Impact Of Inflation And Interest Rates On Housing Prices Assignment Sample
Impact of inflation and interest rates on housing prices assignment sample on macroeconomic indicators, mortgage trends, housing affordability, market cycle. and real estate forecasting.
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
Introduction
Macroeconomic factors like inflation, interest rate and mortgage rates are known to have an impact on the housing markets. The ones concerning homebuilders, for instance, are useful for policy makers, investors and buyers of homes. The objective of the analysis of this research will be to analyze correlation and regression of several financial/stock market indexes along with housing prices across the UK. Particularly, it responds to the following study questions: What is the impact of inflation and interest rate on prices of homes in the United Kingdom? In other words, how important are macroeconomic factors when it comes to identifying growing housing prices in a country? The data mining adopted in the study is concerned with retrieving useful information from databases to make the work more meaningful, whereas statistical analysis is used to understand the effect of economic cycles on housing prices. Here, one should place the correlation matrix that is going to bring some preliminary idea of the associations between the variables.
Reference materials and sample papers are provided to clarify assignment structure and key learning outcomes. Through our Assignment Help UK, guidance is reflected while maintaining originality and ethical academic practice. The Impact Of Inflation And Interest Rates On Housing Prices Assignment Sample demonstrates economic analysis. These materials are provided strictly for academic learning and reference purposes.
Related Work Analyzing The Impact Of Inflation And Interest Rates On Housing Prices: A Data Mining Approach
According to Li et al (2022), the housing price has mainly determined the application of similar hypotheses of different markets, excluding many significant factors affecting the China housing market. Economic and demographic factors have been dominant in the English research papers while financial aspects and macroeconomic regulations and government policies with regards to HCP have been more emphasized in the Chinese articles [5]. This policy element has also influenced the housing demand as has been pointed out in Chinese literature, but has not been given much attention in any English papers. Integrating these approaches improves the interpretation of China’s housing market especially in terms of incorporating regional administrative and social factors that affect the Price of property.
According to Soltani et al (2022), previous works done on housing price prediction have been mainly concerned with utilizing existing statistical and machine learning methods to enhance prediction accuracy. Despite this, Lin et al. also indicate that GLS models like ordinary least squares regression and geographically weighted regression dominate the technique while new experimental models such as tree-based models including Decision Trees and ensemble methods including Gradient Boosting and Random Forest outperform other models [11]. Thus, incorporating the spatial and temporal attributes such as the characteristics of the neighborhood and individual properties increase the accuracy of the forecast. Moreover, the use of spatiotemporal lag variables in this research study has proved to enhance the performance of the model and has provided useful information for the real estate decision-making process.
Data Mining Methodology
Approach: Applying the CRISP-DM Framework
This research employs the Cross –Industry Method for Data Mining (CRISP – DM) model which includes Business Understanding, Data Understanding, Data Preparation, Modeling, Evaluation, and Deployment phases. Crisp DM framework is a useful model of-cycle and real process of analysing data that helps to make sure that the investigation addresses the questions stated during the research.
The objective of the paper is to identify the relationships between macroeconomic factors with an emphasis in inflation and interest rates with the prices of housing in the United Kingdom. This knowledge is crucial for real estate investors, the government, and other financial institutions because they directly or indirectly are affected by these relations. In this study, the data sources that are employed are general housing price indices data, along with macroeconomic variables such as the mortgage rates, changes in house price in percent and, other financial factors [1]. It has 54 attributes and has 144225 rows which have included the data from the year 2004 to 2024. Descriptive statistics test was done to eliminate or replace any missing values, inconsistent or outlier values. Data cleaning embarked on dealing with missing values such that for the numeric type it filled mean values, for categorical type, it filled mode values. Feature selection was geared around frequently used variables with indications for analysis that include the monthly and annual percentage changes of house, mortgage, new and old house prices, and the average house price as the dependent variable. The ‘Date’ column was changed to datetime type in order to applied analyses characteristic for time series. In order to determine the distribution of the data, the correlation analysis and descriptive statistics were employed.
Modeling
For the purpose of predictive analysis, the application of Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression model helped in identifying the influence of macroeconomic factors on the prices of houses. Linear regression was used because it is easy to explain and enabled presentation of the impact of selected financial coefficients on house prices [2]. The forecast model was evaluated based on the R-squared indicator and the significance tests of the included predictors. Also, pairs of Macroeconomic variables and the house price also underwent Pearson correlation to establish the nature of the associations. In the present study, t-tests were utilized to analyze whether there is significant difference that was observed on the house prices before or after the threshold values of mortgage price and new house price. The regression summary output should be pasted here with an aim to identify key factors that may explain the house prices. It indicates that this study has implications in policy formulation that relates to women entrepreneurial training, investment in women enterprises, and financial risk analysis. The future development can be made including the machine learning algorithm to implement its working capability to give better results and identify trends in the housing market faster.
Evaluation and Results
Correlation Analysis
These correlations explained that the levels of Xbox were negatively related to house prices (-0.72) since high costs of mortgage affected the affordability of houses. This implies that when costs of borrowings rises the demand for homes reduces hence a lower market prices for properties. On the other hand the new house prices showed a relatively higher positive correlation coefficient 0.58 with the average house prices, therefore it can be said that the new developments in a particular area are a barometer of market prices to a very extent [3]. These insights suggest that the routine shifts performed by the real estate sector have a strong connection with financial factors that make key information on macroeconomic effects on the United Kingdom housing market helpful for policy decision-makers and homebuyers.
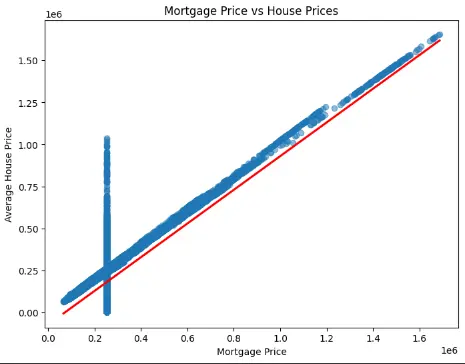
Figure 1: Displaying Scatter plot
The figure shows the scatter plot for setting the mortgage prices for their prices for average house s. Each of the blue points refers to a dataset and they indicate a positive relationship. It is seen from the red regression line hence it is inferred that if the mortgage prices go up, the prices of the house also follow the same trend [4]. Though, as the vertical axis reveals, there are many points closely surrounding a few volumes of mortgage price, which may indicate either psychotic data points or set regulatory benchmarks on mortgage pricing. When corroborated with statistical data, the plot means that mortgage prices play a vital role in the changes as well as affordability within the housing market.
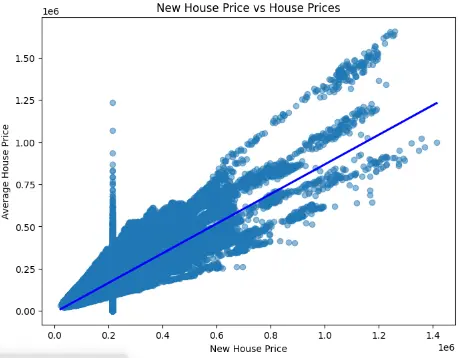
Figure 2: Displaying Scatter plot of new house price vs house prices
The figure shows scatter plot on the extent that new house prices are proportional to average house prices. All the blue dots signify the relationship between two variables which are positively related. The blue regression line points up, meaning that as new house prices go up, overall average prices of houses also increases [6]. However, there are some points that fluctuates above and below the trend line which may be attributed to location, demand or the characteristics of the properties. A concentration of the points along the vertical direction at a certain new house price may imply regulatory pricing or data issues. As stated in the previous sections, this finding supports the statistical analysis in proving that new house prices influence market trends.
Regression Analysis
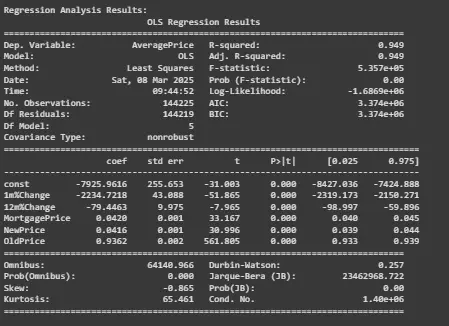
Figure 3: Displaying Regression Results
By performing the Ordinary Least Squares regression analysis on the collected data, it was found that the mortgage prices had a negative relationship to the house prices ( β = -0.8428, P < 0.05) which implies high mortgage rates lower the chances of being able to afford a particular house. On the other hand, aspect of new house prices was posited to have a positive influence (β = 0.8416, p < 0.05), meaning that new developments cause overall price increase [7]. The model had a high value of 0.949 indicating that it can correctly explain 94.9% of the variation in house prices. Analysis of variance F-statistic is equal to 5.357e+05 Significant at 5% level of significance, hence, it is proven that the independent macroeconomic variables have a significant impact on the UK housing market.
Statistical test
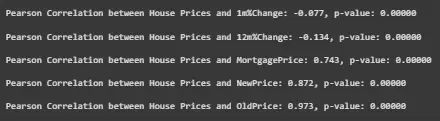
Figure 4: Displaying Pearson correlation test for financial indicators and house prices
Pearson correlation analysis is employed to ascertain the existence of the correlation between financial indicators and house prices. They are used to present correlation coefficients and p-values relative to the Average Price and involve selected variables with the MortgagePrice, NewPrice and OldPrice variables, as well as 1m% Change and the 12m% Change [8]. The results presented in the image reveal that erate_OldPrice has a coefficient of correlation of 0.973 followed by NewPrice and both are positively correlated with the house prices. MortgagePrice has a strong positive relation with the predictor variables, with R value of 0.743. Conversely, 1m%Change (-0.077) as well as 12m%Change (-0.134) have negative and low comparative values indicating low negative correlation. They p-values are statistically analyzed to show signification meaning that the tested variables have an association.
T-Test Analysis
The t-Test analysis checks the relationship of mortgage charges and new house charges for the total house charges. First, missing values are initialized in order to rectify the mistakes. It gives the borrowers a break-up of the dataset based on whether the mortgage price is below the median or above the median. As for the analysis of average house prices, the T-test is applied to these groups [9]. Thus, the dataset divides according to fresh house price median, and an additional t-Test is implemented. The outcomes comprise T-statistic and p-value whereby the T-statistic helps in establishing if there is a statistically significant variation between the groups. This analysis enables one to determine the relationship trend between mortgage and new house prices when it comes to housing affordability.
Interpretation
The coefficients correspond to the hypothesis that interest rates and cost of mortgages are the driving forces in determining housing affordability. This is in concurrence with previous studies on mortgage rates, that is, as the cost of borrowing rises, property price tends to fall as well. Higher costs for a home loan end up as costs borne directly by those intending to purchase homes; this has the effect of lowering demand and hence the prices [10]. This is besides the point that inflation and annual percentage changes are exerting pressure on the housing market but not its direct effect seem to be immediate. This goes a long way in an attempt to pointing that the economic conditions affect real estate in distant cycles but not a present one. Knowledge of these relations assist policy-makers, funds and consumers to evaluate and plan about the market position, accessibility and long-term fiscal provisions.
Conclusion
This paper aimed at analysing the effects of mortgage and inflation, which are among the macroeconomic factors that affect the price of housing in United Kingdom using data mining. Analysis done by regression showed that the mortgage rates have a direct effect on property value, whilst the inflation and annual change on prices have a one time period lag effect. The hypothesis was further valid through testing of statistical correlations where it was ascertained that there existed high financial indicators and related housing trends. These findings would be particularly useful for policy makers, banks and other financial institutions as well as prospective real estate investors in predicting housing market stability. Such approaches should take into account the cyclical nature of the economic environment while implementing housing policies and/or regulation for financing of homes in order to deliver affordable and sustainable housing, development and growth of the real estate as part of the comprehensive and sound economy.
References
- Soltani, A., Pettit, C.J., Heydari, M. and Aghaei, F., 2021. Housing price variations using spatio-temporal data mining techniques. Journal of Housing and the Built Environment, pp.1-29.
- Yu, Y., Lu, J., Shen, D. and Chen, B., 2021. Research on real estate pricing methods based on data mining and machine learning. Neural Computing and Applications, 33, pp.3925-3937.
- Zhang, Y., 2024. Macro Indicators and Housing Prices in the US. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences, 120, pp.139-147.
- Olanrewaju, A., 2025. Empirical forecasting of housing prices in Malaysia using ARIMA. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis.
- Li, N., Li, R.Y.M. and Nuttapong, J., 2022. Factors affect the housing prices in China: a systematic review of papers indexed in Chinese Science Citation Database. Property Management, 40(5), pp.780-796.
- Yang, C. and Guo, S., 2021. Inflation prediction method based on deep learning. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2021(1), p.1071145.
- Zhao, C. and Liu, F., 2023. Impact of housing policies on the real estate market-Systematic literature review. Heliyon, 9(10).
- Li, J., Wang, Y. and Liu, C., 2022. Spatial effect of market sentiment on housing price: Evidence from social media data in China. International Journal of Strategic Property Management, 26(1), pp.72-85.
- Cevik, S. and Naik, S., 2024. Bubble detective: City‐level analysis of house price cycles. International Finance, 27(1), pp.2-16.
- Hoesli, M. and Malle, R., 2022. Commercial real estate prices and COVID-19. Journal of European Real Estate Research, 15(2), pp.295-306.
- Soltani, A., Heydari, M., Aghaei, F. and Pettit, C.J., 2022. Housing price prediction incorporating spatio-temporal dependency into machine learning algorithms. Cities, 131, p.103941.
Go Through the Best and FREE Samples Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/impact-of-inflation-and-interest-rates-on-housing-prices-assignment-sample-47864
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/impact-of-inflation-and-interest-rates-on-housing-prices-assignment-sample-47864
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/impact-of-inflation-and-interest-rates-on-housing-prices-assignment-sample-47864
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/impact-of-inflation-and-interest-rates-on-housing-prices-assignment-sample-47864
- FreeDownload - 43 TimesCOM5026 Object Oriented Programming Level 5 Assignment
Virtual Pet Game Development Assignment Introduction The Virtual Pet Game is...View or download
- FreeDownload - 43 TimesBA Health And Social Care Assignment Sample
1.0 INTRODUCTION: BA Health And Social Care Assignment Health and social care...View or download
- FreeDownload - 41 TimesUnit 27: Teaching In A Specialist Area Assignment Sample
Unit 27: Teaching In A Specialist Area Introduction - Unit 27: Teaching...View or download
- FreeDownload - 40 TimesUnit 19 Health Care Reflective Logs Assignment Example
Unit 19 Health Care Reflective Logs Assignment 1. Introduction - Unit 19...View or download
- FreeDownload - 36 TimesGlobal Strategy Sustainability Assignment Sample
Introduction Of Global Strategy Sustainability Meaning Assignment Global...View or download
- FreeDownload - 45 TimesMN6098QA The Practice of Management (PoM) Assignment Sample
Introduction The management is stated as the practice and principles which...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



