AFM01CD - Communication And Digital Skills Assignment
An AFM01CD report analysing Hilton Group’s revenue per employee, digital skills, HR, and efficiency improvements.
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
1: Report for Management
a) Introduction
This report is intended to determine communication and digital skills for Hilton group in which the main area of consideration will be revenue per employee. The intended audience of this report is the managerial concern of Hilton group and fundamental emphasis will be offered in favour of determining definition and importance of RPE to business. Spreadsheet analysis will be the crucial aspect of this report where multiple calculations and graphical analysis will be performed. Suitable recommendations and how RPE of a company can be improved will be the ultimate section discovered in this report.
b) Main Body
i) Definition and formula of Revenue per Employee (RPE)
RPE is defined as a key organisational metric which establishes contribution of each employee towards revenues generated by a company. According to Przychodzen and Gómez-Bezares (2021), RPE is also defined as an important tool of assessing employee productivity and efficiency generated towards daily operations and activities and how it translates into overall financial development of an organisation. The formula applicable for RPE is the proportion between total revenues of a company and total employee strength available.
ii) Importance of RPE to business
The RPE is an important metric for a business to fundamentally gauge employee performances and productivity achieved in favour of contributing towards business empowerment and growth. As per explanations of Panneerselvam and Balaraman (2022), the secondary importance of RPE to business can be attributed to establishing how a business utilises its workforce in order to complete daily business activities and functions. The third importance of RPE for a business can be attributed to how a company derives profitability from each employee and identifying potential lapses in employee performances which can be strategically mitigated in future to achieve higher organisational efficiency.
iii) Spreadsheet Analysis
a) Expenses
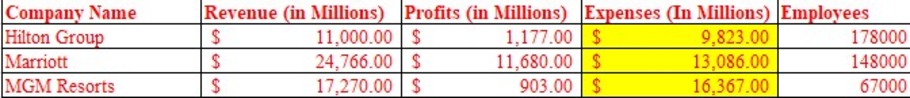
Figure 1: Expenses
According to the above figure of expenses, numerical expressions of $ 9,823 and $ 13,086 are recognised for Hilton group and Marriott respectively. The corresponding expenses identified for MGM resorts are $ expressed as 444,582.40. Based on the above analysis it is identified that the expenses of Hilton group are relatively lower in comparison to the other three companies. As illustrated by Virtuani and Morganti (2023), low expenses for a company are identified as a beneficial indicator due to which higher profit accumulation could be contemplated to magnify competitive market advantage. The higher value of expenses is also instrumental on part of an organisation to ensure operational streamlining for achieving incremental future profits (Bovee and Thill, 2021).
b) Total People Employed
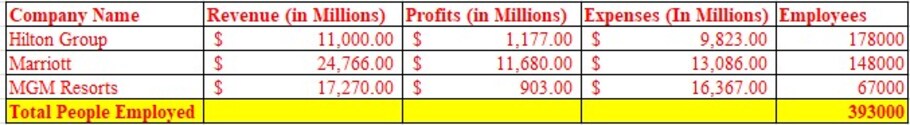
Figure 2: Total People Employed
The total people employed collectively by Hilton Group, Marriott and MGM Resorts are measured as 393,000, where the lowest are employed by MGM Resorts. Bednall et al. (2022), critically viewed that a low employee strength can be a challenging proposition for a company due to which future operational conduct can suffer. The importance of high employment with new age digital skills is necessary on part of a company to delegate activities and achieve a faster completion time in future (Edney, 2021).
c) Revenue per Employee

Figure 3: Revenue per Employee
The revenue per employee for Hilton Group, Marriott and MGM Resorts are measured as $ 0.06, $ 0.17 and $ 0.26 million respectively, indicating a higher value for MGM resorts. As per opinions and illustrations of Antonioli et al. (2022), a high revenue per employee is a beneficial indicator for a company that often translates to higher operational productivity and outcomes achieved by a company.
d) Revenues, Profits and Expenses
Figure 4: Revenue, Profits and Expenses
From the above figure of column chart, the revenues and profits dictate higher figures for Marriott while expenses of MGM resorts are considerably higher. A high revenue and low profit zone for a company can be a challenging situation or a scenario in which future difficulties for monetising operations could be encountered (Bhargava, 2022). The preparation of clustered column chart is critical to assess trends of performances for initiating future improvements (Lambert and Fyre, 2021).
e) Revenue per Employee
Figure 5: Revenue per Employee
According to the above figure of revenue for employees, it can be observed that the least number of employees participating to generate revenue is available in the case of Walmart. Aminova and Marchi (2021), critically narrated that a low revenue for employees can be a conflicting proposition for a company due to which operational difficulties are likely to be experienced in future.
c) Conclusion
This report has mainly outlined that RPE is an important tool to measure employee productivity and efficiency in order to achieve daily operational targets. The graphical analysis section of this report illustrates better RPE available to MGM Resorts whereas the position of Hilton Group and Marriott are relatively inferior in comparison. However, the total number of employees in the case of Hilton Group is higher and a low RPE exists which can affect its future operational code of conduct.
d) Recommendations
On the basis of the above figures identified, it is recommended especially to MGM Resorts for identifying techniques due to which profitability could be maximised in future. This can be potentially achieved by limiting expenses and identifying critical sources of revenue which can deliver lump sum profitability Moreover, it is also recommended to the managerial concern of MGM Resorts to determine how additional talent could be acquired and strategically utilised to deliver higher RPE in future. In the case of Hilton Group, it is recommended to identify additional sources of revenue in order to expand future profit volumes.
2: Application of Digital Skills for HR and Management
a) Introduction
- Determination of digital skills for HR and management of Hilton Group will be uncovered.
- Digital skills and their benefits to employees and employers as well as how it can improve RPE will be determined.
This presentation is intended to determine how digital skills are curricula for developing employee and employer benefits for the concerned HR and management group of Hilton Group. Further emphasis will be offered to outline how digital skills are helpful to improve RPE in the foreseeable future for Hilton Group.
b) Benefits to Employee
- Increase in daily functional efficiency and productivity (Zhang et al. 2025).
- Increased job satisfaction and the ability to innovate and improvise more frequently (Lambert, 2021).
Digital skills are identified to be beneficial for employees in terms of increasing daily functional efficiency and product activity as well as the likelihood of increased job satisfaction experienced by employees. The increasing job satisfaction often translates into more innovation and improvisation being facilitated by employees due to which performance incentives are often received in bulk numbers.
c) Benefits to Employer
- Ability to contemplate a streamlined functional and operations structure (Bluttman, 2022).
- Ability to strategically allocate available resources and the scope of reducing high attrition rates (Stofkova et al. 2022).
The benefits of digital skills available to employers include the ability to contemplate streamlined functional and operations structure as well as the ability to strategically allocate resources and reduce high attrition rates. The availability of a streamlined functional and operations structure is beneficial for Hilton group in terms of increasing service output and productivity which translates into financial gains and growth. The strategic allocation of resources and reduction of high attrition rates is vital on part of Hilton group to retain a high number of employees and open up more employment opportunities on the back of additional services provided.
d) Recommendations on how digital skills can improve RPE
- Promotion of cost savings and creation of new revenue generation streams (Mckernan and King, 2020).
- Better scope of enhancing customer satisfaction and new customer acquisitions by Hilton Group.
In order to improve RPE, digital skills are deemed helpful in terms of promoting cost savings and finding new revenue generation streams due to which companies can maximise operational profitability. Moreover, digital skills are also deemed beneficial for Hilton Group to enhance and empower customer satisfaction and facilitate new customer acquisitions to monetise more business operations in the long run. The consideration of customer satisfaction is also beneficial for Hilton Group to introduce more services in future and establish a higher market competitive advantage.
e) Conclusion
- Key benefits include the facility of increasing productivity and reducing attrition rates.
- Digital skills are also beneficial in terms of increasing customer satisfaction in the long run.
This presentation has discovered that digital skills applicable for Hilton Group are deemed beneficial especially for maximising employee productivity and efficiency as well as for employers to reduce attrition rates. The reduction of attrition rates is critical from the HR and managerial perspective of Hilton Group to retain more employees and create ample scope of acquiring more talent. This presentation has also identified that digital skills are beneficial in terms of increasing customer satisfaction for Hilton group in the long run due to which more profits and business operations could be exponentially monetised.
Reference List
Report
Aminova, M. and Marchi, E., (2021). The role of innovation on start-up failure vs. its success. EuroMid Journal of Business and Tech-innovation (EJBTI), pp.41-72.
Antonioli, D., Ghisetti, C., Mazzanti, M. and Nicolli, F., (2022). Sustainable production: The economic returns of circular economy practices. Business Strategy and the Environment, 31(5), pp.2603-2617.
Bednall, T.C., Sanders, K. and Yang, H., (2022). A meta‐analysis on employee perceptions of human resource strength: Examining the mediating versus moderating hypotheses. Human Resource Management, 61(1), pp.5-20.
Bhargava, H.K., (2022). The creator economy: Managing ecosystem supply, revenue sharing, and platform design. Management Science, 68(7), pp.5233-5251.
Bovee, C. L. and Thill, J. V. (2021) Business Communication Today. 15th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Edney, J. D. (2021). The essential digital skills handbook. Routledge.
Lambert, J., and Frye, C. (2021). Microsoft Excel Step by Step (Office 2021 and Microsoft 365). Microsoft Press.
Panneerselvam, S. and Balaraman, K., (2022). Employee experience: the new employee value proposition. Strategic HR Review, 21(6), pp.201-207.
Przychodzen, W. and Gómez-Bezares, F., (2021). CEO–employee pay gap, productivity and value creation. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 14(5), p.196.
Virtuani, A. and Morganti, L., (2023). Profitability of solar photovoltaic projects: a sensitivity analysis of performance loss curves and operation and maintenance expenses. Solar RRL, 7(8), p.2200663.
Presentation
Bluttman, K. (2022). Excel formulas and functions for dummies (6th ed.). For Dummies.
Lambert, J. (2021). Microsoft Word Step by Step. Microsoft Press.
McKernan, S., and King, M. (2020). Digital literacy and digital inclusion. Routledge.
Stofkova, J., Poliakova, A., Stofkova, K.R., Malega, P., Krejnus, M., Binasova, V. and Daneshjo, N., (2022). Digital skills as a significant factor of human resources development. Sustainability, 14(20), p.13117.
Zhang, G., Wang, L., Shang, F. and Wang, X., (2025). What are the digital skills sought by scientific employers in potential candidates?. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 47(1), pp.20-37.
Go Through the Best and FREE Samples Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/afm01cd-communication-digital-skills-assignment-47788
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/afm01cd-communication-digital-skills-assignment-47788
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/afm01cd-communication-digital-skills-assignment-47788
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/afm01cd-communication-digital-skills-assignment-47788
- FreeDownload - 39 TimesProviding And Evaluating Person-Centred Care Assignment Sample
Providing And Evaluating Care Examples Introduction - Providing And...View or download
- FreeDownload - 40 TimesInternational Marketing Assignment Sample
International Marketing Assignment Are you in need of online assignment help...View or download
- FreeDownload - 40 TimesBTM4BUE Business Environment Poster Example
If you’re preparing a business assignment and find topics like SWOT,...View or download
- FreeDownload - 40 TimesInternational Human Resource Professional Assignment
Task 1 Knowledge An international HR professional needs to possess knowledge...View or download
- FreeDownload - 35 TimesUnit 3: Personal Development In Care Settings Assignment
Introduction The role of a healthcare assistant is pivotal in modern care...View or download
- FreeDownload - 36 TimesGlobal Strategy Sustainability Assignment Sample
Introduction Of Global Strategy Sustainability Meaning Assignment Global...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



