Sustainable Tourism Assignment Sample
This report examines how social media marketing drives sustainable tourism in Edinburgh, highlighting theories, impacts, challenges, and strategic recommendations.
Ph.D. Experts For Best Assistance
Plagiarism Free Content
AI Free Content
Title: To investigate the impact of social media marketing for sustainable tourism within Edinburgh.
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
In the year of 2023, almost 4.98 million people have visited Edinburgh and tourism industry is contributing over 1.3 billion pound in the country’s GDP (Description of Edinburgh, 2023). It has shown a 4% increase in tourists which contribute towards the overall growth and development of the country. Marketing refers to the process of creating awareness and interest of people related to product & services. In the current times, social media has been utilized with the aim of attracting large number of tourist within the limited time and cost. This is the most effective method which helps in reaching out to the large number of customers which ultimately result into enhancement of profitability. SMM also helps in enhancing search engine optimization of company which assists in enticing customers and their decision making as well. Sustainable tourism implies for the tourism activities that are initiated while considering the current as well future social, environmental and economic impacts (Horng et al, 2024). This type of tourism aims at addressing the need and wants of visitors without degrading the environment quality, economic position and cultural of the country. It is the most significant process which helps in strengthening communities by offering more growth opportunity and income sources.
This tourism also contributes in infrastructural development of the country and aids in enhancing understanding regarding its tradition, values and customs. Sustainable tourism also focuses on preserving natural resources and promoting local art & culture which aids in overall socio-cultural development of the country. This type of tourism also focuses over conserving heritage such as natural sites and architects which contribute towards attracting large number of tourist and thereby ensures overall economic development of the country. Edinburgh is the capital of Scotland which is located at the southeast UK and it is bounded by Firth of forth and Pentlands Hill. The country is having population of 506520 people and it is the second most populated city of Scotland. The current report will discuss the impact of SMM in developing sustainable tourism within Edinburgh.
1.2 Rationale
The current study is initiated to determine the role of social media marketing in promoting sustainable tourism within Edinburgh. In the current times, individual’s choices are highly influenced by the product and services showcased through social media marketing. However, due to increase in tourist, countries started cutting off trees and natural resources as to provide adequate services which adversely impact the overall sustainability (Kwon et al, 2024). Therefore, it is significant to determine the influence of social media marketing in promoting sustainable tourism within Edinburgh. In this context, thematic data analysis will be done to shed light on the role of SMM in enhancing sustainable tourism within UK.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Theoretical and conceptual framework of the research
2.1.1 Theoretical framework
In the context of determining influence of social media marketing in developing sustainable tourism stakeholder theory, 5 P’s theory, Tourism Area life cycle (TALC) and triple bottom line theory has been utilized. Stakeholder theory stated that country should initiate actions which does not create negative impact on any of stakeholder rather aids in enhancing their satisfaction (Goh, 2021). This theory covers wider aspect of the tourism which helps in mitigating the scope of any negative impact on society, environment and economy (Stakeholder theory of sustainable tourism, 2025). Moreover, 5 P’s theory of sustainable tourism defines that people, planet, plants, prosperity and peace are the five crucial elements which should be adequately managed for the sustainable growth (5 P’s of Sustainable tourism, 2024). By aligning with all the five crucial elements, country will be able to reduce wastage, pollution, preserve environment, supports local community and thereby contributes in the attainment of sustainability goals.
Along with this, TALC theory of sustainable tourism is also used which defines six crucial stages by which a destination goes through. This theory also defines various eco-friendly and social activities that should be incorporated at each stage for promoting sustainable tourism within the country successfully. Moreover, TALC theory defines various challenges and issues that faced at each stage of tourism based on which the most accurate action can be taken on timely basis for the achievement of overall goals and objective (TALC model of sustainable tourism, 2024). Along with this, Triple bottom line theory of sustainable tourism indicates that equal focus should be paid on society, environment and profit which ensure the overall development of country (Triple bottom line theory, 2024). This theory defines various strategies related to social welfare, economic growth and environment which eventually aids in meeting the sustainability goals.
2.1.2 Conceptual framework
The two major concepts used within the current study are sustainable tourism and social media marketing. Sustainable tourism is associated with the three crucial concepts that include environment protection, economic growth and society welfare (Roxas, Rivera and Gutierrez, 2020). The entire three requirements could be achieved effectively through social media marketing which contributes in the sustainable development. SMM helps in creating awareness regarding all the attractions which assists in influencing the large number of tourist. This ensures economic and financial growth within the country which eventually leads sustainable tourism development. Along with this, SMM also helps in promoting the local shops and businesses of the country which assists in increasing demand for the country’s product and services (Farkić, Filep and Taylor, 2020). This will also help in enhancing the community engagement which eventually contributes towards overall economic growth. Social media marketing is also used to promote the culture and tradition of country which assists in creating culture awareness in the wider market. Beside this, social media marketing is also used to create awareness regarding various measures by which country’s natural resources could be protected which eventually assist in improving overall environment.
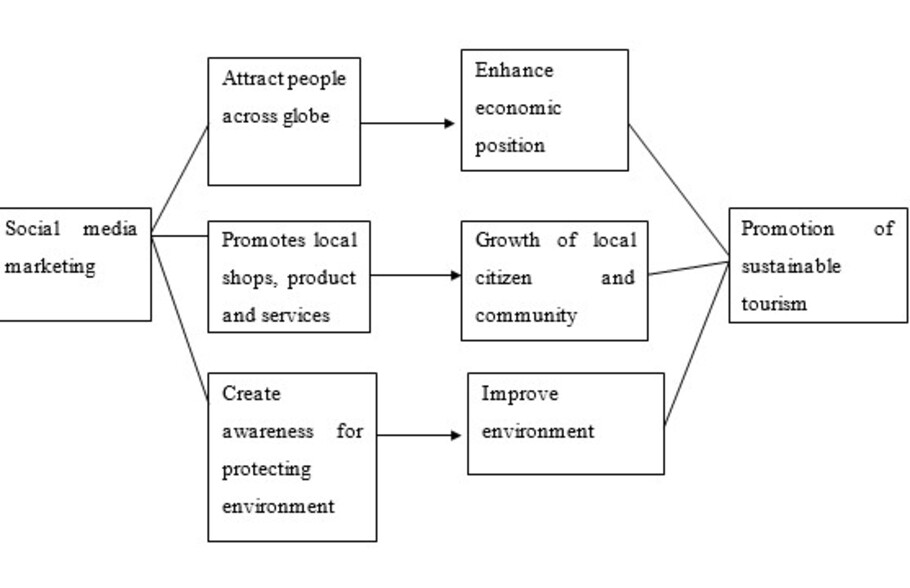
(Self-generated)
2.2 Key concept, theories and studies
2.2.1 Meaning of social media marketing and its significance
According to the viewpoint of Hysa, Karasek and Zdonek (2021) social media marketing implies for the process of utilizing social media platform for connecting with the targeted audiences that assists in enhancing sales and driving website traffic. It is the most used platform for promoting product, services and destination as it aids in reaching out to the larger target market. On the other hand, Shen, Sotiriadis and Zhou (2020) explicated that social media marketing is the group of internet based applications which allows exchange and creation of user generated content. This marketing techniques support in connecting audiences and businesses by sharing information related to the similar needs, values and wants.
Sultan et al, (2020) explicated that SMM supports in enhancing destination exposures and awareness which aids in attracting the larger number of visitors. Social media marketing helps tourism organization to develop engaging content such as videos, photos and travel guides which influences the large number of audience. This marketing helps in offering the real time updates related to destination and also assists in addressing the concern, doubts and question of audiences which enhances their satisfaction. For example: Edinburgh is having its social media presences by name ‘thisisedinburgh” through which information regarding all the attracted places is shared across the world (Social media presence of Edinburgh, 2024). This help in creating awareness within larger target market that eventually results in increasing number of tourist.
On the critical note, Go and Kang (2023) confessed that SMM also spread negative review which damage overall reputation and goodwill of country. Visitor usually shares their negative experience on social media sites which discourage others from visiting the destination leading to negatively influencing overall economic position. Katsikari et al, (2020) stated that social media marketing assists in enhancing customer engagement and interaction which helps in attracting the large number of tourist. This platform helps customer to connect with visitors in the real time and support in responding to their complaints and queries which assists in providing personalized services. Through social media sites tourism organization are able to develop effective experience for their customers which eventually results in enhancing loyalty.
However, Kapoor et al, (2022) argued that social media also provides false advertising or information which misguides the tourist and eventually impact their travel experiences. Moreover, many visitors may provide misleading or in-completed information regarding destination which creates negative impact on tourist mindset and ultimately impacted on destination’s goodwill. For example: In the year of 2023, Coordinators at Edinburgh mislead tourists by charging false prices for children which impact on overall reputation. Purnomo et al, (2020) assessed that social media marketing contributes towards enhancing overall economic position of the local business and country. This marketing strategy assists in influencing the large number of tourist by sharing information regarding local product, services, culture and tradition. This help in enhancing sales of local and small shops which aids in increasing overall financial position. For example: In 2023, Tourism industry has generated over 1.3 billion pounds which aids in enhancing overall economic position of country (Tourism in Edinburgh, 2024). As the number of tourist increased by 30%, country has developed over 30000 jobs which facilitates towards overall country’s development.
Javed, Tučková and Jibril (2020) it stated that SMM is the most cost effective mode of marketing which assists in attracting tourist efficiently. This marketing technique helps organization in sharing information related to all the places through the attractive videos and photos which helps in attracting tourists in the less time, cost and efforts. However, Purnomo et al, (2020) explicated that inaccurate social media posts and marketing could negatively influence overall economic position of the country. There were many cases in which country has provided faulty information or inaccurate massages through social media sites which eventually reduces the individual’s interest to visit certain places that adversely impacts the country’s economic position.
Gössling (2020) entailed in their study that social media marketing helps in providing personalised travel recommendation according to the customer’s needs which helps in increasing overall satisfaction. In the year of 2024, it has been identified that 74% of total revenue is generated with the help of online sales which indicates the benefits of providing personalized recommendations. With the help of social media, company is become able to identify customer preferences based on which customized travel packages and recommendations are offered that ensures increasing number of visitors within the country. Wibowo et al, (2020) argued that social media marketing has created over tourism and overcrowding issues in the country which has negatively influenced routine task of local people. Due to the increasing awareness within the larger target market, numerous tourists has arrived at the particular destination which result into environment degradation, damage to cultural heritage and also creates issue for the local people to carry out routine task and activities.
Along with this, Nekmahmud (2022) articulated that social media has developed the scope of User-generated Content (UGS) which furnishes authentic information related to the destination. This content is shared by the tourist and people visited the destination which helps in gaining the trust and confidence of the potential audiences. According to survey, 85% tourist decisions are influenced by UGC which assists in developing their engagement that leads to overall economic growth of the country. On the other hand, Li et al, (2022) stated that SMM has increased risk of over commercialization which results into losing authenticity. In SMM, country is aiming at describing inaccurate information related to the destination which generates unrealistic expectation among the tourist. However, this creates dissatisfaction among the visitors when their expectation did not attain.
2.2.2 Various type of theories and model of sustainable tourism.
Pop et al, (2022) investigated that sustainable tourism is the process of carrying out tourist activities without degrading the quality of natural resources and adversely impacts the overall economy as well as society. There is large number of theories that should be incorporated for promoting sustainable tourism within the country. This helps in guiding country regarding the various actions that should be incorporated for protecting society, environment and cultural aspects. Rinaldi et al, (2022) argued that triple bottom line theory should be used for developing sustainable tourism. This theory stated that an equitable amount of concern should be paid over profit, society and environment which contributes in the overall; development of country (Triple bottom line theory, 2024). According to theory, concentration should be paid on promoting community wellbeing, preserving local culture and optimum utilization of limited resources which aids in sustainable development.
Moreover, Eid, Abdelmoety and Agag (2020) stated that it is the most optimum theory as it aids in taking holistic decision after adequately identifying interconnection between the three crucial elements of tourism. Further, this theory assists in maintaining the balance between economic development, social well being and environment which result into overall growth of planet, profit and people. On the other hand, Armutcu et al, (2023) argued that it is difficult to maintain balance between society goals and individual’s financial goals. Along with this, triple bottom line theory does not define any basis on which environment and social impact could be measured. For example: Edinburgh is aiming at increasing number of tourist however this is negatively impacting on routine task of the local people. Therefore, it is challenging for the country to prioritize activities which ensures overall growth and development.
Eid, Abdelmoety and Agag (2020) identified in their study that 5 P’s theory of sustainable development should be incorporated for overall tourism growth within country. For effectively attaining goal of sustainable tourism, people, planet, plant, prosperity and peace should be managed while carrying out tourism activities (5 P’s of Sustainable tourism, 2024). In this context, local jobs, product and services should be promoted for development of society. Further, various eco-friendly practices such as banning plastics, reducing wastage and green transportation should be promoted for the betterment of planets and plants. Along with this, Obembe et al, (2021) explicated that it is the most effective strategy as it covers all the crucial aspect related to the tourism that lead overall development. For example: Edinburgh has adapted to major city development such as green spaces and unique city’s landscape which helps in protecting the natural resources (Sustainable tourism practice in Edinburgh, 2024). Moreover, country is using EV vehicles for tourism transportation which contributes towards achieving Net Zero carbon emission goal by 2030.
Lin et al, (2020) argued that stakeholder theory is the most effective framework which promotes sustainable tourism within the country. This theory stated that each policy and actions should be undertaken after critically evaluating its impact on the entire stakeholder such as tourism organization, tourist, customer, local shop and citizens which aids in formulating the adequate strategies (Stakeholder theory of sustainable tourism, 2025). This is the most effective theory as it covers all the individuals and groups involved in the tourism activities which assists in adequately promoting sustainable tourism within the country. According to Khan et al, (2022) Tourism Area Life Cycle (TALC) is one of the most significant theory which should be used for incorporating the sustainable activities within the tourism. Exploration, development, involvement, stagnation, consolidation and decline are the six crucial stages of each destination which should be effectively managed for attaining the sustainability goals (TALC model of sustainable tourism, 2024). TALC theory stated that sustainable and eco-friendly practices should be undertaken at each stage for promoting tourism.
Along with this, Pachucki et al, (2022) stated that exploration phase includes attracting small number of tourist which is interested in exploring the unknown destination. However, at this stage there is a limited infrastructure and facilities and lack of integration with the local communities. Involvement stage includes infrastructural development which aids in increasing the number of tourist. After this, destination becomes popular and there is a continuous development of hotels, resort and market which leads to losing authenticity. However, there is low growth in the number of tourist and eventually the destination loses attraction and unable to influence the tourist.
Talukder and Bhuiyan (2020) found that inaccurate concentration over sustainable activities result into declining and stagnation stage. Decline in the number of tourist generally occurs as local communities have stopped supporting tourism due to overcrowd which creates negative impact on their routine. In this context, country should promote sustainable activity at each stage which helps in avoiding any type of obstacle from society and community that facilitates in overall development of tourism. On the critical point of Grilli et al, (2021) articulated that this theory does not provide a well established measures and strategies that should be initiated for promoting sustainable tourism. Also, this theory does not provide cause and effect relationship of all the measures which may result in ineffective policy implementation.
2.2.3. Impact of Social media marketing in encouraging Sustainable tourism.
According to perception of Moyle et al, (2020) Social media plays a crucial role in preserving environment, conserving resources and overall development of sustainable tourism. It has identified that SMM supports in creating awareness within larger number of tourist which eventually results in overall economic development of county. Further, this assists government in increasing their investment towards developing infrastructure which aids in overall growth of the country. For example: In 2023, over 4.8 million people have visited Edinburgh which results in overall economic growth of country. On the critical point of view, Font et al, (2023) explicated that increase in number of tourist has created various financial issue for local people. Due to increase in demand of local product, various shops have increased prices of products which ultimately reduce purchasing power of country’s citizens.
Along with this, Pilelienė, Grigaliūnaitė and Bogoyavlenska, (2024) confessed that social media marketing help in promoting growth of society and community which aids in adequate development of sustainable tourism. Social media marketing help in attracting large number of tourist towards country which assists in enhancing overall economic position. Increase in number of tourist helps in promoting local product; provide opportunity to local shop to offer their product to larger market segment which help in enhancing overall financial position. For example: Edinburgh is using Instagram to promote local market areas and products which help in influencing large number of tourist. This promotion also assists in developing 30000 job opportunities in country which eventually help in reducing unemployment. On the other hand, Xu, Nash and Whitmarsh (2020) stated that country generally showcase shopping malls and other attracted places and ignores local market which creates issue for small shops to manage their earnings. Faulty information related to unethical practices at market places such as theft and robbery restrict tourist to visit such areas which negatively influences overall sales and profitability of local shops.
Based on the view point of Graci, (2020) it has been identified that social media marketing help in preserving architecture and historical places which ultimately result in promoting sustainable tourism. Through Social media, visitors could provide information related to their experience from particular destination which generally impacts on overall mindset of the audiences. To provide accurate experience, government focuses on investigating towards maintenance of historical places which help in promoting country’s culture. For example: a sum of 16.8 million pound has been invested in last four years with the aim of managing historical places which assists in attracting large number of tourist (Investment towards sustainable tourism, 2024). This help in showcasing attractive videos and photos at social media sites which ultimately influences larger target market.
On the critical point of views, Ngoc, Tien and Trang (2021) stated that individuals may provide misleading or inaccurate information related to their experiences which create negative impact on overall perception and mindset of tourists. This will result in decreasing number of tourist and thereby decreasing economic benefit which may reduce overall investment towards maintaining heritage places and castle. According to Khan et al, (2021) stated that with the help of social media marketing, country could request and guide tourist to maintain cleanliness at the natural places which will reduce overall environment impact on the country. This marketing strategy help in promoting measures by which tourist could reduce wastage that assists in protecting natural resources of country. For example: there is restriction on usages of plastics in Edinburgh which could be communicated with SMM. This awareness will guide tourist to not use plastics bags in Edinburgh which help in reducing pollution within country.
On the contrary point of view, Talwar et al, (2023) stated that issue related to overcrowding and pollution has been increased after promoting destination through social media. This platform has resulted in influencing large number of tourist by providing attractive photos and videos which create issue of overcrowd at the places. This creates issue for local people to adequately carrying out their routine task which creates dissatisfaction among country’s citizen. For example: It has been identified that there is 4% increase in number of tourist as compare to previous year due to which there is rising rent prices and strained infrastructure. From the survey conducted by Scottish business news it has depicted that Restaurant prices in Edinburgh are 15% higher than other places of UK (Rise in price of Restaurants, 2023). This has resulted in reducing purchasing power of local people that eventually impact on their overall satisfaction.
From the perspective of Torkington, Stanford and Guiver (2020) it has been articulated that social media marketing plays a crucial role in preserving culture and tradition of the country. In the current time, people are hugely attracted towards culture and tradition of the country which could be promoted with the help of social media sites. This will help in creating awareness regarding country’s culture in wider target market that eventually assists in preserving country’s culture. For example: Edinburgh is promoting Edinburgh Castle in each of its marketing content which helps in describing the country’s culture, this aids in creating awareness regarding the country’s culture and customs. On the contrary point of view, Rydzik and Kissoon (2024) explicated that social media marketing has resulted in attracting tourist from all around the world due to which local citizens are influenced with culture and traditions of other country. Individuals generally adapt to lifestyle and culture of tourist due to which local culture and tradition start diminishing. This ultimately creates negative impact on society and community that creates obstacles in successfully promoting sustainable tourism.
2.3 Literature gap
Earlier studies has been initiated for identifying the significance of social media marketing in attracting tourism and its impact on enhancing overall financial position. Moreover, studies have also conducted to identify various measures by which sustainability could be promoted in tourism industry (León-Gómez et al, 2021). However, concentration has not been paid over determining the influence of Social media marketing in promoting sustainable activities within country. Along with this, it will also define various positive and negative impact of SMM in tourism industry which aids in taking most accurate and effective decisions.
3. RESEARCH QUESTION, RESEARCH AIM AND RESEARCH OBEJTIVE
3.1. Research questions
Q1. What is meaning of social media marketing and its importance?
Q2. What are various theories and models related to sustainable tourism within Edinburgh?
Q3. What is role of social media marketing in enhancing sustainable tourism within Edinburgh?
3.2. Research aim
The aim behind conducting current study is to determine the impact of social media marketing in influencing sustainable tourism within Edinburgh.
3.3. Research objectives
- To study concept of social media marketing and its significance.
- To analysis theoretical underpinning related to sustainable tourism within Edinburgh.
- To evaluate influence of Social media marketing in enhancing sustainable tourism within Edinburgh.
- To suggest competent strategies for promoting sustainable tourism within UK.
4. IMPLICATIONS AND CONTRIBUTION TO KNOWLEDGE
4.1 Practical implications
The current study will help in creating awareness regarding the positive and negative impact of social media marketing in sustainable tourism which aids in taking the most accurate decision. Further, this will also guide various organization regarding strategies that should be used for increasing sustainable tourism (Sharma, Thomas and Paul, 2021). Moreover, the current will also define various challenges that are creating obstacle in developing sustainable tourism and provides measures by which such issues could be easily conquered.
4.2 Theoretical implications
The outcome of current study will help in enhancing understanding of the reader by providing more in-depth information regarding topic. Moreover, present study will act as the point of references based on which other scholar could conduct studies in future.
If you’re looking to create a polished, academically sound, and well-structured report like the one above, our expert Assignment Help Service is here to support you. Whether you need assistance with literature reviews, research writing, data analysis, or full-length academic projects, our professional writers ensure original, high-quality work tailored to your requirements. Save time, reduce stress, and achieve higher grades—reach out today and let us help you craft exceptional academic reports with confidence.
REFERENCES
Books and Journals
Armutcu, B., Tan, A., Amponsah, M., Parida, S. and Ramkissoon, H., 2023. Tourist behaviour: The role of digital marketing and social media. Acta psychologica, 240, p.104025.
Eid, R., Abdelmoety, Z. and Agag, G., 2020. Antecedents and consequences of social media marketing use: an empirical study of the UK exporting B2B SMEs. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 35(2), pp.284-305.
Eid, R., Abdelmoety, Z. and Agag, G., 2020. Antecedents and consequences of social media marketing use: an empirical study of the UK exporting B2B SMEs. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 35(2), pp.284-305.
Farkić, J., Filep, S. and Taylor, S., 2020. Shaping tourists’ wellbeing through guided slow adventures. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(12), pp.2064-2080.
Font, X., Torres-Delgado, A., Crabolu, G., Palomo Martinez, J., Kantenbacher, J. and Miller, G., 2023. The impact of sustainable tourism indicators on destination competitiveness: The European Tourism Indicator System. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 31(7), pp.1608-1630.
Go, H. and Kang, M., 2023. Metaverse tourism for sustainable tourism development: Tourism agenda 2030. Tourism Review, 78(2), pp.381-394.
Goh, H.C., 2021. Strategies for post-Covid-19 prospects of Sabah’s tourist market–Reactions to shocks caused by pandemic or reflection for sustainable tourism?. Research in Globalization, 3, p.100056.
Gössling, S., 2020. Technology, ICT and tourism: from big data to the big picture. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 29(5), pp.849-858.
Graci, S., 2020. Collaboration and partnership development for sustainable tourism. In Tourism and Sustainable Development Goals (pp. 232-249). Routledge.
Grilli, G., Tyllianakis, E., Luisetti, T., Ferrini, S. and Turner, R.K., 2021. Prospective tourist preferences for sustainable tourism development in Small Island Developing States. Tourism Management, 82, p.104178.
Horng, J.S., Liu, C.H., Chou, S.F., Yu, T.Y. and Hu, D.C., 2024. Role of social media influencers on marketing of sustainable hotels: gratification and the parasocial interaction perspective. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, pp.1-28.
Hysa, B., Karasek, A. and Zdonek, I., 2021. Social media usage by different generations as a tool for sustainable tourism marketing in society 5.0 idea. Sustainability, 13(3), p.1018.
Javed, M., Tučková, Z. and Jibril, A.B., 2020. The role of social media on tourists’ behavior: An empirical analysis of millennials from the Czech Republic. Sustainability, 12(18), p.7735.
Kapoor, P.S., Balaji, M.S., Jiang, Y. and Jebarajakirthy, C., 2022. Effectiveness of travel social media influencers: A case of eco-friendly hotels. Journal of travel research, 61(5), pp.1138-1155.
Katsikari, C., Hatzithomas, L., Fotiadis, T. and Folinas, D., 2020. Push and pull travel motivation: Segmentation of the Greek market for social media marketing in tourism. Sustainability, 12(11), p.4770.
Khan, M.M., Siddique, M., Yasir, M., Qureshi, M.I., Khan, N. and Safdar, M.Z., 2022. The significance of digital marketing in shaping ecotourism behaviour through destination image. Sustainability, 14(12), p.7395.
Khan, M.R., Khan, H.U.R., Lim, C.K., Tan, K.L. and Ahmed, M.F., 2021. Sustainable tourism policy, destination management and sustainable tourism development: A moderated-mediation model. Sustainability, 13(21), p.12156.
Kwon, K., Lee, J., Wang, C. and Diwanji, V.S., 2024. From green advertising to greenwashing: Content analysis of global corporations’ green advertising on social media. International Journal of Advertising, 43(1), pp.97-124.
León-Gómez, A., Ruiz-Palomo, D., Fernández-Gámez, M.A. and García-Revilla, M.R., 2021. Sustainable tourism development and economic growth: Bibliometric review and analysis. Sustainability, 13(4), p.2270.
Li, Z., Wang, D., Abbas, J. and Mubeen, R., 2022. Tourists’ health risk threats amid COVID-19 era: role of technology innovation, Transformation, and recovery implications for sustainable tourism. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, p.769175.
Lin, H.C., Han, X., Lyu, T., Ho, W.H., Xu, Y., Hsieh, T.C., Zhu, L. and Zhang, L., 2020. Task-technology fit analysis of social media use for marketing in the tourism and hospitality industry: a systematic literature review. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 32(8), pp.2677-2715.
Moyle, B., Moyle, C.L., Ruhanen, L., Weaver, D. and Hadinejad, A., 2020. Are we really progressing sustainable tourism research? A bibliometric analysis. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 29(1), pp.106-122.
Nekmahmud, M., Naz, F., Ramkissoon, H. and Fekete-Farkas, M., 2022. Transforming consumers' intention to purchase green products: Role of social media. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 185, p.122067.
Ngoc, P.B., Tien, N.H. and Trang, T.T.T., 2021. Current path to community based sustainable tourism development of Khanh Hoa Province in Vietnam. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 18(09), pp.508-525.
Obembe, D., Kolade, O., Obembe, F., Owoseni, A. and Mafimisebi, O., 2021. Covid-19 and the tourism industry: An early stage sentiment analysis of the impact of social media and stakeholder communication. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 1(2), p.100040.
Pachucki, C., Grohs, R. and Scholl-Grissemann, U., 2022. Is nothing like before? COVID-19–evoked changes to tourism destination social media communication. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 23, p.100692.
Pilelienė, L., Grigaliūnaitė, V. and Bogoyavlenska, Y., 2024. A Bibliometric Review of Innovations in Sustainable Tourism Research: Current Trends and Future Research Agenda. Sustainability, 16(16), p.7124.
Pop, R.A., Săplăcan, Z., Dabija, D.C. and Alt, M.A., 2022. The impact of social media influencers on travel decisions: The role of trust in consumer decision journey. Current Issues in Tourism, 25(5), pp.823-843.
Purnomo, S., Rahayu, E.S., Riani, A.L., Suminah, S. and Udin, U.D.I.N., 2020. Empowerment model for sustainable tourism village in an emerging country. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(2), pp.261-270.
Purnomo, S., Rahayu, E.S., Riani, A.L., Suminah, S. and Udin, U.D.I.N., 2020. Empowerment model for sustainable tourism village in an emerging country. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(2), pp.261-270.
Rinaldi, C., Cavicchi, A. and Robinson, R.N., 2022. University contributions to co-creating sustainable tourism destinations. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 30(9), pp.2144-2166.
Roxas, F.M.Y., Rivera, J.P.R. and Gutierrez, E.L.M., 2020. Mapping stakeholders’ roles in governing sustainable tourism destinations. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 45, pp.387-398.
Rydzik, A. and Kissoon, C.S., 2024. Decent work and tourism workers in the age of intelligent automation and digital surveillance. In A Sustainable Tourism Workforce (pp. 244-261). Routledge.
Sharma, G.D., Thomas, A. and Paul, J., 2021. Reviving tourism industry post-COVID-19: A resilience-based framework. Tourism management perspectives, 37, p.100786.
Shen, S., Sotiriadis, M. and Zhou, Q., 2020. Could smart tourists be sustainable and responsible as well? The contribution of social networking sites to improving their sustainable and responsible behavior. Sustainability, 12(4), p.1470.
Sultan, M.T., Sharmin, F., Badulescu, A., Stiubea, E. and Xue, K., 2020. Travelers’ responsible environmental behavior towards sustainable coastal tourism: An empirical investigation on social media user-generated content. Sustainability, 13(1), p.56.
Talukder, M.B. and Bhuiyan, M.L., 2020. An assessment of the roles of the social network in the development of the Tourism Industry in Bangladesh. International Journal of Business, Law, and Education, 1(2), pp.52-60.
Talwar, S., Kaur, P., Nunkoo, R. and Dhir, A., 2023. Digitalization and sustainability: virtual reality tourism in a post pandemic world. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 31(11), pp.2564-2591.
Torkington, K., Stanford, D. and Guiver, J., 2020. Discourse (s) of growth and sustainability in national tourism policy documents. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(7), pp.1041-1062.
Wibowo, A., Chen, S.C., Wiangin, U., Ma, Y. and Ruangkanjanases, A., 2020. Customer behavior as an outcome of social media marketing: The role of social media marketing activity and customer experience. Sustainability, 13(1), p.189.
Xu, F., Nash, N. and Whitmarsh, L., 2020. Big data or small data? A methodological review of sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(2), pp.144-163.
Online
5 P’s of Sustainable tourism. 2024. Online. Available through: <https://sustainabletourismandresponsibletravel.com/the-5-ps-of-sustainable-tourism/>
Description of Edinburgh. 2023. Online. Available through: < https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/728/#:~:text=Edinburgh%20has%20been%20the%20Scottish,influence%20on%20European%20urban%20planning.>
Investment towards sustainable tourism. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://www.solimarinternational.com/how-green-finance-can-address-the-increasing-demand-for-sustainable-tourism/#:~:text=Investment%20Opportunities%20to%20Support%20Sustainable,%2C%20biodiversity%2C%20and%20cultural%20heritage. >
Rise in price of Restaurants. 2023. Online. Available through: < https://scottishbusinessnews.net/rates-rise-threatens-future-of-town-and-city-centres/
Social media presence of Edinburgh. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://www.euppublishing.com/early-career-researcher-hub/promoting-your-research/social-media>
Stakeholder theory of sustainable tourism. 2025. Online. Available through: < https://www.witpress.com/Secure/elibrary/papers/SDP09/SDP09073FU2.pdf>
Sustainable tourism practice in Edinburgh. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://www.etag.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/Final-Draft-Edinburghs-Tourism-Strategy-2030.pdf>
TALC model of sustainable tourism. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666957923000083#:~:text=Since%20Butler's%20original%20article%20(Butler,2006a%2C%20Butler%2C%202006b).>
Tourism in Edinburgh. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://roadgenius.com/statistics/tourism/uk/edinburgh/#:~:text=How%20many%20tourists%20visit%20Edinburgh,a%204%25%20increase%20from%202019.&text=On%20average%2C%202%20million%20international%20visitors%20travel%20to%20Edinburgh%20annually.>
Triple bottom line theory. 2024. Online. Available through: < https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-the-triple-bottom-line>
Go Through the Best and FREE Samples Written by Our Academic Experts!
Native Assignment Help. (2026). Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/social-media-marketing-for-sustainable-tourism-assignment-45232
Native Assignment Help, (2026),
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/social-media-marketing-for-sustainable-tourism-assignment-45232
Native Assignment Help (2026) [Online]. Retrieved from:
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/social-media-marketing-for-sustainable-tourism-assignment-45232
Native Assignment Help. (Native Assignment Help, 2026)
https://www.nativeassignmenthelp.co.uk/social-media-marketing-for-sustainable-tourism-assignment-45232
- FreeDownload - 47 TimesValues, Ethics, and Working Collaboratively Assignment Example
Values, Ethics, and Working Collaboratively Assignment TASK...View or download
- FreeDownload - 41 TimesComprehensive PESTLE Analysis and Consumer Insights for UK Retail Industry Assignment Sample
TASK 1: GLOBAL DRIVE 1.0 Pestle analysis of the UK retailing analysis Pastel...View or download
- FreeDownload - 52 TimesExploration of the End of Life Care Need Assignment Sample
Exploration of the End of Life Care Need Assignment Sample Chosen Care...View or download
- FreeDownload - 38 TimesACC3135 Accounting Theory Essay Sample
Introduction: ACC3135 Accounting Theory Essay Sample Accounting plays a...View or download
- FreeDownload - 45 TimesGBEN3002 Portfolio Assignment Sample
Part 1: Using AI Artificial Intelligence Implementation to Create the Image I...View or download
- FreeDownload - 42 TimesDesign Management Assignment Sample
Introduction - Design Management Designing management is one of the inquiry...View or download
-
100% Confidential
Your personal details and order information are kept completely private with our strict confidentiality policy.
-
On-Time Delivery
Receive your assignment exactly within the promised deadline—no delays, ever.
-
Native British Writers
Get your work crafted by highly-skilled native UK writers with strong academic expertise.
-
A+ Quality Assignments
We deliver top-notch, well-researched, and perfectly structured assignments to help you secure the highest grades.



