Design An Algorithm For The Optimisation Of Road Alignments Using PSO
2.1 Introduction
Road alignment is an important aspect in the design of highways with a major concern of achieving the best line for the least construction cost, interference with the environment, and safety hazards. These include horizontal and vertical alignments which are engineered to standards and other constraints of the project. Design techniques assist engineers in analyzing many potential solutions and finding a suitable one where different aspects of the construction are taken into consideration in economic and environmental climate.
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is a stochastic optimised admission employed in this paper concerning road alignment optimization. Based on the bird flocking movement, PSO makes changes to numerous parameters to search for the best solution. He is also well-regarded for his ability in the resolution of realistic and multiple objective function problems. The present literature review examines the use of PSO and other optimization solutions related to road alignment design, their key benefits and disadvantages, as well as the directions for further development.
2.2 Empirical Study
2.2.1 Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) for Road Alignment
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), a swarm intelligence algorithm, is developed concerning the behaviour of birds and fish swimming together. This helps in proposing consecutive improvements to solve intricate engineering issues, such as optimal alignment of roads, among others. Hence, horizontal alignment involves factors such as curvature, land use and the environment in its optimization while, in vertical alignment, earthworks costs and safety are taken into consideration. Its application in 3D optimization is both in the horizontal and vertical directions, reduces wastage and enhances the ease of constructing roads economically and with an environmental constraint.
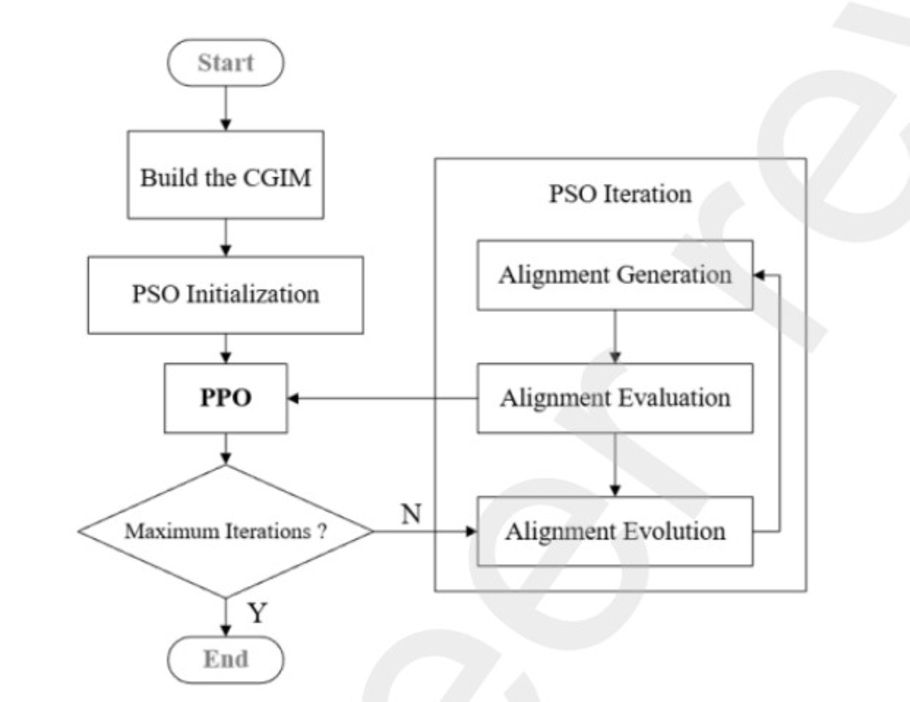
Figure 1: PPO-PSO flowchart.
(Source: Wang et al., 2024)
Wang et al. (2024) proposed a heuristic optimization approach known as Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization (MOPSO) while trying to find the most suitable alignment of highway trajectory. Its key concern was on how the location of the road to be recommended for construction could be established and the effects of such construction on the construction cost and utilities. It was also because, in their context, their model provided a broader solution that considered economic and realistic grounds for the operation. It was established that in their work MOPSO was able to shorten the design time and supplied better solutions than the mechanical approach.
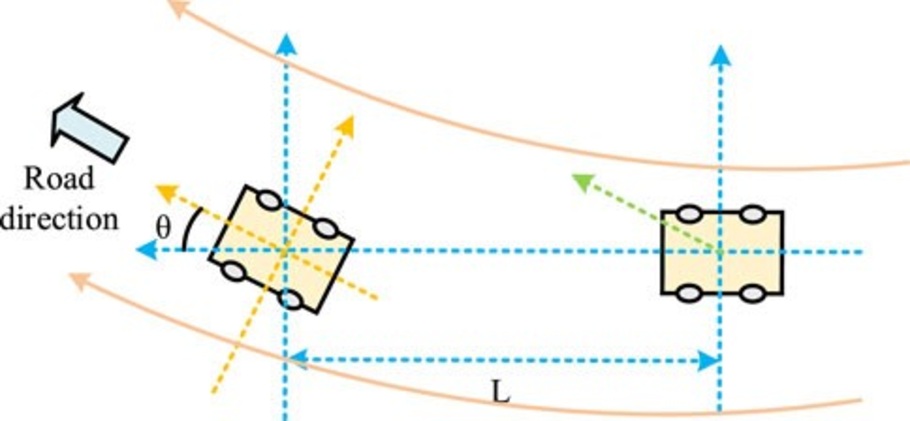
Figure 2: Particle Swarm Optimization
(Source: Wang et al., 2024)
To improve the adaptability of the approach for highway alignment, Pu et al. (2024) utilized Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) with PSO for reinforcement learning. This helped the optimization process to be able to adapt to the points of interest, thus enhancing the search process greatly. Their model also provided better solutions in comparison to traditional PSO by improving the search space approach in complex topologies thus improving cost and safety solutions. The work presented by Pu et al. (2024) is novel as it provides a hybrid solution which allows for dynamic adjustment to the conditions on the go, which is a critical factor in large-scale infrastructure projects. Optimization, specifically the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) approach, is a highly suitable method for optimizing issues related to road alignment designs, using principles based on swarm intelligence (Wang et al., 2018).
2.2.2 Genetic Algorithms (GA) and Hybrid Approaches
Road alignment optimization has seen so much application of Genetic Algorithms (GAs) and other meta-heuristic approaches due to the complexity of problems that can be solved using this technique. In contrast to PSO, GA simulates the OS process and aims at improving a population of potential solutions through selection, crossover, and mutation operators. For this, a travelling salesman tour seems to be a good solution as it allows one to consider various alignments of words while gradually refining the solution across generations.
Al-Hadad et al. (2024) proposed a new technique of applying GIS with GA to improve highway alignment. They also showed it is possible to reduce the search space when the latter adopted a two-step approach, as they identified a zone in which the alignment was most likely to be located. Whereas the Use of GIS enhanced the terrain analysis to near accurate conditions, GA made the exploration of potential alignments easier.

Figure 3: PSO pseudocode
(Source: Gad, 2022)
According to their findings, there was a marked enhancement of the thematic and computational aspects of GIS GA integration as compared to hypothetical search algorithms. The developments in PSO have enhanced an application in engineering optimization aspect, making the technique useful in developing efficient road alignment algorithms (Gad, 2022).
Figure 4: Particle Swarm Optimization
(Source: Gad, 2022)
The use of these two methods has its pros and cons with PSO being slightly better with complex non-linear problems and GA being better with real-valued problems. PSO converges faster, in general, due to the constant updates of the particle's position from the swarm intelligence. But, it may get stuck to a local optimum, especially in rugged search space. On one hand, the GA is less likely to get stuck in local optima because of its genetic difference but entails more computational time because of the iterative evolutionary process. Such a combination is evident in Pu et al. (2024) Stressing on the accomplishment, it was observed that the fusion of these two methods can conglomerate GA's global search potential with PSO's better convergence rate.
2.2.3 Geographic Information System (GIS) and Machine Learning Integration
The merging of GIS and optimization made considerable enhancement in road alignment decisions by offering applicable location data and information on ground features. The integration of GIS makes it easier to determine environmental constraints for site selections, land use and geotechnical conditions which are important in line selection.
Lay normalization will be undertaken in the later step, while Pu et al. (2023) have put forward a GIS-based 3D environmental suitability model for railway alignment optimization. To assess the potential of the considered alignments based on the topographic and geologic conditions, they developed a spatial voxel-based approach. Optimization was made efficient because the model omitted most of the infeasible alternatives for consideration in the search process. They showed that combining the G.I.S with optimization did not only improve computational solutions but also provided environmentally preferable road designs.
Thus, the inclusion of GIS in optimization models can help prevent such problems from arising by avoiding further waste of additional resources as well as environmental impact. As well, the application of machine learning in optimization assets is growing the importance of GIS-based optimization. They could also involve developing more sophisticated mathematical models, such as using artificial neural networks to improve road alignment prediction based on past data and scanning of current terrain.
2.2.4 Multi-Road Network and Flow-Based Optimization Models
Traditional road alignment optimization is normally a sequential procedure which optimizes the geometry of every individual road segment in isolation. But, for planned large transportation networks, several roads have to be inferred at once to have connectivity and contain cost.
Md Ayman et al. (2024) presented a new concept of a multi-road quasi, network flow model which works not on a single road but on all the roads of the network and focuses on the right vertical alignments. Their study proposed an effective approach to analyzing links and nodes of the road segments and the relationships between the various links; thus initiating cost-effective and feasible solutions. The model was proved in small and large-scale road networks and thus provided construction cost reduction without efficiency compromise.
Figure 5: Dynamic Weighted Road Network Model
(Source: Md Ayman et al., 2024)
The multi-road quasi-network flow model is considered superior to single-road optimization in that it optimizes the road segments in an integrated system rather than on an individual level. It is particularly applicable in such instances as urban planning and highway networks whereby several lines need to be located properly. Several advances in PSO algorithm on the theoretical model, as well as the better computational aspects, place it as a feasible tool in enhancing alignments of roads in transportation engineering, as supported by Jain et al. (2018).
2.2.5 Consistency in Horizontal Alignment Design
Aguilar and Pérez (2021) aimed to establish the degree of horizontal alignment design consistency in horizontal curves and radii on road safety. They also provided insights about the continuity of the curves as well as transition curves to avoid confusion to drivers besides ensuring free flow of traffic. They proposed an approach for measuring alignment and thus, it can be incorporated into the models to improve road safety and minimize the rates of accidents. Design consistency was brought into the optimization models so that the alignments are not only cheap but also safe. For future work, the ways to incorporate automated design consistency checks into the frameworks of PSO and GA optimization can be discovered.
Figure 6: Horizontal alignment design
(Source: Aguilar and Pérez, 2021)
2.3 Literature Gap
The following research gaps can be identified about the improvement of road alignment optimization: Therefore, one of the major concerns that may be said to have an impact in this area is the fact that there are few real-life hybrid optimization problems. As the PSO is often implemented combined with reinforcement learning or GA it has been investigated in several papers, yet real-life experiences of integrating PSO into infrastructural projects remain limited. Still, there is a lack of research on how the PSO parameters should be dynamically adjusted to suit the current environment condition. The existing models have certain parameters which are assumed to remain fixed and this may not be advisable for most applications where terrain characteristics as well as constraints are time variant.
However, considering the objectives as well as environmental aspects have not been sufficiently discussed for multi-objective optimization. Some works reflect the consideration of ecological aspects and a better solution that regards the aspects of sustainability, land use planning, and social effects. This implies that future research should aim at developing the field application of PSO hybrid and adaptive PSO models as well as considerations of enhanced and folded environmental assessment models that would improve the feasibility of optimized road alignment models about terrain conditions.
2.5 Conclusion
PSO, GA and hybrid have greatly helped the optimization of alignments of roads. While PSO has been seen to provide a fast convergence the GA has provided improved diversification, the combination of PSO, GA with GIS and reinforcement learning has helped in enhancing the emergence. There are also a few issues – real-world application, limited adaptability of the PSO dynamic and the problem of multi-objective environmental exploration. It is by implementing field solutions, using adaptive models, and using broad environmental audits that these gaps will be closed to improve the efficiency of global optimization.
If completing academic assignments feels overwhelming or time-consuming, professional assignment help can provide reliable support. Expert guidance ensures your work is well-structured, properly referenced, and aligned with university marking criteria. With subject-specific assistance, you can improve clarity, critical analysis, and academic confidence while meeting deadlines without unnecessary stress.
References
Journals
Aguilar, D. G. and Pérez, E. A. 2021. 'Horizontal alignment design consistency: A way to evaluate the geometric design of a road', Asociación Profesional de Egresados UPTC de la Universidad Pedagógica y Tecnológica de Colombia, 211.
Al-Hadad, B. M. A., Nadir, W. H. and Jukil, G. A. M. 2024. 'Intelligent optimization of highway alignments: A novel approach integrating geographic information system and genetic algorithms', Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 133, p. 108037.
Asherlou, S., Yelghi, A., Pancar, E.B. and Oruç, Ş., 2022. An optimization approach for highway alignment using metaheuristic algorithms. Meta-heuristic Optimization Techniques: Applications in Engineering, 10(11).
Babapour, R., Naghdi, R., Ghajar, I. and Mortazavi, Z., 2018. Forest road profile optimization using meta-heuristic techniques. Applied Soft Computing, 64, pp.126-137.
Gad, A.G., 2022. Particle swarm optimization algorithm and its applications: a systematic review. Archives of computational methods in engineering, 29(5), pp.2531-2561.
Ghanizadeh, A.R. and Heidarabadizadeh, N., 2018. Optimization of vertical alignment of highways in terms of earthwork cost using colliding bodies optimization algorithm. International Journal of Optimization in Civil Engineering, 8(4), pp.657-674.
Jain, N.K., Nangia, U. and Jain, J., 2018. A review of particle swarm optimization. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 99, pp.407-411.
Md Ayman, K., Hare, W. and Lucet, Y. 2024. 'A multi-road quasi network flow model for the vertical alignment optimization of a road network', Engineering Optimization, 56(7), pp. 1140-1163.
Pu, H., Wan, X., Song, T., Schonfeld, P., Li, W. and Hu, J. 2023. 'A geographic information model for 3-D environmental suitability analysis in railway alignment optimization', Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 30(1), pp. 67-88.
Pu, H., Zeng, Q., Song, T., Schonfeld, P.M., Wang, G., Li, W., Peng, L. and Hu, J. 2024. A Hybrid Proximal Policy Optimization and Particle Swarm Algorithm for Highway Alignment Optimization.
Song, T., Schonfeld, P. and Pu, H., 2023. A review of alignment optimization research for roads, railways and rail transit lines. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 24(5), pp.4738-4757.
Wang, D., Tan, D. and Liu, L., 2018. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: an overview. Soft computing, 22(2), pp.387-408.
Wang, H., Xie, P., Li, Z. and Gao, J. 2024. 'Highway alignment optimization design method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization', E3S Web of Conferences, 512, p. 03005.



