1. Introduction
1.1 Discussion on the Network
It states that the purpose of this research is to outline the design of a secure network for a small office environment. The increased use of digital solutions requires an overall robust and secure network to not only safeguard valuable data but also to ensure smooth operations. This document will delineate the requirements of the network, its components, and security measures needed in order to complete a more efficient and secure topology.
1.2 Overview of Network Design
In this section it provides information regarding the utilization of specific blocks such as there will be 40 wired PC stations and 12 wireless laptop stations that include web, email, DHCP, print, and domain controllers. DMZ will be configured in order to enhance security on public-facing services. The network will have firewalls, switches, a router, and access points for the wireless in building a safe and efficient topology.
2. Network Requirements
2.1 Device Specifications
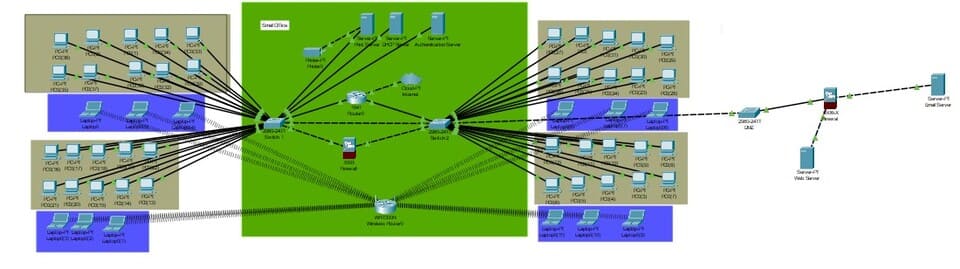
Figure 1: Device Specifications
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
The network will consist of a number of these critical devices to ensure high-performance and security operations. There will be 40 wired PCs connected using switches to ensure that data transfer is reliable. This will be complemented by 12 wireless laptops that will connect to the network wirelessly, giving sufficient freedoms to users with their mobility. Several servers will be included in the network to perform distinct functions (Allison et al.2022). The public website of the company would be hosted on the Web Server so that it could be accessed from outside. The Email Server would thus take up the responsibility of corporate email communications, making the ease of communication both internally and externally possible. A DHCP Server would be used to dynamically assign IP addresses to the devices connected on the network for efficient management of network resources. A Print Server would be used for printing tasks to deal with managing print jobs from users on the network. The Domain Controller will authenticate users and allow them permission to ensure safe access to the network. To keep the network free from attacks from external sources, firewalls will be implemented to be the pivotal layer of protection. The switches will serve to provide direct communication among the various devices, thus allowing for the more efficient transfer of data between them. The router connects the internal network to the internet, overseeing both incoming and outgoing traffic (Ahmed et al.2021). The WAP will offer a wireless connection to the laptops and this can serve as an added facilitation to access the network in a flexible way. The configuration developed is the one that guarantees a strong, secure, and efficient network environment.
2.2 Network Topology Overview
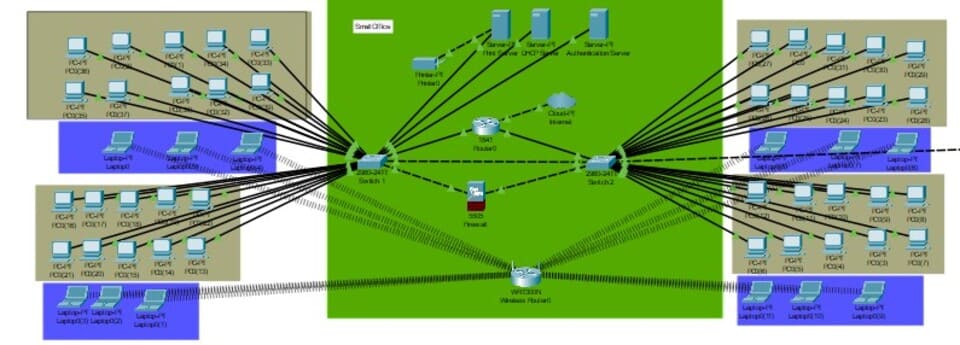
Figure 2: Network Topology Overview
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
The network topology will be a star layout, where every device connects to a central switch or router. This design makes it more reliable in that failure at one site doesn't take down the whole network (Hidayat et al.2024). The network will be divided mainly into two zones: the internal network and the DMZ. This is what allows public-facing and internal services to communicate securely.
3. Logical Network Diagram
3.1 Diagram Explanation
A logical network diagram created in Cisco Packet Tracer that can visually represent the architecture of the network. This network will include all the locations of the devices within the network: the router, switches, servers, and even firewalls. It will also be able to outline how the internal network connects to the DMZ and internet.
3.2 Device Placement Information
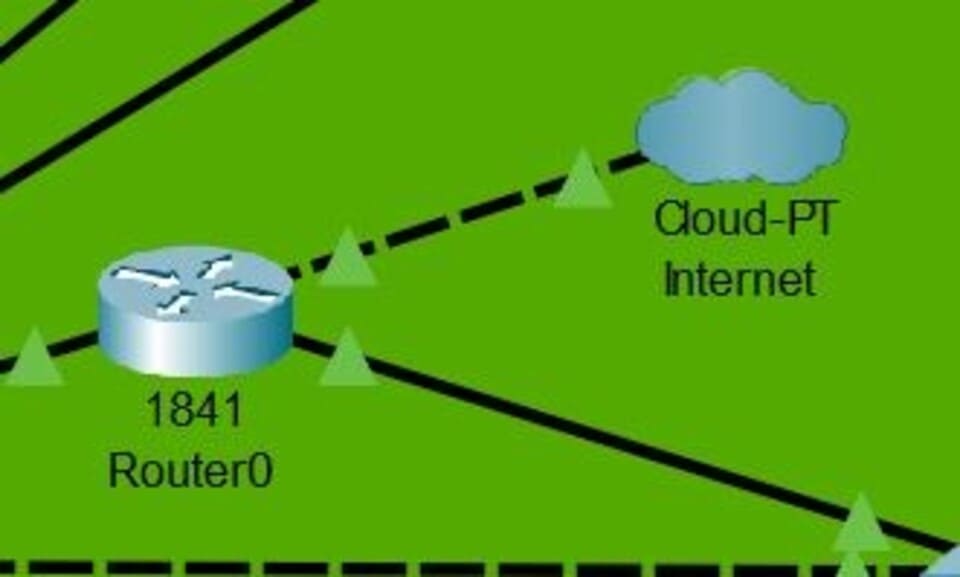
Figure 3: Cloud and Router used in the Model
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Cloud and Router: The Cloud and Router will be at the top because it can be considered as an internet gateway which would forward and route traffic back and forth in the internal network. It also states that the internet is coming from the Cloud.
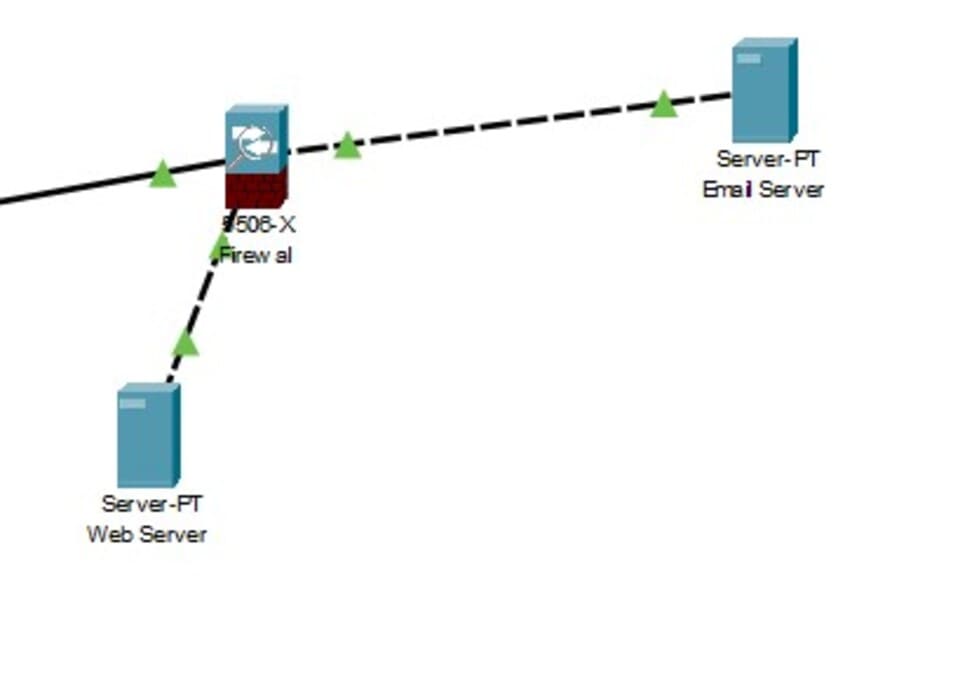
Figure 4: Firewall
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Firewalls: It states that there will be a DMZ-facing outward firewall that would protect the servers at the DMZ and an inward firewall that protects the internal network. The Email server and the Web server is connected with the DMZ through a Firewall.
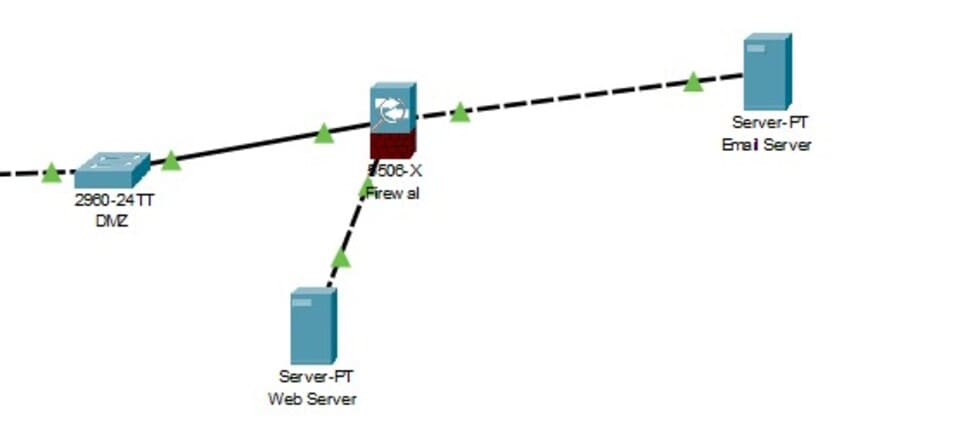
Figure 5: DMZ Server
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
DMZ Servers: The web and email servers are in the DMZ. It is protected so it is open to public access, but it still protects the internal network. It can also be noticed that an Email server and a Web server is connected with the DMZ.

Figure 6: Authentication Server
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Internal Servers: It is placed behind the internal firewall so that they are accessible only from the internal network.
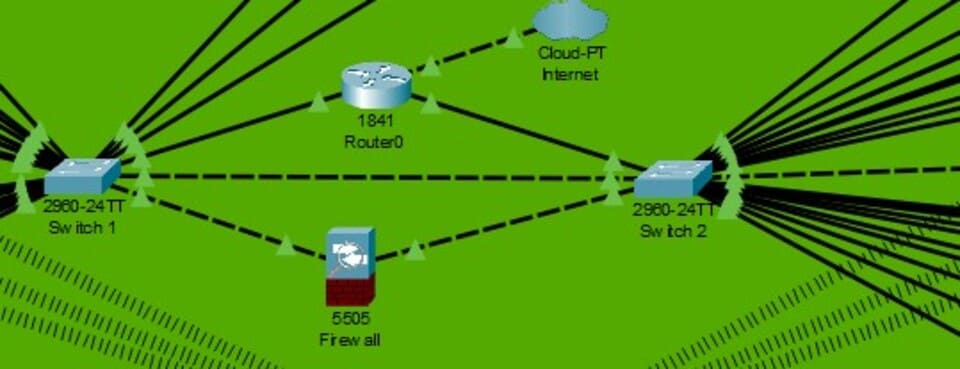
Figure 7: Switch
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Switches: It is placed below the internal firewall, and connects all wired devices, such as PCs and servers, within the network.

Figure 8: Wireless Router
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Wireless Access Point: It is located next to the switch, this facilitates wireless connectivity for laptops.
4. Network Components
4.1 Router
A router is a device that connects the internal network to the internet and controls traffic and data packet routing between internal and external networks. In this configuration, a suitable option would be the Cisco Packet Tracer software, which will provide sufficient throughput for the network traffic required.
4.2 Firewalls
The design of the network includes a crucial firewall in order to enhance security and manage traffic effectively. The Firewall is placed between the router and the DMZ, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic (Reddy et al.2020). This is an adequate position from which to protect the network against harmful external threats, including unauthorized access, malicious attacks, since it examines all data packets entering and exiting the network. Its purpose is to limit access to sensitive information and resources, hence improving the security posture of the network. The design of the firewall assures defense both on internal and external threats, providing maximum protection to crucial information and maintaining network integrity.
4.3 Servers
Figure 9: Web Server Configuration
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Web Server: It states that this is where the company's website is actually hosted and available to the public; placed in the DMZ, so access to this server can be allowed while the internal network is safeguarded.
Figure 10: Email Server
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Email Server: The email server maintains all emails. It is along with all the others, it is placed in the DMZ so that access from the public can be allowed.
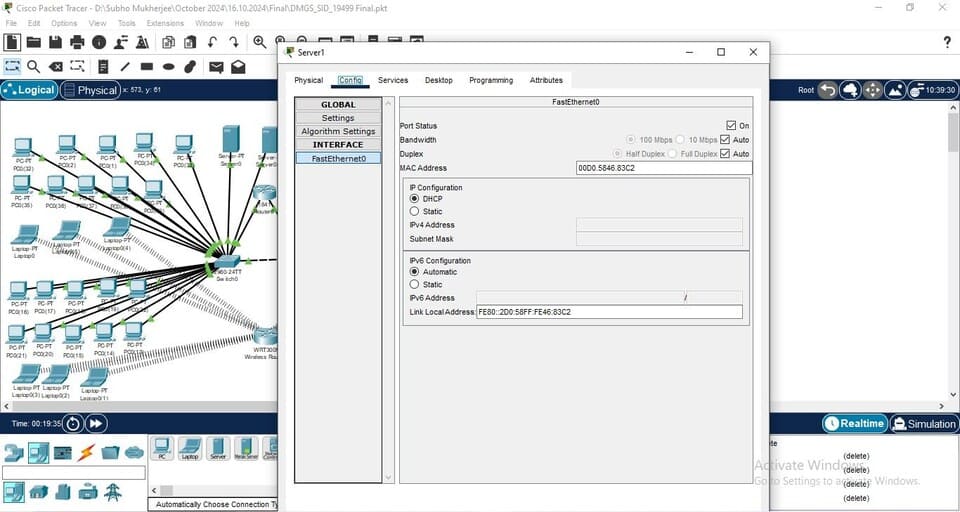
Figure 11: DHCP Server
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
DHCP Server: Dynamic assignment of an IP address to various devices on the internal network is done by DHCP server. This enables proper management of the network.
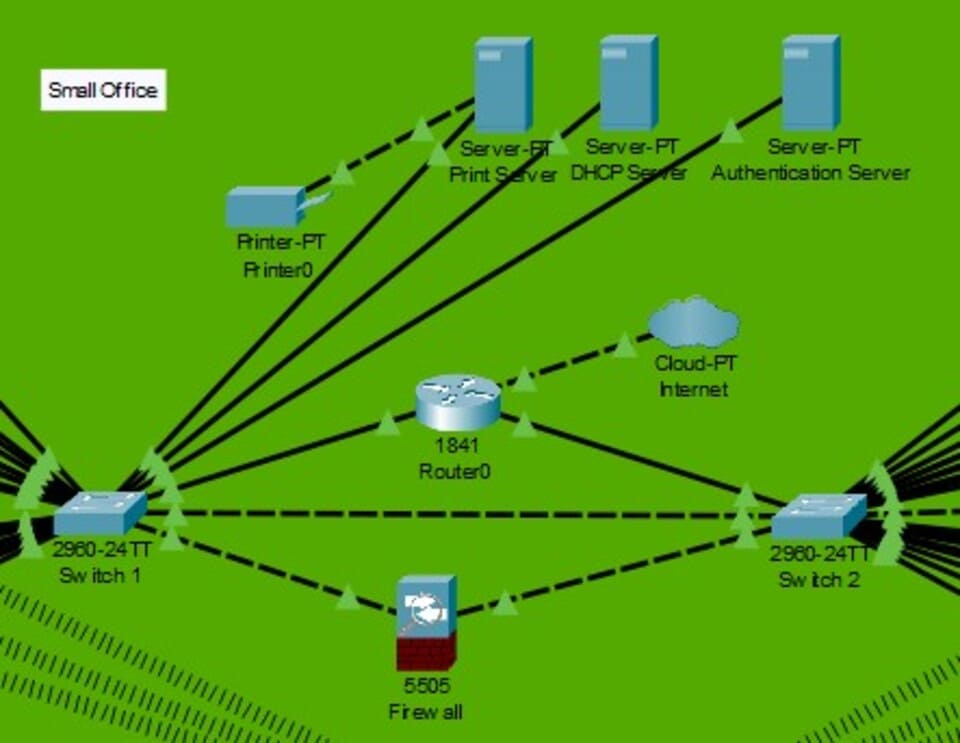
Figure 12: Print Server
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Print Server: This server consolidates print jobs from inside users, making it easy to manage printing resources efficiently.
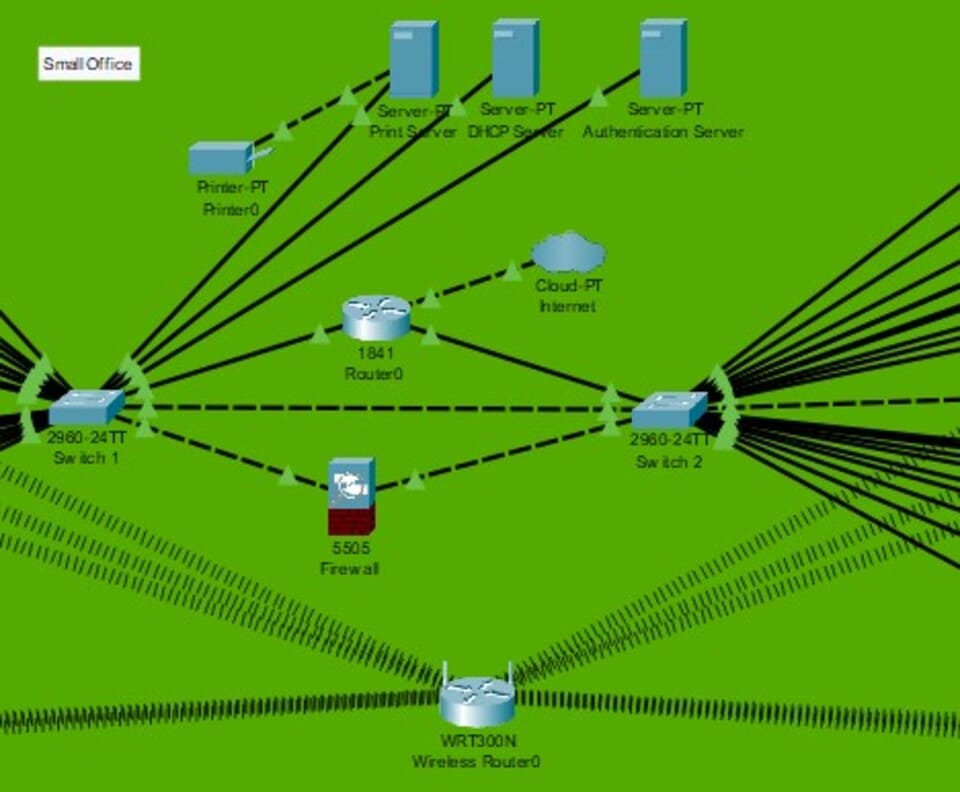
Figure 13: Domain Controller
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Domain Controller: It centralizes managing access to resources in the network while authenticating its users and managing permissions for safe access to resources within the network. It can be noticed in the connections that the print server, DHCP server, Authentication Server are connected to the switch, whereas a pritner is also connected with the print server.
4.4 Switches
It states that two switches are used in connecting PCs and servers; it provides a way of communication with devices that is facilitated to ensure transferring data within the internal network effectively.
4.5 Wireless Access Point (WAP)
The wireless access point permits laptops to connect to the network wirelessly; there are secure settings to avoid hacking.
5. Network Security Measures
5.1 Firewall Configuration
It provides the information that all firewalls in the network will be configured with appropriate security rules so that they can effectively manage traffic and protect critical resources (Peca et al.2022). The firewall will allow HTTP and HTTPS access to the web server and SMTP access for the email server. These configurations permit legitimate communications of the web, as well as the emails, while rejecting all other traffic by default to minimize an unwanted opening of the vulnerabilities from the external threats. The Firewall will limit access to the DMZ from the internal network, thus keeping unauthorized users from reaching any services that are publicly accessible. It will also limit access to sensitive internal servers defined for roles so that only authorized personnel can interact with critical data and applications. In this layered approach to firewall configuration, it would ensure that a well-designed infrastructure has effective controls and monitoring on its traffic flow to enhance the security of its network.
5.2 Internal Security Policies
The organization will implement policies that focus on user access, password management, and data protection measures. It also states that there will be continuous security audits to know where the vulnerabilities lie and be able to address them at the right time.
5.3 DMZ Implementation
The DMZ can be conceptualized as a buffer zone between the external and internal networks. The hosting of public-facing servers restricts direct internet exposure to the internal network. The chances of unauthorized access toward sensitive internal resources are minimized.
6. Testing and Validation
6.1 Connectivity Tests
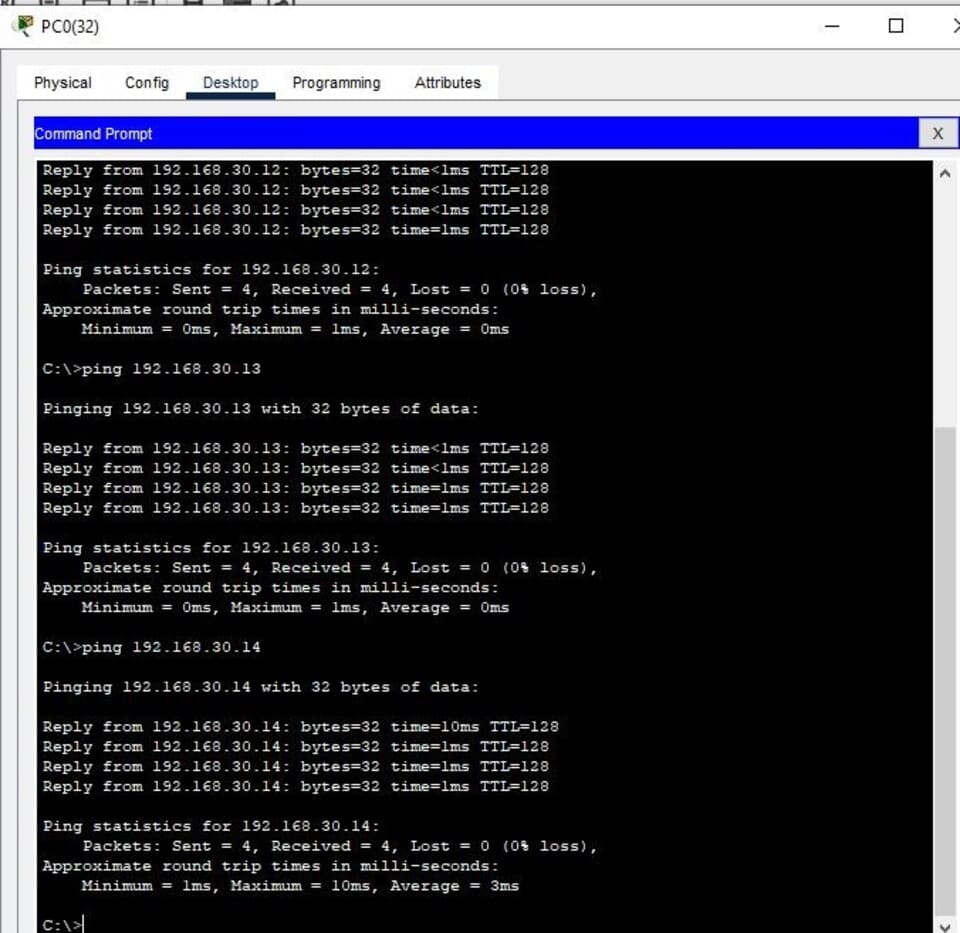
Figure 14: Connectivity Tests through Ping
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
The connectivity tests will then identify whether the network can route data from each device to the other. This has to be done with ping testing between PCs, laptops, and servers. It will also include checking the functionality of web and email servers by internal devices.
6.2 Performance Testing
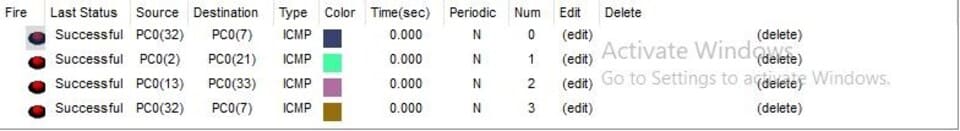
Figure 15: Performance Testing
(Source: Self-Created in Cisco)
Performance testing will seek to understand the total throughput, latency, and responsiveness of the network. Performance testing will then stress the network at different load points to identify the strength at which it will degrade (Azhari et al.2021). In this case, the test will reveal the tolerance level without delivering deterioration.
7. Conclusion
7.1 Summary of Findings
The proposed design for the secure network will accommodate the needs of the small office effectively. It has emphasized security and efficiency. The diagram given is well set because the topology depicted makes for solid functionality, while detailed specifications on each component ensure robust functionality.
7.2 Recommendations for Future Enhancements
The overall upgrades will likely include the network device upgrades to throughput, intrusion detection capabilities, and firmware changes of software. It must be trained for security best practices to ensure the security of a deployment environment from improper staff.
"Designing a secure network that balances efficiency, scalability, and robust protection is complex. Our comprehensive analysis of DMZ implementation, firewalls, routers, and switches demonstrates the expertise required to safeguard data and ensure seamless operations. From star topology layouts to performance and connectivity testing, every detail matters to create a resilient office infrastructure. Don’t risk errors or overlooked vulnerabilities—Do My Assignment services can deliver a professionally written, well-researched network design report tailored to your needs. Let experts handle the technical work so you can focus on achieving top results—order your assignment now for guaranteed accuracy and peace of mind!"
Reference List
Journals
- Ahmed, A.H. and Al-Hamadani, M.N., 2021. Designing a secure campus network and simulating it using Cisco packet tracer. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 23(1), pp.479-489.
- Alkenani, J. and Nassari, K.A., 2023. Enhance work for java based network analyzer tool used to analyze network simulator files. vol, 29, pp.954-962.
- Allison, J., 2022, July. Simulation-based learning via cisco packet tracer to enhance the teaching of computer networks. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM Conference on on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education Vol. 1 (pp. 68-74).
- Azhari, A.D., Sulaiman, N.A. and Kassim, M., 2021, November. Secured Internet Office Network with the Internet of Things Using Packet Tracer Analysis. In 2021 IEEE 11th International Conference on System Engineering and Technology (ICSET) (pp. 200-205). IEEE.
- Gwangwava, N. and Mubvirwi, T.B., 2021. Design and simulation of IoT systems using the Cisco packet tracer. Advances in Internet of Things, 11(02), p.59.
- Hidayat, A.R., Hanggara, I.S. and Sudarsono, R.S., 2024. Analysis of Networking Tools Using Cisco Packet Tracer (CPT). International Journal Software Engineering and Computer Science (IJSECS), 4(2), pp.721-730.
- Obelovska, K., Kozak, I. and Snaichuk, Y., 2022, November. Analysis and Comparison of Routing and Switching Processes in Campus Area Networks Using Cisco Packet Tracer. In The International Symposium on Computer Science, Digital Economy and Intelligent Systems (pp. 100-110). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
- Peca, L. and ȚURCANU, D., 2022. Computer networks: Practical examples solved to be introduced in computer networks.
- Reddy, P.S., Akram, P.S., Ramana, T.V., Ram, P.A.S., Raj, R.P. and Sharma, M.A., 2020, December. Configuration of firewalls in educational organisation LAB setup by using cisco packet tracer. In 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Sustainable Energy, Signal Processing and Cyber Security (iSSSC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Suleiman, A.R., 2021, February. Simulation of IoT Web-based Standard Smart Building Using Packet Tracer. In 2021 7th International Engineering Conference “Research & Innovation amid Global Pandemic"(IEC) (pp. 48-53). IEEE.



