., 2018. Differentially-expressed miRNAs in ectopic stromal cells contribute to endometriosis development: the plausible role of miR-139-5p and miR-375. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(12), p.3789.
Ren, X., Zhang, H., Cong, H., Wang, X., Ni, H., Shen, X. and Ju, S., 2018. Diagnostic model of serum miR-193a-5p, HE4 and CA125 improves the diagnostic efficacy of epithelium ovarian cancer. Pathology & Oncology Research, 24(4), pp.739-744.
Ritter, A., Hirschfeld, M., Berner, K., Jaeger, M., Grundner-Culemann, F., Schlosser, P., Asberger, J., Weiss, D., Noethling, C., Mayer, S. and Erbes, T., 2020. Discovery of potential serum and urine-based microRNA as minimally-invasive biomarkers for breast and gynecological cancer. Cancer Biomarkers, 27(2), pp.225-242.
Sahin, C., Mamillapalli, R., Yi, K.W. and Taylor, H.S., 2018. micro RNA Let‐7b: A Novel treatment for endometriosis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 22(11), pp.5346-5353.
Sarma, A., Phukan, H., Halder, N. and Madanan, M.G., 2020. An in-silico approach to study the possible interactions of miRNA between human and SARS-CoV2. Computational biology and chemistry, 88, p.107352.
Schoolmeesters, A., Eklund, T., Leake, D., Vermeulen, A., Smith, Q., Force Aldred, S. and Fedorov, Y., 2019. Functional profiling reveals critical role for miRNA in differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PloS one, 4(5), p.e5605.
Staicu, C.E., Predescu, D.V., Rusu, C.M., Radu, B.M., Cretoiu, D., Suciu, N., Crețoiu, S.M. and Voinea, S.C., 2020. Role of microRNAs as clinical cancer biomarkers for ovarian cancer: a short overview. Cells, 9(1), p.169.
Sun, D., Wang, Y., Wang, L. and Guo, X., 2021. MicroRNA-342 promotes the malignant-like phenotype of endometrial stromal cells via regulation of annexin A2. Analytical Cellular Pathology, 2021.
Tian, Z., Chang, X.H., Zhao, Y. and Zhu, H.L., 2020. Current biomarkers for the detection of endometriosis. Chinese Medical Journal, 133(19), pp.2346-2352.
Ulisses Monnaka, V., Hernandes, C., Heller, D. and Podgaec, S., 2021. Overview of miRNAs for the non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis: evidence, challenges and strategies. A systematic review. Einstein (16794508), 19.
Wang, D., Luo, Y., Wang, G. and Yang, Q., 2019. Circular RNA expression profiles and bioinformatics analysis in ovarian endometriosis. Molecular genetics & genomic medicine, 7(7), p.e00756.
Wang, Q., Xu, K., Tong, Y., Dai, X., Xu, T., He, D. and Ying, J., 2020. Novel miRNA markers for the diagnosis and prognosis of endometrial cancer. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 24(8), pp.4533-4546.
Wang, X., Parodi, L. and Hawkins, S.M., 2021. Translational Applications of Linear and Circular Long Noncoding RNAs in Endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), p.10626.
Wu, M. and Zhang, Y., 2021. MiR-182 inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and inflammation of endometrial stromal cells through deactivation of NF-κB signaling pathway in endometriosis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 476(3), pp.1575-1588.
Wu, M.H., Hsiao, K.Y. and Tsai, S.J., 2019. Hypoxia: The force of endometriosis. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, 45(3), pp.532-541.
Xu, X., Jia, S.Z., Dai, Y.I., Zhang, J.J., Li, X., Shi, J., Leng, J. and Lang, J., 2018. The relationship of circular RNAs with ovarian endometriosis. Reproductive Sciences, 25(8), pp.1292-1300.
Xu, X.X., Jia, S.Z., Dai, Y., Zhang, J.J., Li, X.Y., Shi, J.H., Leng, J.H. and Lang, J.H., 2018. Identification of circular RNAs as a novel biomarker for ovarian endometriosis. Chinese Medical Journal, 131(05), pp.559-566.
Yang, H., Hu, T., Hu, P., Qi, C. and Qian, L., 2021. miR‑143‑3p inhibits endometriotic stromal cell proliferation and invasion by inactivating autophagy in endometriosis. Molecular medicine reports, 23(5), pp.1-9.
Zhang, J., Baptista, I., Xia, P. and Singh, B., 2019. Endometriosis pathoetiology: The role of microRNAs in the dysregulation of endometrial functions. Reproductive and Developmental Medicine, 3(04), pp.247-251.
Zhang, J.F., Fu, W.M., He, M.L., Xie, W.D., Lv, Q., Wan, G., Li, G., Wang, H., Lu, G., Hu, X. and Jiang, S., 2021. MiRNA-20a promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by co-regulating BMP signaling. RNA biology, 8(5), pp.829-838.
Zhou, S., Huang, C., Wang, W. and Liu, J., 2021. MiR‐370‐3p inhibits the development of human endometriosis by downregulating EDN1 expression in endometrial stromal cells. Cell Biology International, 45(6), pp.1183-1190.
Zhou, X., Chen, Z., Pei, L. and Sun, J., 2021. MicroRNA miR-106a-5p targets forkhead box transcription factor FOXC1 to suppress the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of ectopic endometrial stromal cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Bioengineered, 12(1), pp.2203-2213.
Zhu, R., Nasu, K., Hijiya, N., Yoshihashi, M., Hirakawa, T., Aoyagi, Y. and Narahara, H., 2021. hsa-miR-199a-3p inhibits motility, invasiveness, and contractility of ovarian endometriotic stromal cells. Reproductive Sciences, 28(12), pp.3498-3507.
Zhuo, Z., Wang, C. and Yu, H., 2021. Plasma microRNAs can be a potential diagnostic biomarker for endometriosis. Ginekologia Polska.
Zuberi, M., Mir, R., Khan, I., Javid, J., Guru, S.A., Bhat, M., Sumi, M.P., Ahmad, I., Masroor, M., Yadav, P. and Vishnubhatla, S., 2020. The promising signatures of circulating microRNA-145 in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. MicroRNA, 9(1), pp.49-57.
Zubrzycka, A., Migdalska-Sęk, M., Jędrzejczyk, S. and Brzeziańska-Lasota, E., 2021. Circulating miRNAs related to Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transitions (EMT) as the new molecular markers in endometriosis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 43(2), pp.900-916.
Zubrzycka, A., Zubrzycki, M., Perdas, E. and Zubrzycka, M., 2020. Genetic, epigenetic, and steroidogenic modulation mechanisms in endometriosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), p.1309.
Zafari, N., Tarafdari, A.M., Izadi, P., Noruzinia, M., Yekaninejad, M.S., Bahramy, A. and Mohebalian, A., 2021. A panel of plasma miRNAs 199b-3p, 224-5p and Let-7d-3p as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for endometriosis. Reproductive Sciences, 28(4), pp.991-999.
Liang, S., Song, Z., Wu, Y., Gao, Y., Gao, M., Liu, F., Wang, F. and Zhang, Y., 2018. MicroRNA-27b modulates inflammatory response and apoptosis during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. The Journal of Immunology, 200(10), pp.3506-3518.
Sadri Nahand, J., Moghoofei, M., Salmaninejad, A., Bahmanpour, Z., Karimzadeh, M., Nasiri, M., Mirzaei, H.R., Pourhanifeh, M.H., Bokharaei‐Salim, F., Mirzaei, H. and Hamblin, M.R., 2020. Pathogenic role of exosomes and microRNAs in HPV‐mediated inflammation and cervical cancer: a review. International journal of cancer, 146(2), pp.305-320.
Bhandari, V., Hoey, C., Liu, L.Y., Lalonde, E., Ray, J., Livingstone, J., Lesurf, R., Shiah, Y.J., Vujcic, T., Huang, X. and Espiritu, S.M., 2019. Molecular landmarks of tumor hypoxia across cancer types. Nature genetics, 51(2), pp.308-318.
Ullmann, P., Nurmik, M., Begaj, R., Haan, S. and Letellier, E., 2019. Hypoxia-and MicroRNA-induced metabolic reprogramming of tumor-initiating cells. Cells, 8(6), p.528.
Zhihua, Y., Yulin, T., Yibo, W., Wei, D., Yin, C., Jiahao, X., Runqiu, J. and Xuezhong, X., 2019. Hypoxia decreases macrophage glycolysis and M1 percentage by targeting microRNA‐30c and mTOR in human gastric cancer. Cancer science, 110(8), pp.2368-2377.
Subramaniam, S., Jeet, V., Clements, J.A., Gunter, J.H. and Batra, J., 2019. Emergence of microRNAs as key players in cancer cell metabolism. Clinical chemistry, 65(9), pp.1090-1101.
Zhu, R., Nasu, K., Hijiya, N., Yoshihashi, M., Hirakawa, T., Aoyagi, Y. and Narahara, H., 2021. hsa-miR-199a-3p inhibits motility, invasiveness, and contractility of ovarian endometriotic stromal cells. Reproductive Sciences, 28(12), pp.3498-3507.
Chapron, C., Marcellin, L., Borghese, B. and Santulli, P., 2019. Rethinking mechanisms, diagnosis and management of endometriosis. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 15(11), pp.666-682.
Laganà, A.S., Garzon, S., Götte, M., Viganò, P., Franchi, M., Ghezzi, F. and Martin, D.C., 2019. The pathogenesis of endometriosis: molecular and cell biology insights. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(22), p.5615.
Shafrir, A.L., Farland, L.V., Shah, D.K., Harris, H.R., Kvaskoff, M., Zondervan, K. and Missmer, S.A., 2018. Risk for and consequences of endometriosis: a critical epidemiologic review. Best practice & research Clinical obstetrics & gynaecology, 51, pp.1-15.
Nabiel, Y., ELshahawy, H. and Mosbah, A., 2020. Intrauterine bacterial colonization and endometrial microRNA-17-5p levels in association to endometriosis: a study in an egyptian population. Immunological investigations, 49(6), pp.611-621.
Ravegnini, G., Gorini, F., De Crescenzo, E., De Leo, A., De Biase, D., Di Stanislao, M., Hrelia, P., Angelini, S., De Iaco, P. and Perrone, A.M., 2022. Can miRNAs be useful biomarkers in improving prognostic stratification in endometrial cancer patients? An update review. International Journal of Cancer, 150(7), pp.1077-1090.
Medvedev, M.V. and Pokrovenko, D.A., 2019. Modern view on the etiology, pathogenesis and possibilities of diagnostics of external genital endometriosis. Medicni perspektivi, 24(1), pp.21-30.
Marí-Alexandre, J., Carcelén, A.P., Agababyan, C., Moreno-Manuel, A., García-Oms, J., Calabuig-Fariñas, S. and Gilabert-Estellés, J., 2019. Interplay between microRNAs and oxidative stress in ovarian conditions with a focus on ovarian cancer and endometriosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), p.5322.
Karkia, R., Wali, S., Payne, A., Karteris, E. and Chatterjee, J., 2022. Diagnostic Accuracy of Liquid Biomarkers for the Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Endometrial Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 14(19), p.4666.
Song, M., Zhao, G., Sun, H., Yao, S., Zhou, Z., Jiang, P., Wu, Q., Zhu, H., Wang, H., Dai, C. and Wang, J., 2021. circPTPN12/miR-21–5 p/∆ Np63α pathway contributes to human endometrial fibrosis. Elife, 10, p.e65735.



