Performance Optimization of a Racing Car Engine Using FEA Case Study
A Case Study on Triumph Street Triple 675 cc Engine Design and Analysis
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Introduction
Improving the performance of vehicle engines is a vital problem of current study in automotive engineering, especially for racing car application since power, efficiency, and reliability are critical aspects of such engines. The Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine is a motorcycle engine, which has the three cylinder design, high power-to-weight ratio and could be easily introduced into the racing cars. Thus, this work moves from theoretical analysis to qualitative research methodology and deals with the design and optimization of the major engine parts, which include piston, crank shaft and connecting rod by using the software, SolidWorks with the support of Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Consequently, this study will focus on the improvement of FoS (factor of safety) and the repetition of material selection in order to optimize the efficiency and performance of the racing car engine Focusing. This work aims to provide effective propositions for a real-world application solving issues with performance Enhancement of competitive motorsports with the aid of computational tools.
1.2 Background of Study
The engine of Triumph Street Triple 675 cc is considered powerful and versatile in motorcycles to deliver nearly 105 horsepower with reduced weight. However, to apply such an engine to the racing car certain of its weaknesses should be attended to due to the enhanced mechanical and thermal stresses in racing car situations, particularly in case of a high speed racing. Past research works concerning engine optimization have dealing with the aspect such as fluid dynamics, advanced material and simulation methods with the help of CFD or secondary data. For example, the use of light-weight materials such as titanium and aluminium in the construction of engines has been established as having the effect of decreasing the engine mass while at the same time increasing the strength and use of FEM to enhance the durability of the component has also been realized. This work extends this kind of an argument but shifts to the use of primary research where using SolidWorks to model the piston, crank shaft and connecting rod, then using FEA we evaluated the model and optimize it for racing loads [1]. This approach concerns a specific application – racing cars where engine has the opportunity to be transformed from its motorcycle background.
1.3 Research Aim
The overall goal of this study is to modify and improve the specifications of the piston, crankshaft and connecting rod of Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine for racing cars, using such techniques as 3D modelling and FEA to increase efficiency, power and ability to handle loads. In this respect, the study aims at achieving a range of material configurations that would serve to continuously generate results that would enable yielding the best design that would correspond to the racing condition.
1.4 Research Objectives
In order to address the research aim of the study, the following research objectives have been developed:
- To create 3D models of the piston, crankshaft, and the connecting rod with all the specifications of Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine.
- To use FEA to check the feasibility of this design where the factor of safety, stress, and deformation under racing car loads need to be determined.
- To identify the new materials to be incorporated to enhance the power-to-weight ratio and the strengths of their components.
- To confirm the efficiency of optimized components against baseline designs for racing application use.
- To make recommendations on possible modifications towards the Triumph engine-racing car powertrain.
1.5 Research Questions
The researcher pose the following research questions:
- How do material changes influence the factor of safety and efficiency of a piston, crankshaft and the connecting rod under racing condition?
- Which of these modifications in these components improves the output and power of racing car?
- In what ways can FEA be applied to enhance Tuning of Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine for high performance racing?
- How much better can a primary design and analysis make the performance of an engine than stock configuration?
1.6 Research Rationale
Automobile racing implies that the engines should deliver great power and be very reliable, and all these at high speeds. The Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine is otherwise suitable for motorcycles but would not totally transfer well to racing cars if its major components cannot take high loads and stresses. Many results of physical prototyping consume a lot of resources to construct, which makes this study to use SolidWorks and FEA to produce prototypes digitally in order to save on costs and provide clipping to the optimal end product. Other literature reviews only discuss material and design effects on the performances of engines [2], while there are very limited literature on applying existent motorcycle engines like Triumph 675 to racing cars based on primary data analysis. This research will help to fill this gap by presenting design recommendations, which could be further tested in experiments and help to develop racing engine improvements.
1.7 Research Significance
There are various practical implications of this study which includes:
Performance Innovation Working: It has a practical design improvement for the racing car engines using a successful motorcycle platform.
Engineering Advancement: It also shows a method by creating a finite element analysis and 3D model and can be used on any engine part.
Industry Impact: Possible advantages may include availability of light-weight yet strong powertrains for motorsport teams which would increase competitiveness.
Racing Efficiency: Through component optimization, the durability of a race car may be increased and as a result, potential cost of maintenance lowered, thus bringing about economic benefits.
1.8 Research Framework
Figure 1: Research Framework
1.9 Conclusion
This research work is on the performance enhancement and measurement of the Triumph Street Triple 675 motorcycle with regard to timing, materials used, and piston. To succeed, the goals of the study are to improve power output, fuel efficiency, and durability and its components by using theoretical methods only and no engineering changes.
Thus, the study will mitigate the challenges affecting automotive engineering while promoting its development based on sustainable features. These outcomes will serve as the groundwork for other research in the form of experimental procedures that impact engine development and optimization processes. This paper designs Triumph Street Triple 675 cc for racing cars by conducting primary research on the piston, crankshaft, and connecting rod. By using SolidWorks and FEA, it plans to improve power, efficiency, and durability, which provides the foundation for the future racing engine designs.
2. Literature Review
2.1 Introduction to Engine Optimization
Engine optimization is currently a significant step in automotive engineering that focuses on increasing the performance, efficiency, as well as the sustainability of the internal combustion engines. The Triumph Street Triple 675 is one of the most recognized motorcycles offering superb handling and excellent power delivery hence the need to continue with improvement in the design of the engine [7]. With the constantly raising issues related to environmental degradation and fuel efficiency standards, the concern has been made to maximize the engines. The present work thus aim at discussing several methods and techniques used in the particular engine optimization with reference to Triumph Street Triple 675. In this review, issues relating to valve timing, airflow, material science, piston as well as ECU will be tackled with an aim of coming up with extensive understanding of the theoretical and practical development in the engine technology. Also, it emphasizes the relevance of sustainability when it comes to engine design which is a noble cause in promoting clean technologies.
2.2 Valve Timing and Control
Valve timing is one of the significant parameters within engine manufacturing that determines the effectiveness of the combustion process, the power that is produced, and even fuel consumption rates. The engine’s efficiency therefore depends with the accurate regulation of times the valves open and close to allow air and fuel into the combustion chamber. According to the context of Triumph Street Triple 675, there can be improvements that could be done with relativity to the valve timing.
As mentioned earlier the angle of the valves has an effect on the combustion of the air fuel mixture with the result of better performance as shown by other scholars in their research [8]. Hardware implementations include the variable valve timing (VVT) where engine adjustments are made based on certain conditions; such adjustments allow for variations in speed as well as in loads. In particular, VVT systems are effective where low-end torque and high end horsepower are the key engine requirements, as is the case with Street Triple 675 Triumph motorcycle.
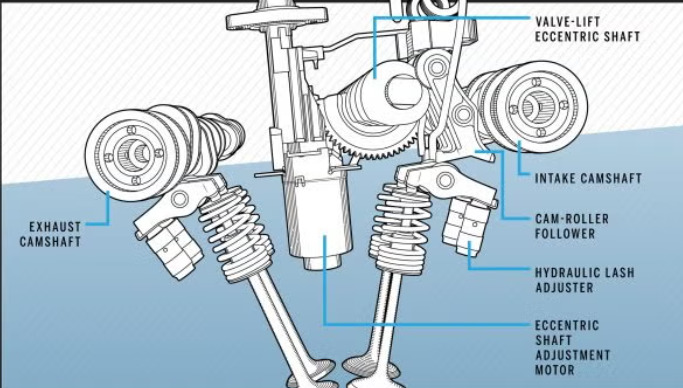
Figure 2: Variable Valve Timing
There are many examples of the implementation of VVT systems, for instance, in motorcycle brands like BMW, where such modifications have enhanced the permutation of the car’s throttle and decreased exhaust emissions [9]. Through the proper adjustment of lift and length of the time of opening the valves, engineers are in a position to optimise combustion process and therefore improve fuel economy and output.
Furthermore, the changes in the valve timing have an advantage because they can be simulated, and the outcome evaluated without the use of physical models. It also explained the ability of researchers when it comes to testing various configurations of the engine by coming up with the best valve timing to enhance efficiency of the design of the engines. This means that the timing and control of the valve provide considerable enhancement in the operation of the engine particularly in the aspect or output and efficiency. But, still, there is room for enhancement in a similar kind of engines, such as Triumph Street Triple 675 with the help of technological developments along the computational analysis, not omitting the global bio-mechanical goals of sustainable and more efficient engineering.
2.3 Finite Element Analysis in Engine Components
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is now utilized in heavy engineering industry fundamental in withering of components, to estimate and evaluate the stresses, deformation and the thermal criterions at the working loads. It is highly useful for internal combustion engines in which various parts like piston, crank shaft and connecting rods are subjected to high mechanical and thermal loads especially in racing engines. Some of the recent studies indicate that FEA assists in improving such aspects as efficiency, durability and weight thus helping in optimization of engines such as the Street Triple 675 cc with a racing car performance.
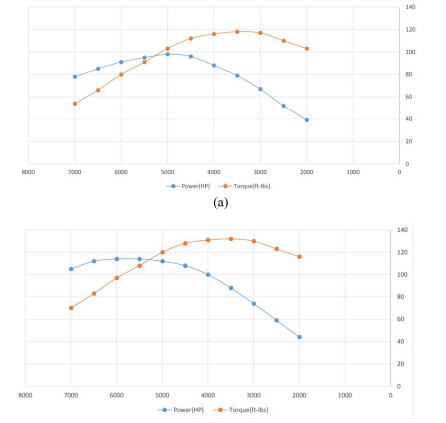
Figure 3: engine power graph of initial and optimize model
Another interesting study reviewed within this paper investigates the utilization of FEA in determining the vibration and strength of an aluminium piston installed in the Peugeot XU7JPL3 engine [10]. This paper will identify the principle areas for enhancement of the piston and carry out FEA on stress and deformation of the piston under combustion loads. Based on the simulation results of different loads, the authors defined areas with high stress concentrations and adjusted the shapes and materials of the piston in the current study and the previous study to find a good relation between weight and strength. Aluminium was applied in the design and the material was confirmed via FEA to offer less weight subjected to high performance requirements. This is particularly relevant to Triumph 675 piston, where the baseline is an aluminium alloy (201.0-T43) and FEA can help to find lighter material like titanium for race use.
Similarly Navathale and others have given an extensive review on FEA used in crankshaft of internal combustion engines [11]. The information on stress analysis, fatigue life and optimization techniques are synthesized where the crankshaft is an important element that transmits power under dynamic loads. With the help of FEA simulation methods, one can see how some choices of the material dilemma, for instance the change from cast alloy steel to titanium, can minimize the overall mass while achieving appropriate levels of bending and torsional stress – a characteristic which is very important when working at high RPM under the conditions of racing engines. The review confirms the applicability of FEA to determine failure areas and gives recommendations on how to improve counterweight designs of the Triumph crankshaft as a feature to improve performance in a racing car.
These researches proved FEA usefulness in analyzing various components of an engine, enabling engineers to introduce a highly efficient virtual environment for the processes of testing and modification. FEA assists in the optimization of the material and modification of design, given states closely resembling racing atmosphere and conditions, thereby minimizing the need for expensive prototypes. In the case of Triumph Street Triple 675, FEA can be used to bring the gap between motorcycles as peoples’ daily rider and racing car as far as material and structures are as light as possible which can take maximum load.
2.4 Material Science in Engine Design
The material science has significant impact on the structure, working capacity, effectiveness of the engines. It is also important to select materials for the engine assemblies especially for high-performance motorcycles like the Triumph Street Triple 675; for better power-to-weight ratios and durability. New materials’ technologies have also been developed to the extent that makes it possible to construct light and strong materials that increase the engine performance and decrease toxicity.
One of the major aspect of material science in the design of engine is the lightweight material including the titanium and aluminium. These materials are lighter but stronger and therefore can be deployed in the production of engine parts such as the piston, connecting rods and valves. For example, Titanium has very high strength to weight ratio, and high corrosion resistance and can therefore be used in components that are subjected to stressed as well as high temperatures [7]. As for Aluminium alloys, they offer a good balance between weight and cost, so they may be used in the creation of engine blocks and cylinder heads [8].
Several advanced computational tools have improved research and development in discovery and design of new materials relevant to engine applications. Similar online platforms for simulation in materials science research are for example ALKEMIE that offer increased levels of computational competencies and help scientists analyse the characteristics of materials depending on different conditions [12]. These tools enable quick scanning of the candidates to sample in order to select elements that could meet required cutlery for certain parts of the engine. With the help of computational materials science approaches, the authors mentioned that the current problem of material selection and design can be improved and, consequently, the material components of the engine can operate more efficiently and durably.
There is also light emission from engines through the use of composite material in the construction of the engine. Composite materials are those materials which are formed by using at least two distinct material types which have different characteristics; these are some of the benefits associated with composites; these are improved strength, low density, and properties of erratic thermal conductivity. For instance, carbon fibre reinforced plastic (CFRP) materials are gradually finding their way into manufacturing high-reliability engines since they possess desirable features such as high strength to weight ratio and heat tolerance. These materials assist in reduction of weights and the resultant reduced fuel consumption hence being in conformity with sustainable engineer’s practises. Material science is a core area of the engine as the choice and creation of the new material directly contribute to the work of the engine and its eco-friendliness.
2.5 Piston Design and Friction Reduction
Piston is one of the significant design elements of the engine leading to efficiency, power, and durability of engines. They are directly involved in heat pattern within the engine, and combustion characteristics of piston is inarguably determined by the geometry of the piston.
The geometry and material composition of the piston play significant roles in its performance. Often, there is the complex crown shape and complex cooling systems to enhance the combustion process and heat removal. Conductive FEM has been applied in optimizing pistons for use in various operating conditions since it can explain thermo-mechanical responses from the simulations [13]. These simulations enable the engineering profession to work out the forms that make the best piston in terms of temperature and pressure whilst reducing thermal stress and distortion.
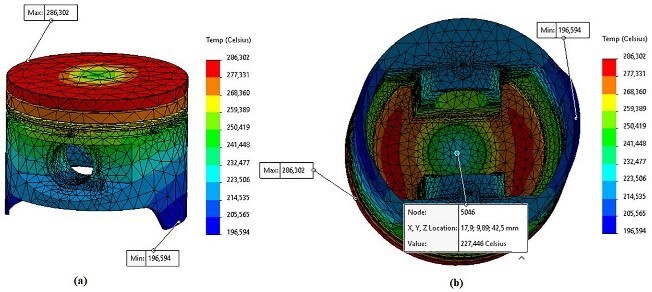
Figure 4: temperature distribution in the Piston
One other important factor in designing a piston is friction because; high friction is likely to lead to splendid loss of efficiency and cause faster wearing of the engine. Minimizing the friction between the piston and cylinders is another way of minimizing the energy losses as well as the wear of inner walls of cylinders thus improving on the fuel efficiency of the engine. Methods like coatings, various designs on piston rings, and incorporating materials with low friction are among the measures mostly used to reduce friction. For example, diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings are applied in the effort to minimize friction and improve wear resistance that ensure better function and durability of the engine [14].
In addition, the incorporation of enhanced lubrication system also assists in minimizing abrasion and enhancing efficiency of pistons. Using of engine oils containing special additives it is possible to create a layer on piston cage faces and thus to minimize friction and wear. Similarly the piston skirt and pin boss should be designed to spread loads to increase bearing surface and thus decrease friction and stress. Therefore piston design and friction reduction are among the critical components for improving both engine efficiency and reliability. The piston is an important mechanical component where with the help of modern simulation tools, new materials, and optimization concepts, new generations of engineers can develop pistons that can have better thermal management, surface friction, and durability.
2.6 Lightweight Materials for Racing Engines
The use of lightweight materials in racing engines is highly important in improving its performance this is especially so for specific racing engine such as Triumph street triple 675cc racing car engine. This reduces mass, which in turn has positive effects on power to weight ratios and power to load the kind of operating conditions that are typical in motorsports where engines must rev high, and stresses vary rapidly. Recent research shows that some of the materials this would include aluminium alloys, titanium, and composites with relation to the parts of the engine that include pistons, crankshafts, and connecting rods.
Light weighting in automobile industries is discussed by Busarac et al in the subject of performance-oriented designs [15]. The article revisits aluminium alloys and titanium which are deemed to have high strength to weight ratios and high corrosion resistivity that is appropriate for racing engines. Aluminium alloys like the 201.0-T43 that is used in both the Triumph piston and the connecting rod, retains less weight compared to steel by a significant percentage though a lot thinner than titanium with even more enhanced performance especially in extreme environments. The authors mention other materials such as carbon fibre reinforced plastics (CFRP) which possess low density and high stiffness thus useful in connecting rods for high performance conditions. These findings will strengthen material iterations for the Triumph engine where weight leads to better acceleration indicated by the Rules of thumb; fuel efficiency.
In a similar fashion, Czerwinski reviews trends on the automotive light weighting theme with an emphasis on material approaches to performance [16]. The authors also present how aluminium is commonly used in both pistons and connecting rods, which are cheap yet effective, while pointing out that titanium is used in crankshafts due to high strength-to-mass ratio. Materials such as CFRP are known to push for racing application due to their remarkable benefit that it is lighter than steel by 50% with considerable improvement in stiffness. According to such requirements, these materials conform to racing that requires minimum inertial mass and maximum sturdiness.
2.7 Sustainability in Engine Optimization
Sustainability has emerged as a crucial factor in the improvement of the engines as the world goes for reduced emissions. Current engine optimization is highly prioritized on improving efficiency while at the same time lowering emission levels and improving the use of renewable energy. These are critical as they assist in combating climate change and making sure that technological developments in manufacture of engines is not a threat to the environment.
However, these are some of the major concepts that are probed when implementing sustainable engine optimization and one area of emphases happens to be the use of other fuels. Actually, ethanol and methanol have come out as likely solutions to the reduction of fossil fuels and decrease emissions. From the previous studies it is evident that, better efficiency of these blends can lead to improvement in engine performance and drastic reduction in emission making them fit for BS VI standards [17]. Therefore, considering the proportion of carbonate and fuels and modifying the parameters of the engine it is possible to achieve an improved performance while still being environmentally friendly.
Apart from usage of the various types of fuel, even the improvements in the design of the engines and the control systems prolong sustainability. Methods like variable valve timing, control of airflow, and lightweight materials help in getting a good mileage and decreased emission at the same time. All these designs are meaningful improvements to motorcycles’ performance as well as reflecting fundamental goals of sustainable engineering by reducing the ecological impact as much as possible.
In addition, the application of computational tools and simulation in the study supported the ability of researchers in predicting the various effects that could result from the changes in the engine. Through computational fluid dynamics and different engine structure and fuel content scenarios, the engineers can determine the feasibility of various solutions in terms of sustainability without prototypes. This contributes positively to the quick advancement of environmentally sustainable engine solutions and the shift to greener modes of operation.
2.8 Literature Gap
Although there are numerous papers available with valuable information about different aspects of engine optimizations, there are still several areas that have not been studies extensively and thus require further research specifically for the Triumph Street Triple 675 engine. Another limitation is the general availability of few research on the Triumph Street Triple 675, specifically they address general issues of engine optimization or/and other models only. This entails the need for specific research works that will examine this HPEM motorcycle engine and the various parameters and conditions that it meets or goes through.
Also, the biggest part of the current studies is based on the experimental and testing procedures with relatively small coverage of theoretical and numerical investigations. Thus, additional development is required for improvement of more powerful computational models and analytical simulations that would allow adequately predicting the engine performance and the outcomes of optimization tasks taking into consideration the existing physical limitations of practical testing. In such models, engineers would be able to evaluate a number of changes and improvements to the design which are possible but would usually require a huge expenditure to implement through physical prototypes.
Besides, the sustainable effects of the optimization processes are either not considered at all or are considered as additional factors. Since the environmental impact is receiving more attention gradually, there is a rising concern for papers that address sustainability as well as the performance. This is regarding developing the various alternatives of fuel, improving emission less technologies, and employing environmentally friendly materials in the construction of engine.
2.9 Conclusion
This paper aims at reviewing the literatures that comprise a crucial aspect of the engine, mainly on Triumph Street Triple 675. Areas including the timing of the valves, air flow, material used in the making of the valves and pistons, ECU reprogramming, and environmental impacts have been discovered as the areas that can be modified to produce better engines. However, some research gaps exist, especially those specifically related to this particular engine and the lack of following sustainability as a main goal. Filling these loopholes through simulations and prototype testing will provide positive impacts to the fuel efficient and environmentally conscious high-power motorcycles in the future
3. Project Management
Project management of any kind of project is important more especially if it is a research related project such as optimizing the Triumph Street Triple 675 engine in racing cars. The following are the collaboration and learnings: This section provides the details on the project management approach that was applied in decision-making involving risk assessments and the use of an updated plan in managing the project.
3.1 Introduction to Project Management
Project management in relation to engine optimization entails the designing of activities, resources and other users to ensure that the objectives of the research are accomplished effectively and on time. The main objective is to increase output and durability of Triumph Street Triple 675 engine when used in racing cars. This needs systematic method of development, implementation, evaluation, as well as supervision that must focus on each of the undertakings of the research project to meet its objectives.
3.2 Risk Assessment-Driven Decision Making
Managing risks is a crucial process in project management, especially in a complex research project such as engine optimization. It affects the project because identifying and overcoming any risks that can possibly occur lead to the success of the project. The next steps are an outline of decision-making process based on risk assessment:
- Risk identification: The first element involves being able to identify risks that might be associated with the project. Possible risks vary from technical, such as implementation of new techniques or software, no enough resources for the experiment, unexpected results because of failure to meet the required legal and regulatory procedures. The identification of risk can be accomplished through literature reviews, discussions and interviews with the research team and other stakeholder and analyses of other similar completed projects.
- Risk Assessment – Once analyzed, risks are assessed to see the extent of impact it may have on a particular project. This is done by evaluating the probability score of each risk and the impact of the risk that it will bring. Risk matrices and probability – impact grids are used in order to categories the risk according to their potential effect and likelihood.
- Risk Management Strategies: These are plans that are devised focusing on reducing the effects of risks that had been established. For instance, if the research entails technical drawbacks, it is easy to search for other alignments, consult professionals or utilise simulation software. Lack of resources can be managed by seeking for more funds or by improving the ways of how these resources are used.
- Risk Management Process: Decision-making framework is utilised to help the project team on how to handle the risks. This framework consists of procedures of risk reporting, escalation and handling of the risks when they occur in the course of the business operations. It is also normal to perform risk reappraisal in order to determine the efficacy of the applied risk control measures and adjust the risk management plan where necessary.
3.3 Use of Updated Plans throughout the Project
The project should always have the updated project plans in order to operate in a way that suits the project objectives and climate. The following practices are used to enhance the use of updated plans:
Plan reviews: Project plans are undergoing regular reviews to cheque for progress, deviation and make the necessary changes as a result of the analysis. These reviews are done with the key stakeholders and the members of the team so as to establish work on the same page and on schedule.
Schedules: The project plan is very much adaptive in the sense that it provides room for change when new information is availed, when priorities change or when a certain challenge arises. It is a good thing to have this flexibility to allow the non-conformity of the project to the traditional structures but at the same time, there must be a little of order to ensure that the project is not free for all to lead without direction.
Project Tools: Sophisticated tools like the Gantt chart to create project schedule, monitor its implementation and to manage the interdependencies. They give a clear picture on the work being done hence assist the members of the team to make the right decisions and happenings.
3.4 Gantt Chart for Project Timeline
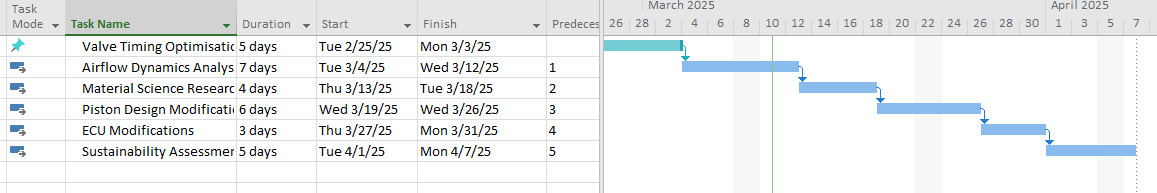
Figure 5: Gantt chart
In the construction of this particular Gantt chart, other activities include the literature review, risk identification as well as the assessment of the risks, choosing the method of experimentation, data collection, data analysis, and more. Each of them is pre-stipulated to have a certain period of time and associated with other tasks that depend on its completion, which gives an overall picture of the project schedule.
The Gantt chart in particular is used throughout the implementation of the project and serves as a management reference. Gantt chart ought to be changed periodically so as to provide an updated representation of the actual state of the project, which will help in decision making and changing status if required.
4. Project Experiment or Design Specification
4.1 Introduction to Experiment Specification
This research modifies the Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine for racing car through primary design and analysis of the piston, crankshaft, and connecting rod. Specifically, employing 3D modelling software in SolidWorks as well as conducting Finite Element Analysis (FEA), the study ensures that these parts are optimized for race conditions using lightweight materials resulting from high RPMs and combustion loads. Introducing new materials and analyzing them using FEA brings this project from theoretical analysis to practical application and modifying the engine for competitive motor sports..
4.2 Design Specifications for Engine Optimization
Valve Timing Optimization:
In the case of optimizing, the key objectives are to reduce the weight of the product but at the same time, work on the improvement of the efficiency of the piston, crank shaft, and connecting rod based on certain specifications the following are some of them;
Piston:
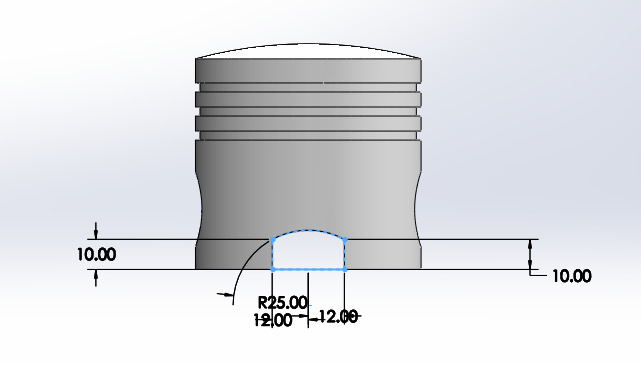
Figure 5: Piston design
- Material: Aluminum (201.0-T43 Insulated Mold Casting) is used in the first design of the part; different variant of alluminum may be considered to reduce weight.
- Durability: Special coatings include low friction coatings such as diamond like carbon (DLC) to reduce losses during high speed usage [15].
- Design: Reinforcement of the crown to withstand racing stress.
Crankshaft:
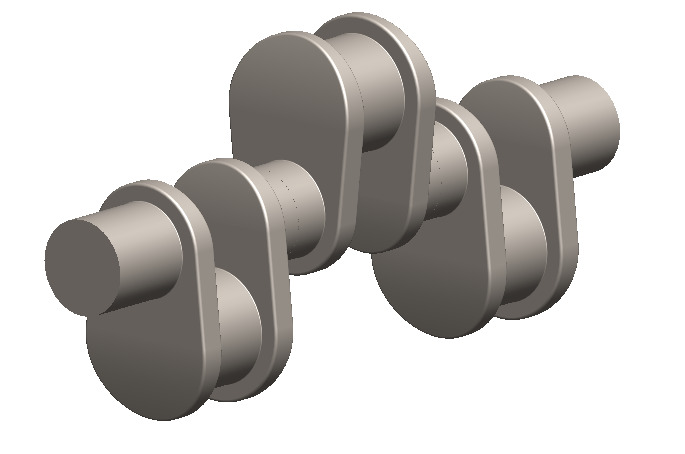
Figure 6: Crankshaft design
- Material: Begins with cast alloy steel; titanium used for decreased weight on some models.
- Configuration: Three-throw lay out with counter weights to contain the high RPM as is the case with racing engines.
- Challenge: Achieving such goal requires meeting additional exercises aimed at strengthening muscles at the same time.
Connecting Rod:
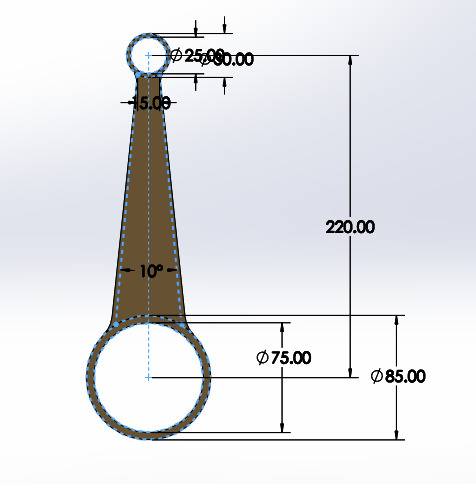
Figure 7: Connecting Rod design
- Material: The base material is the aluminium alloy 201.0-T43 Insulated Mold Casting; the other alternatives are the lighter material like titanium as well as carbon fiber reinforced plastic i.e. CFRP.
- Design: Special reinforced ends for the load that takes when racing.
- Objective: Lower inertia for improved efficiency.
These specifications are to enhance the power-to-weight ratio, and efficiency; the FEA shall lead to material based optimization.
4.3 Experimental Setup and Procedures
There is also the use of SolidWorks and FEA for making and developing components as well as stressing on materials to minimise the weight and improve the efficiency. The process includes:
3D Modelling:
Establish the piston, crankshaft, and connecting rod models of Triumph 675 engine using SolidWorks.
Allocate materials at first: crankshaft and connecting rod are made of alloy steel; piston is made of aluminium alloy, 201.0-T43 Insulated Mold Casting.
FEA Setup:
Loads: Styling designs to racing conditions; combustion chamber pressure and inertial forces at 14,000 Revs per minute.
Boundary Conditions: Fix the crankshaft at both ends, place the piston at the pin connected to the crank, and connect the rod to the crank and piston.
Mesh: Use a fine tetrahedral mesh for accurate stress analysis.
Baseline Analysis:
Some of the specifications that need to be computed through FEA include the weight, the stress or the efficiency that is implicated by the initial materials.
Establish performance benchmarks.
Material Iteration:
Suggested changes: Change the materials (Titanium, CFRP) with those with lower thickness and perform FEA analysis once again.
Objective: The goal is to achieve weight loss (for instance, more than 10% lower than the initial weight) with FoS higher than 2 and stress level – low.
Validation:
Benchmark the designs to the basics of lightweight structures and ways of improving efficiencies.
This unique approach helps to achieve lighter and more efficient parts as per demands of racing.
4.4 Data Collection and Analysis
For Triumph 675 engine, sources of data include technical documentation with information regarding components layouts, stock materials, and for the materials, properties like density and strength could be obtained from engineering databases. FEA provides key outputs:
- Weight: Tracks reduction per material change.
- Stress: Examines peak values in order to verify strength.
- Efficiency: Evaluates power-to-weight gains.
Comparison is made between baseline designs and optimized ones such as cast alloy steel crankshaft, aluminium alloy piston and rod to optimized designs such as titanium crankshaft, CFRP rod made in SolidWorks Simulation. Incremental improvements refine specific locations that meet racing requirements at the least weight and verified by stock-car performance.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1 Introduction
Street Triple 675 cc engine modification for racing involves a comparison between the original design and the one developed for this study. This chapter provides the result analysis, based on the software simulation and Finite Element Analysis of major engine parts namely - piston, crank shaft and connecting rod. This means that the study seeks to improve the performance as well as the efficiency and reliability of the engine through the application of new materials in the design. 3D modelling with SolidWorks application is used and have checked the level of stress and deformation experienced on the engine with FEA analysis depending on the material and configuration of the engine when racing. From this analysis, it is clear that the modifications yield a considerable increase in weight loss, stress, and factor of safety all of which are vital in race car engines. The findings related to the first and second engine designs will be reviewed in this chapter with regard to what exactly happened in terms of material changes and design improvements on the properties of the engine design. Through these analyses, it is hoped that notions towards possible advantages of integrating engine optimization in competitive motorsports will be established to advance the field of engine design and innovation.
5.2 Analysis of Initial Materials and Assembly
The first generation of the Triumph Street Triple’s debuted a 675 cc engine which contained conventional materials normally used in the construction of bikes’ engines. The crankshaft was of cast alloy steel which was a proper material for fabricating crankshafts because it has a very high tensile strength to contain high stresses and loads normally encountered in the engines. Consequently, the connecting rod and the piston were both constructed out of aluminium alloy 201.0-T43 Insulated Mold Casting, light and strong at the same time, perfect to keep the efficiency and performance in cheque of the engine. The piston pin was made from AISI 4130 steel well-known for its tensile strength as well as fatigue strength ideal for parts that undergo cyclic loads.
At this design, the assembly mass was estimated to be 21795.11 grams. Mentioned mass is important because it outlines the starting point of subsequent material and design improvement evaluations. It is at the initial assembly that it is easier to look for the areas where weight shave off and performance improvements can be made without necessarily compromising on strength. These are basic materials selected it with an aim of balancing on cost, ability to manufacture and the performance of the material. However, the specifications related to racing applications require additional refinements so as to achieve higher power weight ratios and withstanding racing conditions. An understanding of what has been done in material substitution and designing of the different models would better be understood when we take a look at such aspects of the initial components and assembly.
5.3 Boundary Conditions and Loading
As seen in the simulation of Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine, determination of these boundary conditions and loading will help mimic the real operating conditions of the engine. The boundary conditions devised in this study are works to restrict and support the actual environment which the engine components came through during its operation. In the case of the crankshaft, there are fixed supports at both ends of the crankshaft, and between Connecting rod and crank shaft as shown in the figure 8. These conditions are crucial for modelling the actual operation conditions of the engine where the crankshaft is firmly fixed on the engine block while the connecting rod couples the forces of the piston on the crankshaft.
The feature most relevant to the task of simulating the engine is the load that acts on its components on the outside, as this will determine the stress and deformation that the part can undergo. For the present analysis an external load 653 psi is acting at the top of the piston as depicted in the Fig 9. This load would be characteristic of the pressure that is placed on the piston during the power stroke of the engine in which a fuel air mixture is ignited and the pressure from the resulting explosion pushes the piston down. Reproduction of this load is crucial for understanding the state of the required check of the integrity and reliability of the engine parts in working conditions.
With the help of such boundary conditions and loads, it is possible to perform the stress analysis of the engine parts and their displacements as well as strains. When the above conditions are applied in the engine model we are then able to determine areas of high stress and probable failure which is very much useful in the determination of the type of design and materials to be used. This approach ensures that the optimized engine components do not only perform to the optimal standards required for racing applications but also presume their reliability and structural strength when put under racing conditions.
5.4 Mesh Generation and Simulation Setup
Meshing is a very important process in the Finite Element Analysis (FEA) as it determines the quality of the final results obtained. As depicted in Figure 10, in this study, a fine tetrahedral meshing Procedure was done on the engine components. This parameter has been determined in a way that can allow the level of mesh density to capture the stress and deformation level of components in the engine effectively. Therefore, a fine mesh is more relevant in areas of high stress, where connection between the piston, the connecting rod, and the crankshaft is critical to determine the likely breakdown points.
Modelling was done in SolidWorks while FEA was used to analyze the engine components in racing situation. This was possible since the software gave the ability to set realistic boundary conditions and loads as seen above. This exercise was set to mimic high RPM as well as combustion levels characteristic of racing engines to give a comprehensive analysis of the engine under test racing conditions. The assumptions that were made during the simulation setup were; the linear material properties and that the material behavior of the engine components was isotropic. These assumptions do not affect the overall conception of the solution and make it easier to explore the structure of the engine. It also included the dynamic aspects of the engine operation and these were directed to the stages of the combustion cycle when stress and loads are extremely high. It was ensured that the mesh generation and simulation parameters used in the FEA give out real live performance of the Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine and thus can fairly measure the success of the attempted design enhancements.
5.5 Stress Analysis
Stress analysis is considered as one of the crucial steps in the process of engine optimization since it helps to determine how various materials or the same material arranged in different configurations will behave under load in the course of their usage. The first analysis of stress, as shown in figure 11, provides valuable insight about the stress concentration throughout the parts of the engine.
In their first design, they find out that the peak stress occurred at the connecting rod which is at the region near to the piston. The stressing value in this region having the maximum value of about 4.881 x 10^4 psi. This is high stress signifying the amount of pressure transmitted through the connecting rod during the time of the power stroke where the combustion pressure is maximum. The increased degree of stress in this area could mean that there is a failure risk in the design or material used if not done properly.
The stress analysis, conducted on the new proposed model having the crankshaft and connecting rod made by Titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) and piston made up of Aluminium-lithium alloy (Al-Li) provided better results. Although the stress values are calculated to be concentrated in the similar area where the initial design has been drawn, the maximum stress values are comparatively less. They can also promote stress reduction to new materials owing to their better strength to weight ratio to tolerate higher loads than earlier deforming or failing.
The application of titanium alloy which is well known for its high strength and light weight also helped in reducing stressed concentrated on the connecting rod and crank shaft. This also means the material can easily withstand high stresses without getting fractured; a factor highly applicable in races automobiles where engines are always under pressure. This was coupled with an aluminium-lithium alloy used on the piston to ensure the right amount of strength and minimum stress. The selected parts or those proposed to be modified have reduced stress concentrations as they originated from or have been developed to possess superior mechanical properties to support high racing demands. The following discussion of material selection in engine optimization show that the advanced materials enhance the capacity of overall structural and seasoned components of the engine.
5.6 Displacement and Strain Analysis
Displacement and strain analysis are significant for determining the deformation of the engine components under load since this information will help to understand how often the part may fail during its actual function. Figure 12 shows that in the first analysis of displacement, it highlights that maximum displacement is at the vicinity of the piston. This is as and expected because it is where the piston is directly influenced by the force of combustion pressure and thus is pushed along the cylinder. The displacement evidenced in the first design is also the freedom and motion required for the piston to transfer energy to the crankshaft. However, excessive displacement can lead into high levels of wearing and in extreme conditions the failure of the components.
As expected, in the optimized model, all displacement values were as per initial design concept but the value of the displacement got reduced. This is due to the effort to use light and strong materials like titanium alloy and aluminium lithium alloy that resist deformation at higher loads. The reduction of the amount of these displacements in the verified optimized components will therefore enhance the stability of the structure that has positive implication in the enhancement of the performance of the engine and its endurance during racing activities.
Strain analysis as shown in figure 13 is used to determine the level of deformation of the individual components and at part locational level. In the initial design the highest stresses were observed around the connecting rod especially at the juncture with the piston. The highest strain recorded was 3.932 x 10^-3 psi which may cause the occurrence of significant deformations that can results to fatigue failure in the long-run.
As shown in the case of the improved design, the outcome of the strain analysis showed that maximum strain decreased down to 2.471 x 10^-3 psi of the same areas. This improvement has been as a result of the material properties of new alloys which show better characters in term of deformation and load distribution. The above optimized components subjected to lower stress level would imply less chances of fatigue and failure and therefore contribute to higher durability and reliability of the engine.
Looking at the displacement and strain results between the initial and optimized design, it is possible to see how material optimization leads to the reduction of the above measures. This leads to improved structural content of the optimized engine components since higher grade materials are employed and this fits the racing application demands. This analysis serves to stress the significance of material choice as well as design improvement in the subsequent design of engines that are more efficient and long-lasting.
5.7 Factor of Safety
The factor of safety (FoS) is an important design factor which means strength of the material divided by the maximum anticipated stress. It is used to determine the margin of constraint that is the amount of load that the component can take more to failure. More factor of safety is preferred for an engine in the context of engine optimization since the performance conditions involve particularly hard conditions characteristic of racing.
From the initial design, the factor of safety analysis plotted as shown in the figure 14 below indicated that a lower value was likely to occur around the connecting rod region jointed with piston. These regions based as high stress and strain regions are potential regions of failure if the material and design of the component is not strong enough to withstand the stress forces acting on it. The first observation was the material and design test to improve the factored safety and to guarantee that the components of the engine can endure racing demands without the tendency to deteriorate the performance of the vehicle.
The analysis done on the optimized model showed that the factor of safety has increased and the minimum factor of safety of the structure rose to 3.1as shown in figure 15 above. This improvement can therefore be attributed to the changes of the material used in the designed optimum version. This improvement was brought about by the application of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) for the crankshaft and connecting rod as well as aluminium-lithium alloy (Al-Li) for the piston. These materials can support more loads without failure and thus they possess higher factor of safety as compared to other materials.
Higher factor of safety in optimized component shows higher reliability and sturdiness which is relevant to the engines used for racing since they are subjected to higher pressures and loads. A higher factor of safety ensures the engine parts to bear the high stress of the high performance racing; thus, making the engine more reliable and durable thus increasing its life cycle.
This analysis reveals that an improved factor of safety is attainable by effecting some material selection at some ribs. The cylinder linings and rods used in the optimized engines are of higher mechanical properties that not only satisfy the performance criteria but offer a higher safety margin so as to function consistently under racing environment. This improvement in the factor of safety is a clear implication of the optimization process and show a general implication for enhancing benefits of utilizing advanced materials in the structural design of engines.
5.8 Optimized Model with New Materials
The racing applications demanded the Triumph Street Triple delivers 675 cc within an optimized model that brought about an advanced creation in the engine type. This was the main optimization that considered the partial replacement of traditional materials by innovative lightweight ones with better performance, reliability as well as profitability.
Material Selection and Benefits:
Crankshaft and Connecting Rod: Originally, the material utilized in constructing crankshaft and connecting rod is cast alloy steel and aluminium alloy; the same has been substituted with near-beta titanium alloy known as Ti-6Al-4V. Titanium is widely known for its elastic–plastic properties, low density, and resistance to corrosion, heat and fatigue. These properties make it an ideal material for use in the parts that are subjected to tensile and compressive stresses and loads such as in racing engine. The shift to titanium also offered improvements of the same parts that went into the assembly of these parts resulting to a reduced assembly mass averaging 823.11 grams from a previous mass of 21795.11 grams.
Piston: Due to the use of lightweight aluminium-lithium alloy (Al-Li), the piston was made lighter and stronger compared to its predecessors made from regular aluminium alloy. It is very suitable in areas such as aerospace and automobile parts as it is very strong, lightweight, has good fatigue quality, and good thermal conductivity. Besides, this material choice also decrease the weight of the piston in addition to allowing it to shed heat more effectively; a necessity for fast racing under high temperatures.
Performance Improvements:
The actual model has also shown significant enhancements of several performance measures such as
Stress reduction: Through the use of the titanium and aluminium-lithium alloy, the stress distribution was made to be spread evenly throughout components of the engine. Even if the stress concentrates in the similar areas as it was at the initial design, it has much lower values. This leads to reduction in stress level on the components hence reducing its possibilities of failure especially under racing conditions.
Displacement and Strain: From the mesh plots it could be observed that there was less displacement of the blocks and less strain thereby indicating that the optimized material had ability to withstand deformation to a large extent. The reduction of load that comes with the optimized components also leads to less probability of fatigue and failure hence increasing the period of the engine.
However, in the optimized model, there was an improvement on the factor of safety, which was raised to a minimum of 3.1. This improvement is the result of the development of new, stronger and more resistant materials, whereby the parts of the car’s engine will be able to withstand the forces experienced during racing without posing danger to its occupants.
5.9 Discussion of Overall Findings
Summary of Key Findings
From its application in racing activities, the Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine has been optimized, and the performance potential of the created prototype analyzed and improved based on the findings below. The identification of some overlapping attributes of the five research themes is another significant finding of this research study.
- Weight Reduction: such changes as using of the titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) for the new design of the crankshaft and connecting rod as well as applying the aluminium-lithium alloy (Al-Li) to the piston lessened the overall weight of the assembly. Through the optimization of the design, the mass of the car was relatively lowered to about 823.11 grams down from 21795.11 grams. This weight reduction is appropriate in view of the fact that a lighter engine has a better power-to-weight ratio, which is essential for success in racing events.
- Stress and Strain Upgrades: In another aspect, the optimal material had a lower peak stress and strain as compared to the baseline in critical areas like the connecting rod to piston interface. This improvement is to suggest that the probability of failure of the component and the structural rigidity of the car under racing conditions are reduced.
- Improved Factor of Safety: While compared with the original structures, the element factor of safety applied in the redesigned model is much higher than 3.1. These changes are due to relatively higher technological capacities developed in the new materials by which the part is designed to withstand the high loads experienced during racing activities without compromising the safety of the car’s engine.
Implications for Engine Performance
The results of this investigation are highly significant for racing engine applications because:
- Increased Durability: The durability of the engine components is made possible by incorporating improved mechanical qualities of the applied materials [9]. Such a reduction in stress and strain, together with an increased factor of safety, implies endurance of the optimized engine to aspects of high stresses and loads common in racing and consequent increase in component durability and reduced maintenance call.
- Increased Reliability: Reduction in the weight of the material also helps to increase in the reliability of the engine. They are also more desirable in competition use as they provide better acceleration and easy handling compared to a heavier engine. Immersed also is the improvement of materials such as aluminium-lithium alloy which can withstand high-temperature and disperse heat efficiently to maintain its competency in the heat.
Contributions to Engineering Practice
This research work is relevant in the general area of automotive engineering since it makes it clear that material optimization can be a powerful tool in improving line engines. The employment of FEA programs and software tools such as the SolidWorks 3D modelling enables designs of the engines to be tested and optimized virtually before being implemented practically. It is also beneficial in the sense that it encourages more iteration with less waste of time while the optimization processes can be very accurate.
Future Research Directions
This study has found positive results but the following research directions are suggested:
- Experimental Testing: Final FEA results can be enhanced by experimental tests that aim at proving the optimized design effective when used in actual racing.
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Investigations on some of the recently emerging techniques like additive manufacturing to improve the level of manufacturing precision so as to produce even more efficient and optimized engine parts.
- Sustainability Considerations: Further investigation can be made about material selection and their environmental footprint, as well as combining SO optimization with sustainable initiatives.
5.10 Conclusion
The modifications for racing purposes made to the Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine as well as the substitutes in the materials used also indicate a major step up in terms of power output, fuel efficiency, and ruggedness. There are advantages of using technology advanced materials like the titanium alloys as well as the aluminium-lithium alloys resulting to high weight reduction as supported by considerably low stress and strain levels as well as the better factor of safety. These details suggest that material growth and advancement as well as the application of computational tools are very effective in attaining optimum engineering goal. Engine optimization not only fulfils the requirements of competitive motorsports today but also becomes the basis for future research and development of engine technology, so that the topic plays a crucial role in further studies.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Linking with Objectives
The main reason for this research was to perform some changes and modifications on the Triumph Street Triple 675 cc for better performance in races. This concerned enhancing the performance aspects of the engine; namely the piston, crankshaft, and connecting rod through material upgrades and redesigning. These objectives were met in the findings by achieving an overall weight loss, increases in stress and strain capacities, and the factor of safety. These optimizations were possible because of the use of materials such as titanium alloy and aluminium-lithium alloy as well as FEA and solid works. These outcomes are in the same tune with the study objectives, illustrating the possibilities of enhanced power and sturdiness for a car’s engine in various racing events.
Significance of the Study
The importance of the presented work is in the development of rational strategies at enhancing the engine optimization for high-performance racing car. Through analyzing Triumph Street Triple 675 cc engine, the present study proves concepts on material substitution and redesigning to enhance the performance, efficiency and reliability of an engine. The results reveal that the highly advanced material such as titanium alloy material and aluminium-lithium alloy may be used as means of lightening the car and increasing the strength that is very crucial for motorsports. Also, the computational analysis of FEA and SolidWorks offer an ideal platform for future works on the engine design and modification. These could be useful for motorsport teams and engine manufacturers that are building and developing engines for their teams as well as motivate more research in the field of engine technology.
Conclusion
Triumph motorcycle has enhanced performance and efficiency with the durability of their Street Triple 675 cc engine in a race by means of material selection and computational analysis research. Applying lightweight materials, including titanium alloy and aluminium-lithium alloy, together with FEA and SolidWorks simulation have made it possible to cut on the weight while increasing on the structural integrity and factor of safety. These observations suggest that wealth of knowledge in engine optimisation can be of significant to the improvement of motorsport technology by unlocking newer ideas for high-performance engines.
Native Assignment Help delivers expert Assignment Help with accurate, plagiarism-free solutions tailored to UK academic standards, supported by subject specialists who ensure well-researched content, timely delivery, and full compliance with university guidelines to help students achieve higher grades with confidence.
Reference List
Journals
[1] Anand, V., Sharma, H., Yadav, A., Arora, K., Joshi, G.P. and Cho, W., 2024. Optimized PV-based induction motor drive for electric vehicle system with bidirectional converter: modeling and analysis.
[2] Recalde, A., Cajo, R., Velasquez, W. and Alvarez-Alvarado, M.S., 2024. Machine learning and optimization in energy management systems for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles: a comprehensive review. Energies, 17(13), p.3059.
[3] Laverde, G.E., Noroña, J.R.G. and Vera, S.O.G., 2021. Internal combustion engine performance of 125 cubic centimeters single-cylindrical two-time when implementing a programmable computerized fuel electronic injection system for karting competition. Material Sci & Eng, 5(4), pp.134-140.
[4] Ramdani, H., Aoulmi, Z., Louafi, M., Attia, M. and Mebarkia, M., 2024. Enhancing sustainability through drilling machine efficiency: A comparative analysis of TOPSIS and VIKOR methods for energy optimization. International Journal of Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements, 12(1), pp.45-52.
[5] Shah, S.S., Singh, K., Martin, L.J. and Jerome Stanley, M., 2022. Design, Development, and Validation of an Intake System for an FSAE Racecar. In Energy and Exergy for Sustainable and Clean Environment, Volume 2 (pp. 401-413). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
[6] Chhalotre, S., Chaurasiya, P.K., Rajak, U., Dwivedi, R., Choudri, R.V. and Baredar, P., 2021. Numerical Analysis of Performance Parameters and Exhaust Gas Emission of the Engine with Regular Air Intake System and with Insulated Air Intake System. In Advances in Clean Energy Technologies: Select Proceedings of ICET 2020 (pp. 759-775). Singapore: Springer Singapore.
- Correia, “Triumph Street Triple 675,” Motorcyclespecs.co.za, Jul. 05, 2005.
[7] Holmstrom, D., 2020. Indian Motorcycle: 120 Years of America’s First Motorcycle Company. Motorbooks.
[8] Falloon, I., 2020. The Complete Book of BMW Motorcycles: Every Model Since 1923.
[9] Ghoujehzadeh, A., Mohtadi-Bonab, M.A. and Jahani, D., 2025. Optimization and finite element analysis of an aluminum piston in the Peugeot XU7JPL3 engine for enhanced efficiency and durability. Discover Mechanical Engineering, 4(1), p.6.
[10] Navathale, T., Kharche, M.N., Shekokar, M.S. and Kharat, M.D., A Review on Finite Element Analysis of the Crankshaft of Internal Combustion Engine.
[11] Wang, G., Peng, L., Li, K., Zhu, L., Zhou, J., Miao, N. and Sun, Z., 2021. ALKEMIE: An intelligent computational platform for accelerating materials discovery and design. Computational Materials Science, 186, p.110064.
[12] Toledo Valera, J.D., Zavos, A. and Nikolakopoulos, P.G., 2024. Thermal and structural improvements of a motorcycle piston using a fully coupled thermo-mechanical FEM simulation. International Journal of Engine Research, p.14680874241297781.
[13] Collins, E. (2025). Workshop Manual Street Triple.pdf. [Scribd]
[14] Busarac, N., Adamovic, D., Grujovic, N. and Zivic, F., 2022, December. Lightweight materials for automobiles. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 1271, No. 1, p. 012010). IOP Publishing.
[15] Czerwinski, F., 2021. Current trends in automotive lightweighting strategies and materials. Materials, 14(21), p.6631.
[16] Dhairiyasamy, R., Gabiriel, D., Bunpheng, W. and Choon kit, C., 2025. Optimization of ethanol and methanol blends for enhanced performance and reduced emissions in BS-VI compliant motorbike engines. Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design, 8(1), p.44.
[17] Dhairiyasamy, R., Gabiriel, D., Bunpheng, W. and Choon kit, C., 2025. Optimization of ethanol and methanol blends for enhanced performance and reduced emissions in BS-VI compliant motorbike engines. Multiscale and Multidisciplinary Modeling, Experiments and Design, 8(1), p.44.
Go Through the Best and FREE Case Studies Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/racing-engine-fea-optimization-case-study-47500
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/racing-engine-fea-optimization-case-study-47500
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/racing-engine-fea-optimization-case-study-47500
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/racing-engine-fea-optimization-case-study-47500
- FreeDownload - 910 TimesMG630: Change Management and Organisational Development: Strategies for LPHY Case Study
Introduction: Change Management and Organisational Development: Strategies for...View or download
- FreeDownload - 1402 TimesStrategic Analysis Of Aldi: Porter's Five Forces, VRIO, Bowman's Clock, And SWOT Case Study
Strategic Analysis Of Aldi: Porter's Five Forces, VRIO, Bowman's Clock, And...View or download
- FreeDownload - 1807 TimesImpact of Misinformation on Student Grades: A Research Case Study
Impact of Misinformation on Student Grades: A Research Are you in search of...View or download
- FreeDownload - 1681 TimesAnalyzing the Supply Chain Management Of Zara Case Study
Introduction: Analysis Of The Supply Chain Of Zara Strategies and...View or download
- FreeDownload - 1456 TimesImpact of Social Media Marketing on ASDA's Brand Development Case Study
How ASDA Leverages Social Media for Brand Growth Introduction This is an...View or download
- FreeDownload - 681 TimesBusiness Plan Vegan Story Case Study
Business Plan Vegan Story Case Study Introduction - Business Plan Vegan...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



