NIP 1902 Summative workbook answers
This document reviews key nursing competencies, including homeostasis, pharmacology, NEWS2 scoring, vital signs assessment, and infection control for safe and effective patient care.
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
NIP 1902 Summative workbook with mark scheme October 2024 cohort
Section 1- Body systems and homeostasis
Q1) Define homeostasis
Homeostasis refers to the procedure through which the body respond towards the changes to maintain the conditions or internal state of the body. In other words, homeostasis is explained as the state of balance between every body systems required to survive and operate correctly (National Cancer Institute, 2024). Homeostasis is a product of amalgamation of biodiversity and ecological interactions which happens between the species. In homeostasis, blood pressure, electrolytes, hormones, oxygen, blood sugar, temperature, levels of acid, energy and proteins are continuously adjusted in order to reacts to transformation inside as well as outside of the body so that it keeps all the functions at normal level. Homeostasis is explained as relatively consistent conditions in the physiological procedure through which such conditions are preserved in the time of external variation (Access Science, 2020). Entire body system is included in homeostasis. The work of organ system within body is to carry out the functions which maintain human body at homeostasis. The human body preserves homeostasis by feedback loops. The body utilises sensors which detect changes and utilises control centre to proceed information which helps in keeping homeostasis.
References
Online
Access Science, 2020. Homeostasis. [Online] Available through < https://www.accessscience.com/content/article/a321400 > Accessed Date: 05-02-2025
National Cancer Institute, 2024. homeostasis. [Online] Available through < https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/homeostasis > Accessed Date: 05-02-2025
Q2) Identify one body regulatory process to discuss an example where the human body maintains homeostasis.
The body temperature that controlled in human is the significant example of homeostasis within biological system. In human body, basically 37 °C (98.6 °F) is the normal body temperature and it fluctuates around this value (Medicine Plus, 2023). However, there are several factors that can impact this value which leads to excessively high as well as low temperatures. Within temperature homeostasis, when human body temperature gets extremely low, the body develops heat by metabolism of fat along with the contraction of muscles (Cramer et al, 2022). On the other hand, when the temperature of the human body gets excessively high then the body enlarges blood vessels and a person sweats overly. Basically, the overall body temperature regulation process is known as thermoregulation (Horianopoulos et al, 2021.). The body should stay at core temperature which is 37 degrees Celsius. The temperature is highly crucial for the biological functions to take place which uphold other system’s homeostasis. Even at resting situation, the brain, heart, muscles, liver and other organs builds constant heat. Body temperature is kept at homeostasis through disintegrating this produced excess heat outside the human body. In addition to this, a human should respond to changes in temperature because of the environment. The nervous system in the body is a biological regulator which reacts to such kind of changes (Petzschner et al, 2021). External factor such as global warming as well as internal factor like long term fever can cause heat stress and affect the human body. Homeostasis is essential life function and it drives the human body functions. Thermoregulation is the procedure to maintain body temperature even when the external temperature is varying.
References
Books and Journals
Cramer, M.N., Gagnon, D., Laitano, O. and Crandall, C.G., 2022. Human temperature regulation under heat stress in health, disease, and injury. Physiological reviews.
Horianopoulos, L.C., Lee, C.W., Hu, G., Caza, M. and Kronstad, J.W., 2021. Dnj1 promotes virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans by maintaining robust endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis under temperature stress. Frontiers in microbiology, 12, p.727039.
Petzschner, F.H., Garfinkel, S.N., Paulus, M.P., Koch, C. and Khalsa, S.S., 2021. Computational models of interoception and body regulation. Trends in neurosciences, 44(1), pp.63-76.
Online
Medicine Plus, 2023. Body temperature norms. [Online] Available through < https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001982.htm#:~:text=The%20average%20normal%20body%20temperature,by%20an%20infection%20or%20illness > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Q3) a. What is sickle cell disease and what role does genetics play in sickle disease?

Sickle cell disease is explained as an inherited blood disease or disorder which impacts the hemoglobin, a main protein which carries oxygen in the body. It is also known as anemia. Usually, red-blood cells are in disc-shape and flexible so they can move through blood vessels without any difficulties (Ataga, Saraf and Derebail, 2022). Red blood cells in body are misshaped in sickle cell illness which impacts the hemoglobin molecule. It is the kind of genetic disease caused through a mutation in HBB gene. A person gets one set from mother and one set from father and if child born with this disease which means a child received a copy of sickle cell gene from the parents (Adekile, 2021).
References
Books and Journals
Ataga, K.I., Saraf, S.L. and Derebail, V.K., 2022. The nephropathy of sickle cell trait and sickle cell disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 18(6), pp.361-377.
Adekile, A., 2021. The genetic and clinical significance of fetal hemoglobin expression in sickle cell disease. Medical Principles and Practice, 30(3), pp.201-211.
Q4) What medication may be prescribed for patient who is experiencing an acute episode or crisis of sickle cell disease?
Management and treatment of sickle cell disease is often aimed at reducing the pain episodes, releasing symptoms and avoiding complications. Hydroxyurea is medicine which frequently prescribed by the doctors in order to treat sickle cell disorder (Kavanagh, Fasipe and Wun, 2022). It is the kind of oral medicine which can decrease the sickling of the red blood cells and facilitate in prevent severe symptoms or signs of this disorders, including pain crises. Moreover, daily Hydroxyurea decreases the pain crises and might also reduce the requirement for blood transfusions as well as hospital stays. Gene therapies are being developed that may provide cures for patient with anemia. The techniques of pain relief in sickle cell disease rely on whether the pain is chronic or acute or combination of both as well as whether a patient is opioid tolerant.
References
Books and Journals
Kavanagh, P.L., Fasipe, T.A. and Wun, T., 2022. Sickle cell disease: a review. Jama, 328(1), pp.57-68.
Section 2 - Pharmacology and Medicines Management
Q1) Define the term “pharmacology”?
Pharmacology refers to the scientific study of the impacts of drugs as well as chemicals on the living organisms in which drug can be widely explained as any chemical element, whether natural or synthetic, that impacts a biological system. Pharmacology can include how organisms manage drugs, recognition and authentication of new targets regarding the drug action, plan and creation of new drugs in order to prevent as well as treat disease (Alexander et al, 2023). It is an important element in terms of development of contemporary personalised medicine. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics are two major branches of pharmacology. Pharmacokinetics means what human body does to the drugs and pharmacodynamics means what drugs do to human body.
References
Books and Journals
Alexander, S.P., Kelly, E., Mathie, A.A., Peters, J.A., Veale, E.L., Armstrong, J.F., Buneman, O.P., Faccenda, E., Harding, S.D., Spedding, M. and Cidlowski, J.A., 2023. The concise guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2023/24: introduction and other protein targets. British Journal of Pharmacology, 180, pp.S1-S22.
Q2) Define the term “covert drug administration” and explain when a medication may be administered this way?
Covert drug administration refers to give medication in a hidden form without the consent and knowledge of an individual receiving medicine. In simple terms, covert administration is explained as practice or action of hiding medicine or drug in any food or drinks so that it cannot be noticed by other people. It involves put on a patch without the person’s knowledge or administering tablets by feeding tube (Specialist Pharmacy service, 2025). Anyone must only give medications covertly if a particular person is not in state or does not have the capability to take decisions regarding taking the medicines. Tablets can be crushed as well as fluid form the drugs can be utilised for the patients who are not in situation to give approval or refuse permission due to the lack of insight (Hegde et al, 2023). Doctor or anyone who is giving medicine to the patient should not overrule the decision of the capable person to decline treatment; even if a person who is giving medicine think patient’s decisions are wrong. It is a crucial for person to follow the proper procedure when they require administering medicines covertly. Hospitals and healthcare organisations in which drugs may be administrated must make sure local policies and regulations are in place and national protocols are followed. The Mental Capacity Act (2005) is important for healthcare practices and it applies to all persons who involved in the treatment, support and care of individuals aged 16 & over and living in the England & Wales. The main aim of the Act is to promote and protect decision-making in legal framework (SCIE. 2022).
References
Books and Journals
Hegde, P.R., Gowda, G.S., Vajawat, B., Basavaraju, V., Moirangthem, S., Naveen Kumar, C. and Bada Math, S., 2023. Study on covert administration of medications practices among persons with severe mental illness: A cross-sectional study. International Journal of Social Psychiatry, 69(1), pp.28-37.
Online
SCIE, 2022. Mental Capacity Act 2005 at a glance. [Online] Available through < https://www.scie.org.uk/mca/introduction/mental-capacity-act-2005-at-a-glance/ > Accessed Date: 08-02-2025
Specialist Pharmacy service, 2025. Covert administration of medicines: legal issues. [Online] Available through < https://www.sps.nhs.uk/articles/covert-administration-of-medicines-legal-issues/ > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Q3) What healthcare professionals can administer medications and what checks are made prior to medication being administered?
Doctors along with the registered nurses are those healthcare professionals who can supply or administer the drugs as a part of professional health scheme. Though, a registered nurse can only administer drugs if they have any kind of written instructions from hospital or doctor (Haleem et al, 2022). Licensed practical nurses may also lawfully administer drugs which are prescribed from doctor, physician or practitioners. There are mainly six areas which are needed to be checked before administering a medicine to patient. It involves right patient, right medicine, accurate dose, right time, route and documentation. It is important to note that nurses should check the patient’s identity before giving medication and verify the medicines to reduce the side effects or any major harm. A healthcare worker must confirm whether the medicine is right or wrong as well as give indications for using medicines. Selecting right dose and right time is equally important for the recovery of patient. At every safety checkpoint, medicine is verified with electronic MAR of the patient that confirm the above six areas (WTCS, 2024). Before giving medicines, the nurses must be aware about patient’s allergies and history of drug interactions. Moreover, nurses should gather accurate data related to patient’s medical history, present situation and latest lab results to find out flaws for patient to receive approved medicine.
References
Books and Journals
Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Singh, R.P. and Suman, R., 2022. Medical 4.0 technologies for healthcare: Features, capabilities, and applications. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, 2, pp.12-30.
Online
WTCS, 2024. 15.2 Basic Concepts of Administering Medications. [Online] Available through < https://wtcs.pressbooks.pub/nursingskills/chapter/15-2-basic-concepts-of-administering-medications/#:~:text=Nurses%20must%20administer%20medications%20via,the%20prescribing%20provider%20before%20administration > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Q4) How would an adverse drug reaction be managed?
Medicines or drugs can cause side effects. Several patients do not have side effects on the other hand, some people have minor side effect that reduces after a while. However, sometimes, it can be problematic or can be severe for patients. It is the responsibility of a doctor or nurse to immediately look adverse drug reaction matter. Supposed adverse drug reactions (ADRs) must be reported immediately (British Pharmacological Society, 2022). It is the crucial for the healthcare professionals to be aware with known adverse drug reactions of medications and pre-existing signs of patient. If patient faces drugs effect at home, then they should immediately talk to doctor to recover from the conditions (Barbaud, Castagna and Soria, 2022). A doctor would also reduce the dose of medicines and prescribe other medicine in place of those drugs which cause ADRs. Document the drug reaction in medical record of patient is important step so that doctor and nurses can aware about it in future terms. By informing patients regarding possible adverse drug reactions can help to manage it (Greenhawt et al, 2021). Healthcare professionals can also use decision support software in order to prevent ADRs. Patient can manage ADRs at own level through using medicines safely. Patient needs to be safe with medications and take their tablets exactly as prescribed. Nurses and other healthcare professionals who face this kind of situation should use the S-E assessment to manage the negative drug reaction. ABCDE approach means Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure is systematic method that helps in giving immediate treatment to manage the injured patients or critically ill patients (GOV.UK, 2025). Healthcare professional must report adverse incident with medicine to MHRA (Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency) by utilising the yellow card scheme.
References
Books and Journals
Barbaud, A., Castagna, J. and Soria, A., 2022. Skin tests in the work‐up of cutaneous adverse drug reactions: a review and update. Contact Dermatitis, 86(5), pp.344-356.
Greenhawt, M., Abrams, E.M., Shaker, M., Chu, D.K., Khan, D., Akin, C., Alqurashi, W., Arkwright, P., Baldwin, J.L., Ben-Shoshan, M. and Bernstein, J., 2021. The risk of allergic reaction to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and recommended evaluation and management: a systematic review, meta-analysis, GRADE assessment, and international consensus approach. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, 9(10), pp.3546-3567.
Online
British Pharmacological Society, 2022. Identifying and managing adverse drug reactions: Qualitative analysis of patient reports to the UK yellow card scheme. [Online] Available through < https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bcp.15263 > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
GOV.UK, 2025. Report a problem with a medicine or medical device. [Online] Available through < https://www.gov.uk/report-problem-medicine-medical-device > Accessed Date: 08-02-2025
Section 3 - Patient monitoring and vital signs
Q1) What is NEWS2 (Royal College of Physician RCP, 2017) and what does it aim to do?
NEWS2 or The National Early Warning Score 2 is a type of established track and generate systems in order to evaluate disease seriousness and deterioration of risk for the patients in acute incidents of treatment or care within the United Kingdom (National Library of Medicine, 2022). The system is based on easy aggregate scoring system which involves 0 to 7 score. Also, it is increasingly utilised globally. The aim of the NEWS2 is to make sure a quick reaction to deteriorating patient. It works as a common language of alertness and deterioration which allows steadiness of communication, training and practice. Now, NEWS2 is also utilised from ambulance services.
References
Online
National Library of Medicine, 2022. Using NEWS2: an essential component of reliable clinical assessment. [Online] Available through < https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9761428/#:~:text=The%20National%20Early%20Warning%20Score,is%20also%20increasingly%20used%20internationally > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Q2) Scenario
Vee is a 78-year-old woman, with a past medical history of breast cancer which is currently in remission. She is has never smoked. She has been admitted to a respiratory ward from the Emergency Department to low oxygen saturations, a productive cough and a high respiratory rate. She did a later flow test at home and it was positive for Covid-19. In the ED her NEWS score was 3 due to SPO2 93% and 2L oxygen.
Vee has just arrived at the ward and the Nursing Associate takes a set of observations:
Her respiratory rate 28 breaths per minute, SPO2 is 90% on 2L of oxygen, systolic 100mmHg, heart rate is 110 beats per minute, she is alert. She has said she feels hot and sweaty, when the Nursing Associate take her temperature it is 38º C.
Calculate the NEWS2 score (RCP, 2017) from the scenario above and outline the response required?
As per the above analysis, the NEWS2 of Vee was 3 because of SPO2 was 93% along with 2L oxygen. After that, when Vee arrived at ward a nursing associate takes a new observations. According to NEWS2 score, her respiratory rate is 28 which got 3 score and SPO2 is 90% on 2 litre of oxygen which also got 3 score. Moreover, Vee’s systolic blood pressure is 100 mmHg and heart rate is 110 that obtained 2 and 1 score. Vee’s achieved 1 score in temperature and her AVPU (alert, voice, pain and unresponsive) score is 0 as she is alert.
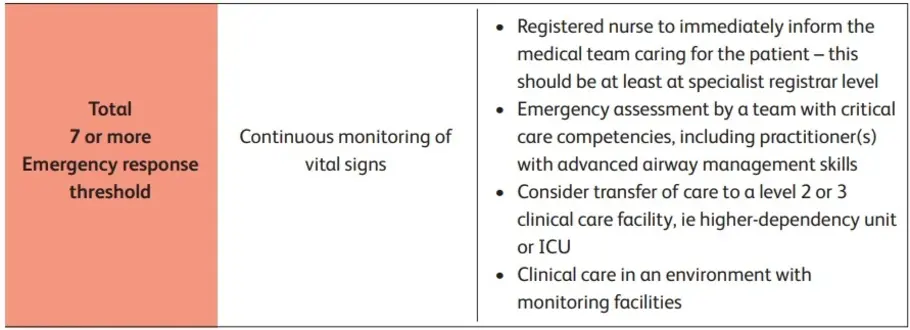
After adding all scores (3+3+2+1+1+0), the total is 10 points which is high score. It means Vee needs emergency assessment from clinical care team and should transfer to higher dependency care area for further treatment.
- Use full sentences to describe the above observations using medical terminology (for example hypoxic, bradycardiac), what could be causing the change in the patients’ observations?
If a person gets aggregate score 7 or more then it means there is a high level clinical risk. Patient needs emergency evaluation from the critical care team. In this situation, a patient often transfer to higher-dependency treatment and care area. From the above observation, it has been identified that SPO2 is 90% on L2 oxygen level which seems low and it shows that Vee is hypoxic (Hay et al, 2022). Normal oxygen level of a person usually range from 95% - 100%. In this case, 90% is low value and patient needs hospital care. Heart rate of Vee is 110 beats/minute which is known as Tachycardia. Normal heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats/per minute but Vee’s heart is faster compared to the normal. Her body temperature is also 38 degrees Celsius that falls under the category of fever. Respiratory is also not normal because normal rate range from 12 to 20 breaths/minute. Covid-19 could be a reason behind increasing health problems. She was infected with Covid-19 which make condition more severe. Vee needs proper treatment and care so that she can recover from her health situation. She also requires appropriate support to manage her health problems and reduce symptoms.
Q3. What actions would you implement based on the NEWS2 score above, in line with the Royal College of Physician’s National Early Warning Score thresholds and trigger report (2017) and who would you notify?
Vee is facing severe problems related to her health and need care and support. Necessary set of action is required for her treatment. NEWS2 score shows a high risk condition that needs quick action and attention (NHS, 2022). Align with Royal College of Physician’s instructions, there are numerous actions give below:
It is important to inform senior doctor or physician so that they can quickly assess the patient. According to health problems and symptoms, the situation must be assessed by specialist. Medical team should start the treatment process as soon as possible and offer clinical assistance (Holland and Kellett, 2023). Monitoring is important during the process of patient’s signs such as; oxygen rate, heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate. Respiratory support to her is needed so that she can start to breath normally. It is necessary for doctors or nurses to always adjust the observation frequency and note accurate value because incorrect value can create complications for patient. Doctor should utilise the NEWS2 score in order to decide on accurate treatment pathways by considering patient’s health situation, clinical judgments as well as hospital guidelines (Forster, McKeever and Shaw, 2022). Because score is high, a patient needs to get ICU level treatment otherwise it can make condition more worse. So, doctor should admit Vee in ICU. Documentation of essential reports and lab tesrts results are also needed so that the information can use in future as well (Nadaf et al, 2024). Senior medical team must supervise overall treatment and care procedure and patient’s condition and include next level of treatment.
References
Books and Journals
Forster, S., McKeever, T.M. and Shaw, D., 2022. Effect of implementing the NEWS2 escalation protocol in a large acute NHS trust: a retrospective cohort analysis of mortality, workload and ability of early warning score to predict death within 24 hours. BMJ open, 12(11), p.e064579.
Hay, A., Dziewulska, K., Gamboni, F., Nerguizian, D., Dzieciatkowska, M., Zimring, J.C. and D’Alessandro, A., 2022. Hypoxic storage of murine red blood cells improves energy metabolism and post-transfusion recoveries. Blood Transfusion, 21(1), p.50.
Holland, M. and Kellett, J., 2023. The United Kingdom’s National Early Warning Score: should everyone use it? A narrative review. Internal and Emergency Medicine, 18(2), pp.573-583.
Nadaf, C., Bench, S., Halpin, Y. and Terry, L., 2024. Critical Points of Risk in Registered Nurses' Use of a National Early Warning Score—Perceptions and Challenges. Journal of Advanced Nursing.
Online
NHS, 2022. CLINICAL GUIDELINE. [Online] Available through < https://rightdecisions.scot.nhs.uk/media/2564/news2-874.pdf > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Section 4 – Handwashing and PPE
You arrive on shift and are allocated a patient who is positive for Clostridium difficile, more recently re-defined as Clostridioides difficile
A patient who is assigned to healthcare professional is positive with Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) which is a gram-positive and spore-forming bacterium. It is identified for its capability to build toxins and it can cause diarrhea that is usually related to antibiotic usage. Clostridium or Clostridioides difficile is a germ which diarrhea as well as colitis which is an inflammation of colon and it can be life-threatening situation for patient.
Universal precautions
As a healthcare professional, it is crucial to take care different things and follow the universal precautions in order to control the infections. Since a healthcare professional cannot figure out each patient who can spread infection so, a healthcare professional should treat all human body liquids as if they were considered as infectious.
Hand washing
Hand-washing is one of the most crucial things to reduce the spread of infection in the organisation. A worker of healthcare organisation should adhere to CDS (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) and WHO (World Health Organisation) guidelines. Washing hands frequently with soap and water is considered as an excellent method to stop the transfer of infection from one person to another person. A healthcare professional must wash their hands at starting and end of their duty (NHS, 2024). Healthcare professional must utilise sanitizer for safety purpose. They should wash hands before and after each time when they contact with the patient who is suffering from C. diff. Healthcare professional needs to wash hand earlier and later using gloves, before eating and giving drugs to the patients. In case, if skin comes in direct contact with blood then it is most crucial for a person to wash with water urgently as it can harmful.
Gloves
As a responsible healthcare worker, it is crucial to wear gloves when there is expectation of hand contact with patient’s blood, possibly infectious materials or mucous membranes while conducting oral motor check-ups or aggressive treatment processes (NHS England, 2024). An appropriate utilisation of gloves while treating patient with Clostridioides difficile is highly beneficial to reduce the risk of transmits infection in other patients and workers. A workers need to follow the right procedure to remove the gloves after use. They need to be careful while removing gloves that no substances from dirty gloves contacts own hands.
Rooming
Patient who has Clostridioides difficile infection must place in private hospital room. If private room in the hospitals is not available that time then there must be separation between two beds. If there is space problem then, hospital can utilise privacy curtain to separate two patients and reduce chances of spread. Healthcare worker must supervise the patient all the time so that they cannot leave their place except medically compulsion. Patient room of must be cleaned time to time by hospital cleaner.
So, a healthcare worker who is supervising the patient with C. diff follow guidelines, protocols and take proper precautions. After each session, they must remove materials and things from therapy room, clean mouthed equipment and wear mask. They need to disinfect therapy table and wash their hands thoroughly after contacting with patients, utilising toilets or while exposure to possible spore-forming pathogens is suspected including throughout outbreaks of Clostridioides difficile infection. These precautions not only help to improve recovery process of patient but also reduce the spread and prevent other patients from infection.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal protective equipment (PPE) refers to equipment which is worn by healthcare professionals such as; doctors, general practitioners and nurses in order to reduce exposure to different hazards and risks. Before undertaking any kind treatment procedures, hospital staff must evaluate any potential exposure to blood as well as other body fluids, mucous membranes and chapped skin. As a patient is suffering Clostridioides difficile infection, it is essential for worker to wear PPE which protects sufficiently against the dangers related with the treatment processes (International EnviroGuard, 2024). Doctors undertake all the possible ways for providing care to the patients. It’s up to professionals to possess high-level knowledge regarding related risks and uphold sanitary environment. Disposable protective clothing considers as defence system against Clostridioides difficile spread. These are rules, a worker must know regarding increasing the utilisation of PPE.
Healthcare professional must wear aprons, masks, eye covers and gloves while offering treatment for people with C. diff. It is important to note that PPE kit which includes gloves, mask and aprons must be discarded quickly after patient-care activity. After discarding PPE, hand hygiene should be performed for further prevention of infectious disease (Barker et al, 2024). Personal protection equipment minimises the risk of C. diff transmit among providers, staff members and patients and can remove issue of facility-wide colonization. Elderly patients are taken as most contagious when symptoms of Clostridioides difficile like diarrhea are show before treatment as initiated. At this phase, skin to skin as well as skin to clothing contact is prospective to communicate C. diff infections.
Healthcare workers and cleaners are advised to wear personal protection equipment as it provides high level of protection. Antibacterial soap is useful for hand wash after removing clothes. Gel sanitizers in also good option for hygiene purpose. After existing C. diff patient room, a worker should remove and dispose PPE in particular order. First they must remove gloves, then eye coverings and lab coat and at last remove mask. Complete their exit strategy through carefully washing hands before going to other patients, team members or home. It is crucial for the worker who supervise patient with C. diff to dispose gloves and other things which are not reusable in dustbin with the proper safety. A worker must clean their clothes separately and not with other clothing as it helps in reducing the transmit of infection.
It is vital that elder care services and healthcare settings offer staff members with the essential personal protection equipment at each level to preserve the high level of health and safety standards. While Clostridioides difficile ranks among most common health illnesses in senior care services, workers, care givers and cleaning staff should remain attentive regarding unknown dangers as well. There is also proof that PPE significantly helps in reducing C. diff. In general, preventing as well as controlling transmit of all kind of diarrhoeal illness is necessary. Hand hygiene plays a most crucial role in it. Correct method for hand hygiene and wear PPE is always implemented to improve the patient outcomes.
References
Books and Journals
Barker, L., Gilstrap, D., Sova, C., Smith, B.A. and Reynolds, S.S., 2024. Reducing Clostridioides difficile Infections in a Medical Intensive Care Unit: A Multimodal Quality Improvement Initiative. Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing, 43(4), pp.212-216.
Online
International EnviroGuard, 2024. PPE and Protective Clothing for C Diff. [Online] Available through < https://int-enviroguard.com/blog/protective-clothing-for-c-diff/ > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
NHS England, 2024. Chapter 1: Standard infection control precautions (SICPs). [Online] Available through < https://www.england.nhs.uk/national-infection-prevention-and-control-manual-nipcm-for-england/chapter-1-standard-infection-control-precautions-sicps/ > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
NHS, 2024. Clostridium difficile (C. diff) infection. [Online] Available through < https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/c-difficile/ > Accessed Date: 30-01-2025
Mastering complex nursing concepts—such as pharmacology, NEWS2 scoring, and infection control—is essential for delivering safe, competent care. However, students often struggle to understand clinical frameworks, medical terminology, and evidence-based practice under tight deadlines. If you’re preparing similar coursework or need guidance structuring academic nursing tasks, online assignment help can make learning clearer, faster, and far less overwhelming, ensuring you submit accurate, high-quality work that reflects professional standards.
Go Through the Best and FREE Answers Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/nip-1902-summative-workbook-answers-45699
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/nip-1902-summative-workbook-answers-45699
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/nip-1902-summative-workbook-answers-45699
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/nip-1902-summative-workbook-answers-45699
- FreeDownload - 207 Times3.1 Analyse factors that influence the capacity of an individual to express consent
Introduction - Analyse factors that influence the capacity of an individual to...View or download
- FreeDownload - 158 Times1.2 Explain the main points of health and safety policies and procedures agreed with the employer
Introduction: Explain the main points of health and safety policies and...View or download
- FreeDownload - 661 TimesCare Certificate Standard 7 Answers: Privacy and Dignity
Standard 7: Privacy and Dignity Workbook Answers The "Standard 7: Privacy and...View or download
- FreeDownload - 913 TimesKey Answers and Explanations for Standard 9 Awareness Workbook
Standard 9: Awareness of dementia, mental health, and learning disability...View or download
- FreeDownload - 1929 TimesAnalysis Of The Strategy Of KFC Compared To Other Fast-Food Brands
Analysis Of The Strategy Of KFC Compared To Other Fast-Food...View or download
- FreeDownload - 223 Times3.1 Describe different types of accidents and sudden illness that may occur in own work setting
Introduction - Workplace Safety: Common Accidents and Sudden...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



