- Unit 1
- Learning outcome (LO) 1
- Conception
- Embryonic stage
- Foetal stage
- Screening test in pregnancy
- Factors affecting the foetus and the infant
- After birth health-checkups for new born
- The Apgar scores
- The physical examination test of a newborn
- Vaccinations
- Learning Outcome 2
- Understanding sequences and stages of baby’s development from birth to upcoming 7 years
- Early childhood (Birth to 7 years)
- Physical
- Body proportions
- Muscle/Fat proportions
- Skeletal growth
- The communication, speech and language
- The social, personal and emotional
- The cognitive domain
- Learning outcome (LO) 3
- Piaget's Cognitive Theory
- Social learning theory
- B.F.Skinner’s theory
- Noam Chomsky theory
- Lev Vygotsky
- Gesell's Development Maturational Theory
- Friedrich Froebel’s theory
- Montessori's theory
- Jean Piaget (Constructive Theory)
- Vygotsky (Social Constructive Theory)
- B.F.Skinner (Behaviourist Theory)
- Learning outcome (LO) 4
- Early Year’s practitioner role during child development promotion from new-born to 7 years
- Providing resources
- Providing guidance and support
- Learning outcome (LO) 5
- Communication and language
- Physical
- Cognition
Unit 1
Learning outcome (LO) 1
The concept of birth and baby’s development understanding along with regular screening programs analysis in the initial life stage
1:1. Birth conception, by understanding and describing life stages
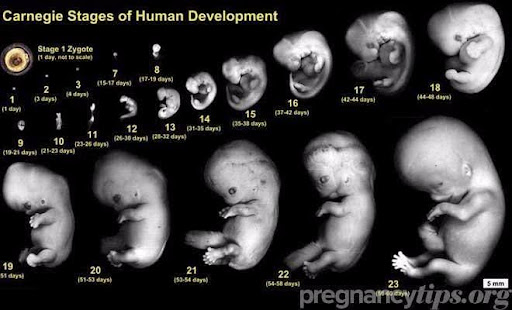
Prenatal period in this period, the conception of the zygote is being formed to evaluate the concept of a baby’s birth. Throughout these stages the baby is effectively grow from a zygote to tiny human.
Conception
Conception is united of one egg and one sperm. It happens from out of 100 eggs and millions of sperms. This is called fertilization, happens in a women's fallopian tube. Fertilized egg called zygote. After the fertilization the egg divides into small balls. It travels through the women’s fallopian tube to the uterus.
There are three stages of trimesters, germinal stage, embryonic stage, foetal stage.
- Geminal Stage: Germinal stage is shortest stage of foetal development. Around 2 weeks of pregnancy. It begins when egg and sperm unit in fallopian tube. The zygote divides during germinal stage. The blastocyst divides into embryo and trophoblast. The blastocyst is made with 3 basic layers. The development of different body structure is started through this stage.
- Ectoderm –nervous and skin system
- Endoderm –respiratory and digestive
- Mesoderm –skeletal and muscle
Embryonic stage
The embryonic stage is from 3rd week to 8th week of pregnancy. The embryonic period is being started after the 3rd week of conception mark occurrence. In this stage, the mass cell evolves and is differentiated by human characteristics. This stage plays a very important role in the brain and spinal development and also ears, nose and eyes. The umbilical cord, amnion and placenta all develop from fertilised eggs that deliver relevant life sustaining elements for the development of a baby in the mother's womb. The amniotic fluid supports the foetus from temperature, humidity controlled and shockproof. One vein and artery go through the umbilical cord to attach the embryo with the placenta. Through placenta, the child's and mother’s blood arteries connect without merging. This is the segment of pregnancy where dizziness starts.
Foetal stage
Until birth the foetal stage is continued and it starts during 9th pregnancy weeks. Embryo is turned into a foetus during this week. The assigned sex is obtained by the foetus during the 9th week of pregnancy. The body system and foetus is constantly growing. At this stage the foetus starts to move its legs and arms as well as closing and opening its mouth as well as its head is twisted. The lower portion of the baby’s body quickly extends in the meantime. Baby’s leg and arm movement is now felt by the mother.
End of the fifth month foetus is about 12 inches long, weight is approximately 1lb. Fingernails and Toenails have structure in the skin surface. This duration is more active and larger. Foetus starts to progress from one part to another part in the mother's womb.
Early pregnancies normally happen between 24 and 37 weeks. By the 7th month of pregnancy, the foetus becomes 3 pounds heavy and 16 inches long.
Over 40 weeks, half of the pregnancy was covered. Few babies are born on time, some babies born premature. Mother may feel fatigue and uncomfortable. Baby's height is about 20 inches from the top of their head to their heel and may reach 8 pounds at 40 weeks. At 40 weeks, the baby may arrive any day.
The medical professional will keep an eye on the baby's movement and heart rate if the mom doesn't go into labour within a week of the scheduled delivery date. The baby's body is curled up, and its head is most likely in the pelvis. If not, the carer can apply firm pressure to the baby's abdomen to turn it. The doctor advises the mother to have a C-section if that doesn't work. Each trimester carries its own risk. Most healthcare providers advise that the first 13 weeks are the most dangerous phase. Risk of the miscarriage happens during the first trimester.
1.2. Routine checks explanation carried out during postnatal care, antenatal care, and first year of life
Routine examinations carried out in the course of prenatal care. Throughout the pregnancy, certain tests will be available, such as blood tests or ultrasound scans. These tests are performed to help make pregnancy safer, to check and evaluate the mother's development and well-being, and to screen for certain conditions. There is no requirement for the mother to take any of these exams. However, to come to an informed choice about the decision to take the tests, you must be aware of every aspect of them.
- Weight and Height checkup: After 20weeks of pregnancy the mother expects to gain weight 10 to 12.5Kg during pregnancy. The growth of a baby is a primary component in terms of its weight gain. Developing a healthy weight is highly required; it is suggested to check weight day-to-day.
- Blood pressure: Each expectant overtake of the blood pressure will be evaluated. The pre-eclampsia development, departed in pregnancy, might be represented by a hike of blood pressure.
- Blood test and Rhstatus: A blood test is going to be conducted to ascertain the mother's rhesus status—positive or negative.Jaundice and anaemia may result from the body producing antibodies that target the red blood cells of the baby if the infant is rhesus negative.
- 12-week scan: During the 10-14 weeks of pregnancy the mother will be taken for an ultrasound scan. She can be aware of how far long babies and her progress will be monitored. The results of a scan may be used to diagnose Down syndrome in a patient.
- 20 weeks scan: In between 18 –21 weeks of the pregnancy, a scan is performed to investigate any specific abnormalities, which evaluates the baby’s growth. During this 20-week scan the baby's heart, bones, brain, kidneys, spinal cord, face and belly are all assessed. It can help to find some rare conditions.
- Anencephaly
- Cleft lip
- Gastroschisis
- Diaphragmatic hernia
- Exomphalos
- Bilateral renal agencies
- Serious cardiac abnormalities (SCA)
- Patau's’ syndrome
- Edwards’ syndrome
Screening test in pregnancy
At a greater risk of people with major health concerns found out through this screening and they can get the treatment sooner or take better decisions in health care. Pregnancy screening includes ultrasound and blood tests. Most of hereditary abnormalities can be diagnosed through blood screening.
1.3. Descriptions of some factors the influence the baby’s development
Factors affecting the foetus and the infant
The womb provides protection the foetus indirectly connects to the outside of the world through its mother. Some components that are connected to the mother can harm the fetus.
*Toxin
*Poor nutrition
*Age of exposure
*Use of alcohol
*Dose
*Smoking
*X-rays and other lend of radiation
*Stress
After birth health-checkups for new born
After the delivery, the newborn baby will be the centre of attention. Doctors and midwifes carry out a serious of routine test to ensure that the baby’s health. In terms of finding any early concern, treatment needs to be started earlier
The Apgar scores
The first test baby will have been the apgar score. It will complete one minute after the baby born and again 15minute later. Apgar stands for baby's pulse, Grimance, Appearance, reflex, muscle tone and respiration. If the midwife noticed any strange, she could get extra help. The Apgar score evaluates a baby's reflexes, muscle tone, skin colour, heart rate, and breathing. Each check will receive a score of 0, 1, or 2, for a total of 10. Seven or higher is the typical score. In addition, the baby will be weighed, have her fontanelle examined, have her body length and head circumference measured, and have any latent abnormalities or bruises from the birth examined.

The physical examination test of a newborn
All new parents are eligible for a compressible checkup as soon as their child is born. The medical professional should explain the examination. The baby's doctor might advise more testing if they find anything that could indicate a problem.After six to eight weeks, the baby has another physical examination because some of the conditions being screened for may take longer to manifest.
- Heel prick test / Blood spot screening: This test given to all newborn between five and ten days old and can identified potentially critical genetic disease. These contain hypothyroidism, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, phenylketonuria.
- Hearing screening: This test is conducted by professional-level hearing screeners. Probing the outer ear of baby with a soft, little tipped earphones send sound through the ear canal.
- Abdomen: The doctor will try to sense tummy of the baby to scrutinise liver, kidneys and spleen.
- Ears and mouth: The mouth of the baby is trying to check, to investigate it does not has a cleft palate any other abnormal discharges
- Clicky hips: The infant's knees will be brought up towards her chest by the doctor, then lowered and opened into the shape of a frog.A jerk or clunk will be felt by the healthcare provider if the hip joint is dislocated. It is successfully treatable if caught early.
- Spine: The sign of spina bifida will check by doctor, to analyse any type of tissue for exposed spinal cord.
- Genitals: A boy's penis will be examined to ensure the establishing at the tip is secure, and his scrotum will be examined for an undescended test.A baby girl's discharge of white or slightly bloody due to exposure to her mother's hormones is normal.
- Back passage: This test to make sure whether baby has yet to pass meconium.
- Physical features: This will be investigating for analysing further chance of occurrence of Down syndrome.
- Eye test: A midwife will visually check the position and appearance of baby’s eyes. Any problem as ophthalmic infection, cataracts, or cross eyes will be lift up during this kind of test.
- Reflexes: The nurse will test sucking reflex of baby by putting down a finger with glove in baby’s mouth.
- Vitamin K: The newborn baby will be offered an injection of vitamin K. oral dose also available.
- Heart and lung: Baby’s breathing pattern and heart will be monitor by midwife with stethoscope immediately after baby's arrival.
Upto one year baby’s health check-ups with personal health record management
The mother is responsible to deliver a personal health record of her child. This is termed as the “red book” as it has some crimson cover. Baby's physical records will be entered into the system. Any accidents and illness that are experiences by an infant, along with any specific medications should be noted in the recorded log-book.
- 6 –8 weeks: The baby will be going through a complete physical exam. A general practitioner will do this exam. The baby's weight, height, and head circumference will be measured in addition to examinations of their heart, eyes, hips, and, in the context of boys, their testicles.
- 9 –12 weeks: During this period kid will examine their language and leaving abilities, food, safety and specific behaviour.
Vaccinations
Vaccination is more beneficial to protect the newborn against diseases such as measles, tetanus, rubella and meningitis.
- The infant will give the first shots at 8weeks, respectively 16 weeks, 12 weeks, and 1 year.
- First dose of the 6-in-1 vaccine at 8 weeks of age
- RV vaccination
- MenB vaccine: Initial dosage
- Six-in-one vaccination at 12 weeks old: second dose
- PCV vaccination
- Two doses of the RV vaccine
- Third dose of the 6 in 1 vaccine at 16 weeks of age
- Vaccine MenB: second dose
Learning Outcome 2
Understanding sequences and stages of baby’s development from birth to upcoming 7 years
2.1. Recognise sequences and stages of growth from newborn to 7 years in the different areas
Early childhood (Birth to 7 years)
A baby develops into a young adult who can interact socially and take care of themselves. Along with the changes in appearance that take place from early childhood to adolescence, development also involves some changes in a child's thinking, speech, behaviour, emotions, and personality as they start to comprehend and engage with the world that is around them. This is the reason that this stage primarily concentrates on skills. Three-year-olds grow physically quickly; they can sit, walk, run, and catch. Children's development of fine motor skills and growth open up between the ages of three and five.
Young children grow their verbal vocabulary level of 300 – 1000 words within their initial 3 years of life. Child's social and emotional developments will change around one year. From three to seven years old, children obtain social emotional skills.
Physical
Infants develop at their own rate. The children come in a variety of healthy sizes and shapes. The factors that affect a child's height and weight include gender, hormones, physical activity, nutrition, heredity, and environment. A child's birth weight has increased by twofold, tripled, and quadrupled by the time they are two years old.
Body proportions
The body growth of a child varied at different rates. These are two kinds. Cephalocaudal, proximodistal.
- Cephalocaudal: The head and chest grow faster than lower body after birth.
- Proximodistal: this stage is associated with from head to toe growth along with a clockwise direction
Muscle/Fat proportions
Baby's body fat increase during last week of pregnancy and it persist to do immediate after child’s birth, reaching high at 9 months of age. Due to this “baby fat” baby’s temperature remains stable. Second year of the life most toddlers start to lose weight. During adolescence and childhood, muscle mass gradually increases, and then rapidly accelerates in adolescence.
Skeletal growth
Cartilage is a soft, elastic material that forms the basis of the embryonic skeleton. From the 6th week of pregnancy through adolescence and childhood, it persists. Skeletal growth may differ in the same age group children.
The communication, speech and language
Children have to learn how to communicate with surrounding people. Evidence shows children's gestures predict future language development, even before they start to talk. When they acquire the language, they also learn how to categorise their surroundings and how to take turns in conversations. A baby should be able to pronounce their first meaningful word at 12 months.
The social, personal and emotional
Children improve phycological well-being improve a lot when they create connection, captivate in social interactions and achieve a good understanding on the capability to control their emotions. Children identifies, self-images and perceptions of feelings evolve as they grow. Developing strong bond is critical to social and emotional growth. Long term relationships are identified by strong feeling of intimate with others. There is more to the attachment between a mother and her child than just feeding. The concept of safeguard feel base served as the foundation for both parent and child. Children also begin to form relationships with other people and acquire social skills and manners.
The cognitive domain
Cognitive progresses are the highest-level function of the brain. Children improve their memory, concentration and understanding of the world. It is including thinking, remembering, and problem solving and knowing. This preoperational stage in between 2years to 7years.
2.2. Explain ‘Holistic’ development
In holistic development, the interdependence of the mind, body, and spirit is acknowledged. A holistic strategy for child development by early childhood educators takes into account not only the cognitive aspects of learning but also the physical, personal, social, emotional, and spiritual wellbeing of the children. The five approach of Holistic growth are follows,
- Emotional
- Social
- Spiritual
- Physical
- Intellectual
Cognitive development
A child’s knowledge, understanding and problem solving
- Recognise families faces, imitate facial expressions, react familiar sounds.
- Understand the difference between the animate and inanimate objects. Learning to comprehend written and spoken information
- Learn via information and data as well as by developing a specific action.
- Recognise their own name, reflection and know their utilisation.
- Begin to ask questions
- Numbering till 20, draw understanding, shapes, and communicate about rules, increase vocabulary.
Physical activities
- Gross and fine motor skills
- Move head, roll over, sit up, walking and running
- Able to move whole body
- Improve wide range of fine motor skills. Chopping vegetables, fruits, colouring, building models, using keyboards, playing with vehicle
- Emotional development: The awareness of child of themselves and their recognition and how they manage and express their emotions.
- Improve to manage and control their feelings and emotions
- Learning to communicate effectively with others.
- A key component of improving one's intrapersonal skills is realising one's capabilities as well as strengths and weaknesses.
- Share and understand the feeling and emotions of every individual
- Language, Speech, and communication development
- In terms of initiating conversations eye-contact is required
- Develop joint attention
- Ability to comment and describe activities
- Showing interest to learning new words
- Talk empathetically
- Initiate conversation with new people
- Sequence of development and development rate: The sequence in which a baby develops; for example, a baby must learn how to hold his head up before he can sit up on his own will analyse here. The time range provided for a child's typical development that is anticipated at a specific age is known as the rate of development. Every child is different and will grow at their own pace. Differentiating between a child's growth-oriented sequence and rate is essential to determining the child's developmental demands. To guarantee that the child gets all the support they require in the areas where they may require it most, effective strategies are required.
2.3. children’s development and its related development factor
Biological factors
- Genetics: Genetic transfer to our children without any interference is main concern here. Positive and negative factors transfer to the children. Positive physical aspects as, eye colour, height, hair texture and mental and physical attitude etc are and negative physical approach such as any diseases, ill conditions or present ill.
- Habitual factors of the mother: Even before the child is born, the mother's actions have an impact on them. A mother who eats a healthy diet, exercises, and maintains positive relationships is a greater probability of giving birth to a healthy child.
- Development delays: There are various developmental delays in children. Numerous delays impact a child's capacity to execute various tasks, encompassing social, cognitive, physical, and emotional growth. A child's intelligence may be impacted by delays in their cognitive development. Autistic child could struggle to interact with others. Social and emotional difficulties are common in children with developmental delays, e.g attention deficit hyperactivity disorder or autism, but they may react in different ways than peers of the same age.
- Environment: The child’s growth and mental health is affected by the geographical location and the physical surrounding environment. Surrounding environment can influence child’s interest and activities mainly, while the emotional and mental surrounding will influence how the kid surrounds themselves during their growth. It is better to consider and investigate the environment to create for the child.
- Diet and nutrition: Nutrients are necessary for our bodies to grow and heal, and malnutrition can result in deficiency illnesses that have an impact on a child's development and health. The bodies and minds of children require a varied diet high in vitamins. For a baby's body and brain to develop properly, the first two years of life are critical. For newborn babies breast milk is a main nutrition source. Kids who drink formula milk are most probably suffer from different digestive issues including diarrhoea.
- Family and social life: The social life and family environment will affect the growth and development in children. Additionally, the relationships they acquire through their surroundings—such as their families and friends—will be extremely helpful to them throughout their entire lives.
- Education: The type of education children acquire will conveniently influence child development and growth. Not only should they be educated in school, but there should also be enjoyable and mentally stimulating learning opportunities.
- Socio Economic Conditions: Socio economic conditions are very much affecting the benefits of development and growth in a child. If the family's financial situation is disclosed, it might assist the child in growing up with limited possibilities and, if they are privileged enough to have them, teach them about privilege, which can help them grow up to be humble and compassionate adults.
- Centile charts: Centile charts use to track child’s growth. This will be used for kids 0–18, with different charts for every age group. The child's health is depicted in centile charts about other kids their age. This will enable medical professionals to check a child's growth to make sure it is typical. Two metrics are used to measure a child's growth: weight and height. 3 measures are beneficial in the context of this chart
- Weight (Kg)
- Height (cm)
- Head circumference (cm)
Learning outcome (LO) 3
Recognising the theoretical underpinnings and educational frameworks that underpin early childhood practice knowledge and comprehension
3.1. Theoretical perspective analysis
Piaget's Cognitive Theory
The most significant ideas within the child development are the work of Piaget. Children’s Cognitive development is not only associated with knowledge acquisition, however, children eventually require to develop or build a mental neighbouring environment model.
A four steps procedure:
- Assimilation
- Equilibrium
- Disequilibrium
- Accommodation
Social learning theory
Bandura’s theory suggests, learning process for children is depending on their surroundings via active cognition termed observant learning.
Kid learns via their adults and peers surround them daily. According to the social learning theory, children learn through imitating rather than being instructed.
B.F.Skinner’s theory
This theory based on operant and behaviour conditioning. The founder of this theory suggests that behaviours are grasping via positive reinforcement.
Noam Chomsky theory
This theory is an idea that shows individual have a congenital capability to gain and learn knowledge. According to Chomsky, parents who repeat the sounds of babbling and associate them with phrases help their kids learn the language.
Lev Vygotsky
According to Lev Vygotsky, children pick up language through problem-solving with the assistance of their carer, parents, and other family members. Children learn and practise language skills by means of observing and listening to the people around them, including their parents.
Gesell's Development Maturational Theory
Gesell advice a development Maturational theory based on several assumptions. He believed that the reason for developmental changes in children lies primarily in aging processes. He suggested that learning and life experience are not the cause of development. The age norms for physical growth suggested by Gesell are still used in childcare as they enable the specialists to monitor the child’s development.
Friedrich Froebel’s theory
Froebel believed that the most crucial way for young children to learn is through play. Everyone has embraced his views regarding the value of having fun and gaining knowledge from nature.
Montessori's theory
The educational approach known as the Montessori Method, after its creator Maria Montessori, prioritises student autonomy and choice over textbook utilisation in the classroom. This teaching philosophy acknowledges that a conducive learning environment fosters kids wanting to learn.
3.2: Child development and its related theoretical perspective analysis in specific framework
Jean Piaget (Constructive Theory)
Piaget's theory informed the development of the present EYFS and foundation phase, highlighting the notion that children learn best when actively exploring a stimulating and demanding environment.
- EYFS 1.9: When planning and directing activities, educators need to take the way that kids learn into account.
- EYFS 1.6: Early childhood educators need to focus on the three core areas because they lay the groundwork to achieve success in each of the four areas.
Vygotsky (Social Constructive Theory)
According to Vygotsky, children acquire knowledge through building. His argument is that language is how kids learn. It highlights the social aspects of development. Play, both adult and child, is emphasised.
- EYFS 1.8: Include both adult-led and child-led operations throughout each learning area, as well as intended, deliberate play.
B.F.Skinner (Behaviourist Theory)
His theory is children learn certain behaviours base on prior positive and negative experience. Skinner characterised operant into 3 basic categories
- Punishment
- Positive reinforcement
- Negative reinforced
- EYFS 1.5 - Assisting children in their personal, social, and emotional development involves, helping them to create positive relationship and respect for others, develop social skills to control their feelings.
Learning outcome (LO) 4
Early Year’s practitioner role during child development promotion from new-born to 7 years
Early year practitioner: Early year practitioners are specialist of newborn and young children’s mental, social, emotional and educational development. In the context of early year practitioner, they are capable to work in any nursery, school, or childcare management with kids under 5 years.
4.1. What does Early Years practitioner do?
Early year practitioner provides huge support to kids with best possible beginning in their life. Children are entitled to the development of their skills, interests, and personalities. UN conventions outline children's rights, irrespective of their cultural background, religion, or learning disabilities.
Adults can better understand and support each child's growth path by following this advice.
Many early childhood educators are characterised as responsible, empathetic, and caring individuals who have a passion for assisting young children. The practitioner performs additional duties as a "key person." Maintaining positive relationships with both the child along with the parent is crucial for practitioners, as is making sure that every child is thoroughly observed, evaluated, and planned for during "settling in discussions" and the duration of the child's stay.
4.2. Evaluate the role of the early year’s practitioner in assisting holistic development of children
Some of the Early years practitioner’s roles and responsibilities
- Monitoring children's development and keeping a record of it; assisting parents in communication and collaboration; attending to children's daily physical needs, health, and wellbeing, e.g. diaper changing, feeding babies, and teaching them to use the toilet.
- Supporting kids in acquiring fundamental abilities like literacy and numeracy.
- It might involve playing number games or reading stories.
- Creating a setting that is both safe and supportive for kids to work in.
- Respecting the rules and regulations of the learning environment would be necessary for this
- Adhering to the Basis Stage of the Early Years Framework's curriculum requirements
- Encouraging physical activities to keep children engaged.
- Assisting social and communication skills building to help children interact with others.
- Helping children with their special need educational need or disabilities with their education.
- Allow youngster to initiate dialogues
- Repeat sounds, words, tones and phrases so children can recognise them
- Encouraging movement of children
- Inspire children to follow and lead games such as: duck goose, follow the leader and role plays
- Help kids care and be compassionate for one another
- Help isolated children merge with the larger crowd and interact
- Story telling with various voices and roles
- Use tidy up time to improve memory and organise things
- Stop and listen carefully for environmental sounds
Early years of practitioner observant
| Age | Cognitive and neurological development | Speech, communication, and language development | Physical development | Emotional and social development |
| BIRTH to 6 MONTHS | Babies will grow fast and start to notice what is | Babies begin to recognise their family or | Newborn babies will grow very fast, and they | Babies will build emotional relationships |
| Going on around them. They will capable of how to feel physical things hungry, sleepy and recognise their caregivers. | caregiver and start to interact with them by smiling, gurgling or listening. | will soon be capable to jerk their legs, limbs keep their look around by heads up | with their caregivers who care for them the most. | |
6-12 MONTHS |
Babies are beginning to know important words and tone such as “mum” and “dad” and they will also develop an attachment to a favourite toy who they will be able to recognise. | Starting to understand key voices, key words, their name, self-talk and many more | Babies can turn around from their front, move legs and gain strength- they can pick things up, start moving and maybe move | They may become distressed when caregivers leave- when presented to strangers and also enjoy cuddling and touch |
1-2 YEARS |
Children will understand and use object such as hairbrushes and spoons. | Children can follow gentle simple commands and gestures- there will be a higher understanding of language also | They could be potty trained, walk with the help of an object or caregiver and also proactively engage with their environment such as: flipping books, using building blocks, dancing etc | Babies will thrive for more attention- they'll become more confident and interact with people more thoroughly. This is near the peak of their exploring. |
2-3 YEARS |
They will grasp complex ideas, vocabulary, gestures and self-reflections. They may start learning nursery rhymes or grow fond of a particular show. | Children will vocalise more often and know a sufficient bank of vocabulary. | Motor skills will improve (climbing, running etc), and children will start to develop a preference for a dominant hand. | Children can express feelings better which can lead to increased tantrums and reliance on adults. They may start appreciating alone time. |
3-4 YEARS |
They will have a greater conscience and grasp more complex | Children will think more, remember more and also participate in | Kids will have better spatial awareness; draw passionately; | Children will want more independence, interact with other children |
| situations such as: time, questioning and events. | simpler conversations. | movement will become proper such as using stairs, walking and navigation. | and gain a greater confidence. | |
4-7 YEARS |
Children can explain and solve difficulties; memory will be precise, and they’ll start associating colours and objects to ideas and places for example: birthdays and easter. | Children can solve dilemmas and speak fluently- use vaster vocabulary and speak fluently they may also start learning how to read and write. | Children will improve physically, and hand movements will become more stable, and they can enjoy games such as football; basketball and tennis. | An appreciation for company will become profound and they’ll learn how to cooperate with others so they can contribute to their greater environment and positively impact them and others around them. |
The process of Early Year practitioner facilitates towards growth?
Infants and young children learn and grow in a variety of ways, most of which at first are connected and encompass various developmental domains. As children get older, their developmental pattern shifts from being simpler to more intricate. To support the child's holistic growth, the early childhood educator must ascertain what the child demands and should make accommodations for them.
Providing resources
Children can use these resources to learn about materials and their characteristics as they investigate and talk about them. They will need soft play access such like sand, play dough water and physical development tools like balls, colouring pencils and tricycle. This will eventually assist to children improve their development of language when they communicate with others.
Providing guidance and support
Adults must need to support and guide children and babies as they expand. This might be encouraging them, eulogise them or by how to build the blocks.
4.3. Working partnership with parents/carers
The parent-child partnership is emphasised in the EYFS. Because of their early educational experiences, they help parents continue their children's education at home and practitioners create successful educational experiences in the setting. Parents can find out about their children's progress in learning by having regular conversations and offering assistance during class.
Learning outcome (LO) 5
Plan opportunities for learning and development of children
5.1. From birth to 5 years in relation, plan opportunities for children
- 0-6 months
- A person who aware of and understand babies' needs and their demands always want to be there.
- Consistent, love and care that immediately responds to the requirement of the newborn is important
- Handle and cuddle the babies will growth of security and attachment
- The carer should greet the child and hand them back to their guardians at the start and conclusion of each session. This will guarantee that the infant receives support and that the parents' communication is sustained. six to twelve months
- supportively interact with newborns influence relationship in between them and caregiver
- Show the infant that caregiver fully listening to what the infant is trying to say
- Seek parents help to find out baby’s interest and games 1 – 2 years
- Talk with babies about their families
- Show fully attention towards to baby
- Provide child with safe base actions so they can explore new things 2 – 3 years
- Make sure to give participant chance to child
- Teach the social interaction e.g sharing, waiting for one’s turn
- Touched with emotions bond
- – 4 years
- Assist child in developing healthy connections with others
- Playing with different group develop sense of acceptance and belonging in a community
- Labelling emotions will help to understand child to other feelings
- and up
- Support children to move confidently and openly with every individuals
- Demonstrate that carer can be helpful and thoughtful for co-worker by evaluating this type of trait in proper interactions
- Deliver chance for converse and children, explain and listen their actions
- Take into account the particular requirements of students learning English as their second language.
Communication and language
- 0 – 6 months
- Children should encourage to engage with playful activities
- Early discussion between adults and newborn and between babies can be facilitated by physical proximity, touch or eye contact
- 6 – 12 months
- Encourage them to listen and mimic various noises.
- Talk to kids about the sounds they sense while they read.
- Teach young children to recognise specific sounds, for 1 to 2 years old:
- As you go about your day, recite and sing rhymes.
- Use lively voice to get babies to listen carer
- – 3 years
- Use intonation and tone to stimulate songs rhyme and reception rhyme, poems and stories
- Help the demands of children who are speaking English as a second language.
- – 4 years
- Be role model to children how to be a good listener by attentioning to what they have articulated and responding accordingly.
- Before each lesson or task, children who struggle with "listening and doing" should be called by name. • Introduce children learning English as an additional language to rhymes, stories, and literature from diverse cultures, occasionally incorporating languages other than English.
- years and above
- Scheduled regularly singing a short song or telling story or discussing something they like.
- Make sure that the needs of children learning English as a second language are covered so that they can participate completely
- Give children enough time to listen and talk
Physical
- 0 – 6 months
- Baby’s hands needs to be clap together, shake their foot 6 – 12 months
- Play with child in fun activities 1 – 2 years
- Touch and movement can help child become more aware of their bodies
- Take babies outdoor or indoor to moving around
- It is significant to teach kid to keeping attention to the movements of other people around them
- Prodding, patting, and Swirling the play paint or dough with baby’s own hand
- – 3 years
- Encourage the child’s sense of reliance
- Make picnic or mealtime to teach children how they can eat and using spoon, fingers and cup
- Encourage toddler to grasp, hold and use paint brushes or tools
- – 4 years
- Ensure children to cool down and recharge their energy because they are prone to bursts of energy.
- Appreciate children’s choices of their move
- Teach exercises such as stretching, curling, turning should be emphasised
- Important to keep an eye out of children 4 years and up
- Important teaching children how to use the scissors or utilising tools or equipment safely
- Encourage children to speak in terms of movement
- Teach youngsters how to play together in activities
Cognition
- – 4 years
- The usage of the name and labels and the words highlighting in books and the surrounding can assist children understand what a word is
- Assure that children use books in two languages so they can study scripts
- Encourage children to guess the story ending and draw parallels between the emotions and plots of the individuals
- Teachers can integrate home bilingual and language story discussions into the curriculum with the help of qualified bilingual parents and adults
- 0 – 6 months
- Use finger plays, rhymes, or songs to get young children moving. six to twelve months
- By watching their reactions, assist infants as they learn how to anticipate and take part in finger and wordplay. between one and two years
- Encourage and support reactions of children while read stories or picture books
- Tell the stories in a moderate of voices and encourage them to joining
- – 3 years
- Assist kids in using their narratives in their play;
- Encourage kids to continue reading the next word by pausing at regular intervals. It is an effective teaching method for reading comprehension.
- years and up
- Discuss and model the use of non-fiction substances to gather information. • Parents can assist their children in building a resilient vocabulary by teaching them to keep in mind their names as well as the identities of their friends and families
- Playing games like World Letter the bingo game can help kids develop their phoneme-grapheme correlation. • Show kids that simple words can be divided into their component sounds and rearranged to form new words.
References
- Child Development from conception to seven years
NCFE CACHE LEVEL 3 AWARD IN CHILDCARE AND EDUCATION
- Your baby’s first hospital tests www.motherandbaby.com
1962-2023 Bauer Media group
- Early childhood development www.highspeedtraining.co.uk
Rosalyn Sword January 15th 2021
- Child development www.Birthto5matters.org.uk Early education
- Factors that affect Growth and Development in kids www.smartivity.in
- Describe sequential development from birth to seven years in the following area
- Describe the role of the early years practitioner when promoting physical development in children from birth to 7 years www.studybullet.co.uk
STUDYBULLETS 2023
- Child Development Theories www.structural-learning.com
Paul Main November 22,2022
- Physical Developmental milestones www.virtuallabschool.org Virtual Lab School 2023
- Early Years Practitioner/childcare qualification www.twinkle.co.uk
- What is an Early years practitioner? www.Allaboutchildren.co.uk
- Learning and Development – Early Years Matters www.earlyyearsmatters.co.uk Early Years Matters 2023
- 1.2 Explain the difference between sequence of development and rate www.studymode.com
- Developmental theories www.verywellmind.com
- Look who’s talking An In-Depth look at language www.teachkloud.com



